Indexeddb 简明教程
IndexedDB - Introduction
数据库管理系统提供了一种存储和检索数据的方法。有各种类型的数据库可以使用,其中最常用的有 -
A database management system provides a mechanism for the storage and retrieval of data. There are various kinds of databases available mostly used ones among them are −
-
Hierarchical databases
-
Network databases
-
Object-oriented databases
-
Relational databases
-
NoSQL databases
NoSQL databases
NoSQL 数据库(有时称为非 SQL)是一种提供存储和检索数据的方法的数据库,而不是关系数据库中使用的表格关系。这些数据库是无模式的,支持轻松复制,具有简单的 API,最终一致,并且可以处理大量数据(大数据)。
A NoSQL database (sometimes called Not Only SQL) is a database that provides a mechanism to store and retrieve data other than the tabular relations used in relational databases. These databases are schema-free, support easy replication, have simple API, are eventually consistent, and can handle huge amounts of data (big data).
还有不同类型的 NoSQL 数据库,例如 -
There are different types of NoSQL databases also like −
-
Document databases.
-
Key-value stores. Column-oriented databases. Graph databases.
What is IndexedDB
Indexed Database 是一种 NoSQL 数据库或非关系结构化查询语言。它是一个事务数据库系统,类似基于 SQL 的 RDBMS。但是,与使用固定列表的基于 SQL 的 RDBMS 不同,IndexedDB 是基于 JavaScript 面向对象数据库。
Indexed Database is a type of NoSQL database or Non−relational structured query language. It is a transactional database system, like an SQL−based RDBMS. However, unlike SQL−based RDBMSs, which use fixed-column tables, IndexedDB is a JavaScript−based object-oriented database.
当我们需要在服务器端存储大量数据并且比本地存储更快时,就会使用它。由于它将数据存储在浏览器中,因此也可以在线和离线使用。使用此功能,您可以创建一个 Web 应用程序(具有丰富的查询功能),无论是否有互联网连接都可以运行。
It is used when we need to store significant amounts of data on the server side and faster than local storage. Since it stores the data in the browser it can be used online and offline too. Using this, you can create a web application (with rich query abilities) that can run whether an internet connection is available or not.
Key Characteristics of IndexedDB
以下是 IndexedDB 数据库的主要特征 -
Following are the key characters of the IndexedDB database −
IndexedDB 是一个 NoSQL 数据库,存储键值对。它可以通过键或多种键类型存储几乎任何类型的值。
IndexedDB is a NoSQL database that stores key−value pairs. It can store almost any kind of value by keys or multiple key types.
-
As mentioned, IndexedDB follows a transactional database model − Transaction is a wrapper class around the operation or group of operations so that data integrity is maintained. You don’t want data to be altered or missed so if the transaction is failed a callback is rolled out.
-
IndexedDB does not use Structured Query Language − Since IndexedDB uses a NoSQL database it doesn’t use SQL, instead, it uses queries on Indexes to produce data via cursors or the getAll() method to iterate around different sets.
-
IndexedDB uses a lot of requests − Requests are objects that receive the success or failure of DOM events (DOM - HTML DOM events allow JavaScript to register different event handlers on elements in an HTML document). DOM events are success or error which has a target property that indicates the flow of the request. Success events can’t be canceled but, error events can be canceled. There are a lot of requests in IndexedDB like on success, onerror and addEventListener(), removeEventListener() on them. For getting to know the status of the request we also have ready state, result, and error code properties.
-
IndexedDB needs to follow the same origin − Origin is the URL of the document in which the script is being written, each origin has some databases under it and each database has its name to be identified by the origin. The security boundary imposed on IndexedDB prevents applications from accessing data with a different origin. For example, if we take a URL and take different subdirectories of it, it can retrieve data but if we change location to port 8080 and try to retrieve data from the usual URL and the changed port, we cannot retrieve the data.
Terminology
以下是 IndexedDB 中重要的各种术语,在继续之前你应该了解这些术语:
Following are various important terms in indexedDB that you should know before proceeding further −
-
Database − In IndexedDB database is the highest level which contains the object stores that contain the data.
-
Object Stores − Object stores are the data storage entities of IndexedDB. Think of it as tables in RDBMS where we store data based on the type of data we want to store (ex: id, name, roll no, etc).
-
Transaction − For any database operation we do the following process. Get database objectOpen transaction on the databaseOpen object store on the transaction and then, operate on object store.So basically, a transaction is a wrapper function that is connected to every database and it ensures data integrity such that if the transaction is canceled or any error happens it will call back to where the transaction has not yet been begun.
-
Index − Think of object store as a table and we use indexes to retrieve data of a single property from them. Ex: Name, age, etc.
-
Cursor − In a database, if we need to traverse multiple records from object stores we use cursors.
Support for IndexedDB
IndexedDB 是浏览器中的数据库,因此我们需要检查它是否受当前/现有浏览器支持。为此,请将以下代码粘贴到文本编辑器中,将其另存为 test.html ,并在浏览器中运行它。
IndexedDB is a database in a browser so, we need to check if it is supported by the current/existing browser. To do so, paste the following code in an text editor save it as test.html and run it your browser.
const indexedDB =
window.indexedDB ||
window.mozIndexedDB ||
window.webkitIndexedDB ||
window.msIndexedDB ||
window.shimIndexedDB;
if (!indexedDB) {
document.write("IndexedDB could not be found in this browser.");
}
const request = indexedDB.open("MyDatabase", 1);如果你的浏览器支持 IndexedDB,此程序将成功执行,并且将创建数据库。
If IndexedDB is supported by your browser this program gets executed successfully, an a database will be created.

IndexedDB - Installation
Visual Studio Code 是重新定义并针对构建和调试现代 Web 和云应用程序而优化过的代码编辑器。
Visual Studio Code is a code editor redefined and optimized for building and debugging modern web and cloud applications.
-
You can download the visual studio code from its official website - https://code.visualstudio.com
-
Select the version you want based on your PC configuration and OS.
-
Once downloaded you can install it directly on your computer.
Installing the Visual Studio Code installer on Windows
首先,按照上述说明下载适用于 Windows 的 Visual Studio Code 安装程序:
First of all download the Visual Studio Code installer for Windows as specified above −
-
Once it is downloaded, run the installer.

-
Then, accept the agreement and click on next.
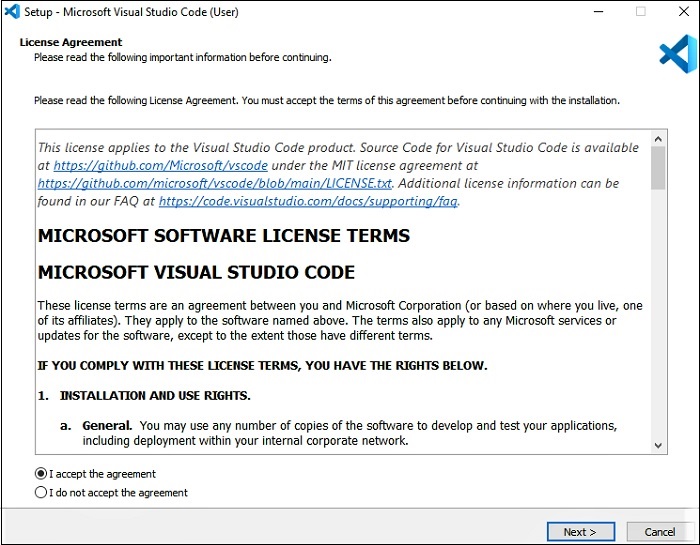
-
Now, click on “create a desktop icon” so that it can be accessed from the desktop, and click on Next.
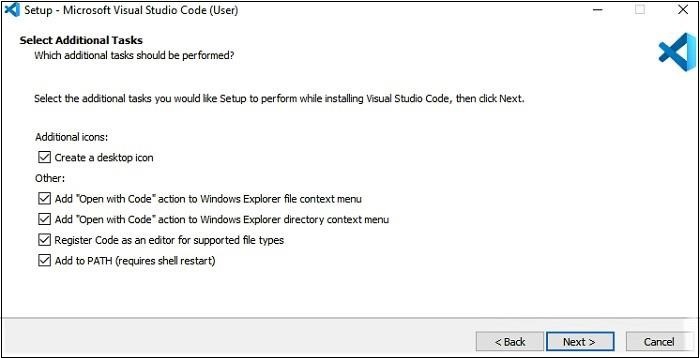
-
Then, click on the install button.
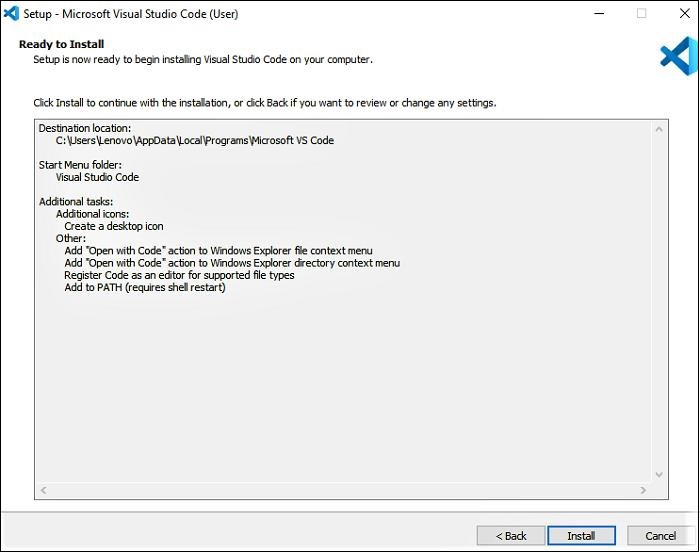
-
Finally, after installation completes, click on the finish button, and the visual studio code will open.

-
Now Visual Studio code is successfully installed on your device, start writing code on this code editor.
Downloading, Installing, and Creating a Node.js project (optional)
现在,在安装 Visual Studio code 后,我们需要安装 Node.js
Now after installing the visual studio code we need to install Node.js
Downloading Node.JS
-
You can download Node.js from its official website which is [role="bare"]https://nodejs.org/en/.
-
Select the version of your choice based on your computer’s configuration.
-
The LTS version is preferable as it is a more stable version and it stands for Long Term Support.
Installing Node.js
按照以下步骤在系统中安装 Node.js:
Follow the steps given below to install Node.js in your system −
Step 1 - 在 Node.js 打开后。你会发现这个窗口弹出。点击下一步。
Step 1 − Now that the Node.js has opened. You’ll find this window pop up Click on next.

Step 2 - 你将被重定向到 “End-User License Agreement” 窗口。接受协议并点击 @[s4}。
Step 2 − You will be redirected to the “End-User License Agreement” window. Accept the agreement and click on Next.
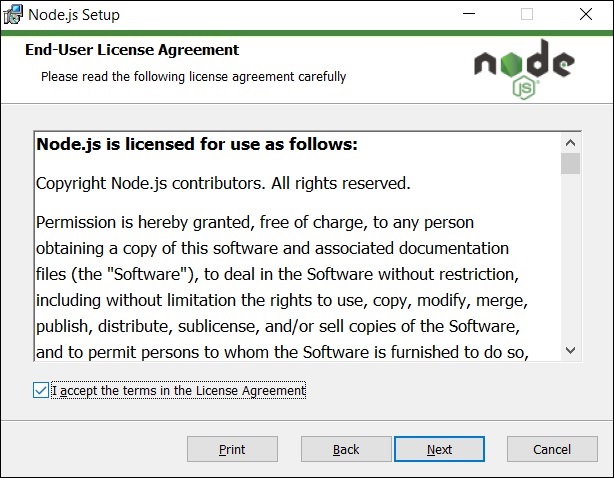
Step 3 - 在下一个窗口中,你需要选择 “ Destination Folder ”。更改现有文件夹或使用提及的默认文件夹,然后点击 Next 。
Step 3 − In the next window you need to select the “Destination Folder”. Change the existing folder or, use the default folder mentioned and then click Next.
Step 4 - 在 “ Custom Setup ” 和 “ Tools For Native Modules ” 中点击 Next 。
Step 4 − Click Next in the “Custom Setup” and “Tools For Native Modules” windows.
Step 5 - 现在,安装设置已就绪,点击 Install ,以安装所选模块。
Step 5 − Now, thw setup is ready click Install, to install the selected modules.
IndexedDB - Connection
数据库是一个有序的、结构化数据集合,这些数据存储在计算机系统中。为了对数据执行操作,我们需要连接到数据库。在本章中,我们将讨论如何创建/连接到数据库、打开数据库和删除数据库。
A database is an organized collection of structured data stored in a computer system. To perform operations on data we need to connect to a database. In this chapter, we will discuss how to create/connect to a database, open a database, and delete a database.
Creating a database - 你可以使用 open() 函数在 IndexedDB 中创建一个数据库。以下是此函数的语法。
Creating a database − You can create a database in IndexedDB using the open() function. Following is the syntax of this function.
let openRequest = indexedDB.open(name, version);其中,
Where,
-
name is the name of the database you need to create.
-
version is the version of the database that is to be created. The default value of this parameter is 1. If you omit this value, the version is considered as 1.
你要传递给此函数的版本值不应低于当前版本(IndexedDB 的版本)。如果成功创建了数据库,则此函数返回 1;如果创建失败,则返货 0。
The version value you pass to this function should not be less than the current version (of the IndexedDB). This function returns 1 if the database is created successfully and it returns 0 in case of a failure.
Example
以下是 IndexedDB 中创建数据库的示例:
Following is the example to create a database in IndexedDB
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Indexed db</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//Creating a database
const request = indexedDB.open("myDatabase", 1);
if(indexedDB){
document.write("Database Created......");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output
如果您把上面的代码保存在文件“ test.html ”中并运行它,浏览器将显示以下消息:
If you save the above code in a file “test.html” and run it, the following message will be displayed on the browser −
Database Created......Verification
因为 IndexedDB 是浏览器内置的数据库,所以在浏览器中就能看到创建的数据库。
Since IndexedDB is the browser’s built-in database you observe the created database in the browser itself.
右键点击生成页面,点击“检查元素”并选取“应用标签”。如果展开此选项卡,您可以在其中看到 IndexedDB 数据库,您可以看到创建的数据库文件,如下所示:
Right-click on the resultant page, click on inspect element and select the Application tab. You can see the IndexedDB database there if you expand it you can see the created database file as shown below −

Generating Handlers
event 是在 HTML 元素上执行的操作。我们可以使用 JavaScript 处理这些事件。从现在开始,我们将使用 JavaScript 处理程序(为了让此更清楚)。
An event is an action performed on an HTML element. Using JavaScript we can handle these events. From now on we use JavaScript handlers (to make this clearer).
如果请求成功,我们将使用 onsuccess 事件。
If the request is a success, we use the onsuccess event.
request.onerror = event => {
// Do something (ex: document.write("error");
};如果请求失败,我们将使用 onerror 事件。
If the request is a failure, we use onerror event.
request.onsuccess = event => {
// Do something (ex : document.write("success");
};当创建一个数据库或增加现有数据库的版本号时,我们将使用 onupgradeneeded 事件。
When you create a database or increase the version number of an existing database we use onupgradeneeded event.
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
};Example
以下示例显示消息“ database creation success ”。如果数据库创建成功。在这里,我们使用 onsuccess 和 onerror 处理程序来显示这些消息。
Following example displays the message “database creation success”. If the database creation is successful. In here we are using the onsuccess and onerror handlers to display these messages.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Handlers</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("DATABASE", 1);
request.onsuccess = function (){
document.write("Database created successfully...")
}
request.onerror = function(){
document.write("database creation error");
}
request.onupgradeneeded = function(event){
var db = event.target.result;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Connecting to an existing database
为了与 IndexedDB 交互,我们使用 JavaScript。我们用 JavaScript 撰写的代码并不会直接与数据库交互。我们需要使用连接对象连接到数据库,以操作数据库的对象。
To interact with IndexedDB, we use JavaScript. The code we write in JavaScript doesn’t interact with databases directly. We need to connect with the database using a connection object to manipulate the objects of the database.
直接打开数据库会创建一个连接。一个数据库可以有多个连接。当创建连接之初,它处于打开状态。
Opening a database directly creates a connection. There can be multiple connections to a database. When a connection is initially created it is in the open state.
您可以使用 open() 函数连接到 IndexedDB 数据库(我们用来创建数据库)。
You can connect to an IndexedDB database using the open() function (which we used to create a database).
Syntax
下面是连接到现有数据库的语法。
Following is the syntax to connect to an existing database.
let openRequest = indexedDB.open(name, version);Example
下面给出了一个使用带有连接对象的 JavaScript 示例,它与现有数据库交互:
A JavaScript example that interacts with an existing database using a connection object is given below −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>OPENING A DATABASE</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("DATABASE", 1);
request.onsuccess = function (){
document.write("<br> Database created successfully")
}
const requestone = indexedDB.open("Database1",2);
requestone.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("<br> Database created successfully");
}
const requesttwo = indexedDB.open("DATABASE",1);
requesttwo.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("<br> Database opened successfully");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Another way to check databases in the browser
除了检查元素之外,还有另一种方法可以在浏览器中检查 IndexedDB 数据库。
In addition to the inspect element, there is another way to check the IndexedDB database in the browser.
在右上角将有一个“自定义和控制”按钮,点击它。
In the top right corner, there will be a customize and control button, Click it.
在列表中选择 More tools 选项,然后选择 Developer tools 。
Select the More tools option in the list and then select Developer tools.

在下一页中选择“应用程序”选项卡,您可以在其中看到 IndexedDB 数据库。
On the next page select the Application tab where you can see the IndexedDB database.

Deleting a database
如果有我们不需要的或没有必要占用空间的任何数据库,我们可以将其删除。要删除数据库,我们可以使用 deleteDatabase() 函数。
If there is an excess of any database which we do not need or it unnecessarily occupies space, we can delete it. To delete a database we can use the deleteDatabase() function.
以下是 deleteDatabase() 函数的语法 −
Following is the syntax of the deleteDatabase() function −
let deleteRequest = indexedDB.deleteDatabase(name)这里, name 参数是我们想要删除的数据库的名称。
Here, the name parameter is the name of the database that we want to delete.
Example
以下示例创建了一个名为 TestDatabase 的数据库并使用 deleteDatabase() 函数将其删除。
Following example creates a database named TestDatabase and deletes it using the deleteDatabase() function.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Indexed db</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("TestDatabase", 1);
request.onsuccess = function () {
document.write("Database Created Successfully");
};
var req = indexedDB.deleteDatabase("TestDatabase");
req.onsuccess = function () {
document.write("Database Deleted Successfully");
};
req.onerror = function () {
document.write("Couldn't delete the database");
};
</script>
</body>
</html>Deleting a database Directly From the browser
创建数据库后,您可以直接从浏览器中删除它。要执行此操作,请按照以下步骤操作 −
Once you create a database, you can directly delete it database from the browser. To do so, follow the steps given below −
Step 1 − 使用以下方式之一在浏览器中打开可以看到 IndexedDB 数据库(存储)的页面
Step 1 − Open the page where you can see the IndexedDB database (storage) in the browser, using one of the following ways
-
Inspect option − Right−click → Inspect → Application or,
-
Developer tools − Customize and Control Options → More tools → Developers tools → Application
Step 2 − 如果您展开 IndexedDB 存储,可以看到如下图所示的已创建数据库列表。
Step 2 − If you expand the IndexedDB storage, you can observe the list of databases created as shown below.

Step 3 − 单击要删除的数据库。在右侧,您将找到 Delete Database 按钮。如果单击它,将删除此数据库。
Step 3 − Click on the database you want to delete. On the right−hand side, you will find the Delete Database button. If you click on it, this database will be deleted.

Closing a database
要关闭数据库,我们需要使用函数 IDBDatabase.close()
To close a database we need to use the function IDBDatabase.close()
Syntax
IDBDatabase.close();IDBDatabase 接口的 close() 方法会立即返回并关闭连接。
The close() method of the IDBDatabase interface returns immediately and closes the connection.
在所有事务都完成之前,连接并未关闭,但是无法对此连接创建新事务,并且如果挂起关闭操作,方法会引发异常。
The connection is not closed until all transactions are complete but, new transactions cannot be created for this connection and methods throw exceptions if the closing operation is pending.
IndexedDB - Object Stores
Object stores 是 IndexedDB 的数据存储。这是存储数据的地方。数据库可以包含多个对象存储。可以将它们视为 RDBMS 中的表,在其中我们根据想要存储的数据类型存储数据。
Object stores are the data storage of IndexedDB. It is where data is stored. A database may have multiple object stores. Think of them as tables in RDBMS where we store data based on the type of data we want to store.
为了确保数据库完整性,只能使用回调函数 idb.open() 来创建和删除对象存储。它包含一个名为 createObjectStore() 的方法,用于创建对象存储。
To ensure database integrity, object stores can only be created and removed using the callback function idb.open(). It contains a method named createObjectStore() which is used to create an object-store.
Creating object Stores
可以使用 createObjectStore() 方法来创建对象存储。以下是此方法的语法 −
You can create an object store using the createObjectStore() method. Following is the syntax of this method −
IDBDatabase.createObjectStore(name);
Or,
IDBDatabase.createObjectStore(name, options);其中,
Where,
-
The name is the name of the object store.
-
The options object can let us define various configuration properties.
Example
以下示例创建了一个新数据库并在其中创建了一个对象存储 −
Following example creates a new database and creates a object store in it −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Creating Object Store</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var request = indexedDB.open("myDatabase", 2);
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("customers");
document.write("Object store Created Successfully...");
};
</script>
</body>
</html>Defining primary keys
类似于 RDBMS,我们需要主键来唯一地定义对象存储中的某些数据。可以使用密钥路径或密钥生成器以 2 种方式来实现这一点。
Similar to RDBMS we need primary keys to uniquely define some data in an object store. It can be done in 2 ways using a key path or a key generator.
Keypath and Key generator
key path 是总是存在的属性,并且包含惟一的值。我们可以选择一个惟一的值,如电子邮件地址。
A key path is a property that always exists and contains a unique value. We can choose a unique value such as an email address for example.
key generator 为添加到对象存储中的每个对象创建一个惟一的值。默认情况下,如果我们不提及密钥生成器则会进入该图像。例如,自动递增。
A key generator creates a unique value for every object added to the object store. By default, if we don’t mention a key generator comes into the picture. Ex, auto-increment.
Syntax
以下是对象存储上创建密钥路径的语法。
Following is the syntax ro create a keypath on an object store.
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("ObjectStoreName", { keyPath: "primary key, autoincrement/autoDecrement : true" });Example
在下面给出的示例中,我们正在使用 JavaScript 创建到对象存储的密钥路径 −
In the example given below, we are creating a keypath to an object store using JavaScript −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>keypath</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var request = indexedDB.open("myDtabase", 2);
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("customers",{keyPath:"id", autoIncrement:true});
document.write("Object store Created Successfully...");
};
</script>
</body>
</html>Output
执行上述示例后,它将在浏览器上显示以下文本 −
On executing the above example, it will display the following text on the browser −
Object store Created Successfully...Verification
如果上述程序执行成功,当您展开 “myDatabase” 时,您可以看到新创建的对象存储,如果单击它,则可以看到为 “id” 创建了密钥路径。
If the above program is executed successfully if you expand “myDatabase” you can see the newly created object store, if you click on it you can observe that the keypath is created for “id”.

创建新的对象存储时,它们会像上面一样在 IndexedDB 文件夹中提及。
When new object stores are created they are mentioned in the IndexedDB folders like above.
你可以同时使用键路径和键生成器。如果数据总能是唯一的,我们可以使用一个 keypath,否则如果值更改,你可以使用一个键生成器,如果你想为每一个值更改值,但希望提供唯一地表示存储的值,我们可以两个都用。
You can use both a keypath and a key generator. If the data is always unique we can use a keypath else if the value changes you can use a key generator, if you want to change the values for every value but want to give a value that uniquely represents the store we can use both.
Defining Indexes
索引是一种对象存储。它们用于从存储在指定属性中的引用对象检索数据。索引使用指定属性作为其键路径,而不是引用存储的主键。
Indexes are a kind of object-store. They are used to retrieve data from the reference object, stored by a specified property. An index uses the specified property as its key path instead of the reference store’s primary key.
要创建索引,你需要在 createIndex() 实例上调用 object store 方法。
To create an index, you need to call the createIndex() method on an object store instance.
Syntax
下面是 createIndex() 方法的语法 −
Following is the syntax of the createIndex() method −
var myIDBIndex = objectStore.createIndex(indexName, keyPath);
var myIDBIndex = objectStore.createIndex(indexName, keyPath, Parameters);其中,
Where,
-
An indexName is the name of the index created.
-
Keypath is the primary definition while creating an object store
-
The value of the last parameter can be unique or multi-entry In case you “pass unique: true”. The index will not allow duplicate values for a single key. If you pass “multi-entry: true”. The index will add an entry for each array element when the keyPath resolves to an Array. If false, it will add one single entry containing the Array.
Example
以下 JavaScript 示例演示如何创建索引。
The following JavaScript example demonstrates how to create indexes.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>OPENING A DATABASE</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const dbName = "myDB";
const studentdata = [
{name : "jason" , rollno: "160218737028" , branch : "IT"},
{name : "lokesh" , rollno: "160218735020" , branch : "CSE"},
{name : "tarun" , rollno: "160218733057" , branch : "EEE"},
{name : "pranith" , rollno: "160218737029" , branch : "IT"}
];
var request = indexedDB.open("myDB", 2);
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("student",{ keyPath :"rollno" });
objectStore.createIndex("name", "name", { unique: false });
objectStore.createIndex("branch", "branch", { unique: false });
objectStore.transaction.oncomplete = event => {
var objectStore = db.transaction("student", "readwrite").objectStore("student");
studentdata.forEach(function(student) {
objectStore.add(student);
});
};
};
</script>
</body>
</html>Output
如果您去验证 IndexedDB 数据库 myDB 的内容并展开它,您将观察被创建的表如下 −
If you go and verify the contents of the IndexedDB database myDB and expand it youj can observe the created table as −

如果您点击名称和学生值,您将观察索引值如下 −
If you click on the name and student values you can observe the index values as −
Name index
Name index
# |
Key(Key path:"name") |
Primary key (Key path:"rollno") |
Value |
0 |
"jason" |
"160218737028" |
{name: 'jason', rollno: '160218737028', branch: 1. branch: "IT" 2. name: "jason" 3. rollno: "160218737028" |
1 |
"lokesh" |
"160218735020" |
{name: 'lokesh', rollno: '160218735020', branch: 'CSE'} 1. branch: "CSE" 2. name: "lokesh" 3. rollno: "160218735020" |
2 |
"pranith" |
"160218737029" |
{name: 'pranith', rollno: '160218737029', branch: 'IT'} 1. branch: "IT" 2. name: "pranith" 3. rollno: "160218737029" |
3 |
"tarun" |
"160218733057" |
{name: 'tarun', rollno: '160218733057', branch: 'EEE'} 1. branch: "EEE" 2. name: "tarun" 3. rollno: "160218733057" |
Branch Index
Branch Index
# |
Key(Key path:"branch") |
Primary key (Key path:"rollno") |
Value |
0 |
"CSE" |
"160218735020" |
{name:'lokesh', rollno:'160218735020', branch: 'CSE'} 1. branch: "CSE" 2. name: "lokesh" 3. rollno: "160218735020" |
1 |
"EEE" |
"160218733057" |
{name:'tarun', rollno: '160218733057', branch: 'EEE'} 1. branch: "EEE" 2. name: "tarun" 3. rollno: "160218733057" |
2 |
"IT" |
"160218737028" |
{name:'jason', rollno: '160218737028', branch: 'IT'} 1. branch: "IT" 2. name: "jason" 3. rollno: "160218737028" |
3 |
"IT" |
"160218737029" |
{name:'pranith', rollno: '160218737029', branch: 'IT'} 1. branch: "IT" 2. name: "pranith" 3. rollno: "160218737029" |
Deleting Object Store
对象存储与数据库中的表类似,当不需要该表时,我们可以删除表。类似地,当不再使用对象存储时,您可以删除该对象存储。要删除对象存储,您需要调用 deleteObjectStore() 函数。
Object stores are similar to tables in a database and when a table is not needed we delete it. Similarly, you can delete an object store if it is no longer in use. To delete the object store you need to invoke the deleteObjectStore() function.
Syntax
以下是 deleteObjectStore() 函数的语法 −
Following is the syntax of the deleteObjectStore() function −
db.deleteObjectStore("store_name");其中,store_name是您需要删除的对象存储的名称。
Where, store_name is the name of the object store you need to delete.
Example
让我们看一个删除不再必需的对象存储的 JavaScript 示例 −
Let us look at a JavaScript example that deletes an object store which is no longer necessary −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>OPENING A DATABASE</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const dbName = "Database";
var request = indexedDB.open("Database", 2);
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("student",{ keyPath :"rollno" } );
var objstore = db.createObjectStore("college",{autoIncrement : true});
db.deleteObjectStore("college");
};
</script>
</body>
</html>IndexedDB - Creating Data
在创建数据之前,我们需要了解如何传输数据。IndexedDB 打开事务,其每项数据操作都在这些事务中执行。每项操作有四个步骤 −
Before creating data we need to know how data is transferred. IndexedDB opens transactions and each of its data operations are carried out inside each of these transactions. Each operation has four steps −
-
Get database object
-
Open transaction on the database
-
Open object store on the transaction
-
Operate on the object store
IndexedDB 中的操作 −
Operations in IndexedDB are −
-
create
-
read
-
update
-
delete
首先,为了在数据库中执行任何操作,我们需要打开一个事务。打开事务后,我们需要获取所需的存储对象。这些对象存储仅根据创建事务时指定的存储要求提供。然后,稍后可以添加任何所需的数据。
Firstly, to perform any operation in our database, we need to open a transaction. After a transaction is opened, we need to get the object store we require. These object stores are provided only according the requirements mentioned when the transaction is created. Then whatever data that is needed can be added later.
函数用于执行给定操作(如果有)。例如,我们使用 add() 函数向数据库中添加数据或添加新条目。
Functions are used to perform the given operation (if any). For example, we use the add() function to add data into the database or to add a new entry.
Syntax
以下是向数据库中创建数据的语法 −
Following is the syntax of creating data into a database −
ar request = objectStore.add(data);我们可以使用 add() 或 put() 函数向对象存储中添加数据。
We can add data to an object store by using the add() or put() function.
Example
在以下示例中,我们使用 JavaScript 中的 add() 方法向对象存储中插入数据 −
In the following example, we are inserting data into the object store using the add() method in JavaScript −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>creating data</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const dbName = "Database";
var request = indexedDB.open("Database", 2);
request.onupgradeneeded = event => {
var db = event.target.result;
var objectStore = db.createObjectStore("student",{ keyPath :"rollno" } );
};
request.onsuccess = event => {
document.write("Database opened successfully");
var db = event.target.result;
var transaction = db.transaction("student", "readwrite");
var objectStore = transaction.objectStore("student");
objectStore.add({ rollno: 160218737028, name: "jason", branch: "IT" });
objectStore.add({ rollno: 160218733028, name: "tarun", branch: "EEE" });
objectStore.add({ rollno: 160218732028, name: "lokesh", branch: "CSE" });
objectStore.add({ rollno: 160218737025, name: "abdul", branch: "IT" });
objectStore.add({ rollno: 160218736055, name: "palli", branch: "MECH" });
}
transaction.oncomplete = function () {
db.close();
};
</script>
</body>
</html>Output
0 160218732028
{rollno: 160218732028, name: 'lokesh', branch: 'CSE'}
1 160218733028
{rollno: 160218733028, name: 'tarun', branch: 'EEE'}
2 160218736055
{rollno: 160218736055, name: 'palli', branch: 'CSE'}
3 160218737025
{rollno: 160218737025, name: 'abdul', branch: 'IT'}
4 160218737028
{rollno: 160218737028, name: 'jason', branch: 'IT'}IndexedDB - Reading Data
我们将数据输入数据库,并且我们需要调用数据以查看更改以及用于其他各种目的。
We enter data into the database, and we need to call the data to view the changes and also for various other purposes.
我们必须对对象存储调用 get() 方法才能读取此数据。get 方法接收要从存储中检索的对象的主键。
We must call the get() method on the object store to read this data. The get method takes the primary key of the object you want to retrieve from the store.
Syntax
var request = objectstore.get(data);在这里,我们请求 objectstore 使用 get() 函数获取数据。
Here, we are requesting the objectstore to get the data using get() function.
Example
以下示例是如何实现请求 objectstore 以获取数据的 −
Following example is an implementation of requesting the objectstore to get the data −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
const idquery = store.get(4);
idquery.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("idquery",idquery.result);
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>IndexedDB - Updating Data
创建数据后,下一步是执行各种操作;因此,我们需要定期更新数据。在数据库中输入数据不正确的情况下,还需要更新数据。在这里,我们必须指定一个读写事务,因为我们希望写入数据库,而不仅仅是从数据库中读取。
After we created the data, the next step is to perform various operations on it; so we need to update the data regularly. We also need to update the data in the case where we entered data incorrectly into the database. Here, we have to specify a read−write transaction because we want to write to the database, not just read from it.
如果我们要修改或进行数据库中已存在的条目,我们将使用 put() 函数。
If we want to modify it or make an entry which is already present in the database we use the put() function.
Syntax
var requestUpdate = objectStore.put(data);我们对事务发生的对象存储使用 put() 函数,并且我们需要更新数据。
We use the put() function on the object store for which the transaction happened and we need to update data.
Example
让我们看下面的脚本,以了解如何使用 put() 函数更新或修改 objectstore 中的数据 -
Let us look at the script below to understand how to update or modify the data in objectstore using put() function −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
const idquery = store.get(4);
idquery.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("idquery",idquery.result);
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>IndexedDB - Deleting Data
在许多情况下,我们需要从数据库中删除数据,无论是出于存储目的,还是只是为了删除不想保留的数据以释放空间。如果我们希望从数据库中删除此不必要的数据,则可以使用 .delete() 函数。
There are many situations where we need to delete data from the database; be it for storage purposes or just removing unwanted data to free up space. If we want to delete this unnecessary data from a database we can use the .delete() function
Syntax
const request = objectStore.delete(data);我们使用 delete() 函数删除不需要的数据库字段。
We use the delete() function to delete the fields of the database which are not required.
Example
我们来看一个用于删除数据的示例脚本 −
Let us look at an example script to delete data −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE
const deletename = store.delete(1);
deletename.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("id : 1 has been deleted");
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>IndexedDB - Using getAll() Function
在前几部分中,我们一次只从存储中检索对象。现在,我们可以检索所有数据或对象存储的子集。获取 all 方法使用 getAll() 函数返回对象存储中的所有对象
In the previous sections, we only retrieved objects from the store one at a time. Now we can retrieve all the data or subsets of the object stores. The get all method returns all the objects in the object store using the getAll() function
Syntax
ObjectStore.getAll(optionalConstraint);我们可以直接调用 getAll() 以返回存储在对象库中的所有对象,或者我们可以指定一个可选约束,例如从汽车数据库中获得红色轿车
We can directly call getAll() to return all the objects stored in the object store or else we can specify an optional constraint for example red colored cars from a car database
Example
在以下示例脚本中,我们正在调用 getAll() 方法以一次性返回存储在对象库中的所有对象
In the following example script, we are calling the getAll() method to return all the objects stored in the object store at once −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
store.createIndex("branch_db",["branch"],{unique: false});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
const branchIndex = store.index("branch_db");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
const query = branchIndex.getAll(["IT"]);
query.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("query",query.result);
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>IndexedDB - Indexes
索引是一种用于从由指定属性存储的参考对象检索数据的对象存储。即使索引在参考对象存储中并且包含相同数据,但它不使用参考存储的主键,而是使用指定的属性作为其关键路径。
Indexes are a kind of object store used to retrieve data from the reference object stored by a specified property. Even though an index is inside the reference object store and contains the same data, instead of the reference store’s primary key it uses the specified property as its key path.
索引用于定义针对数据唯一约束,它们在创建对象存储时创建。要创建索引,请在对象存储实例上调用 createIndex 方法 -
Indexes are used to define a unique constraint on your data and they are made when the object stores are created. To create an index, call the createIndex method on an object store instance −
Syntax
var myIDBIndex = objectStore.createIndex(indexName, keyPath);
var myIDBIndex = objectStore.createIndex(indexName, keyPath, objectParameters);此方法创建一个索引对象并返回它。该方法创建包含以下参数的索引 -
This method creates and returns an index object. The method creates an index that takes the following arguments −
-
Index name − The name of the index.
-
Keypath − We mention the primary key here.
-
Object Parameters − There are two object parameters.
-
Unique − Duplicate values cannot be added.
-
Multi entry − If true, the index will add an entry in the index for each array element when the keyPath resolves to an Array. If false, it will add one single entry containing the Array.
Example
以下示例显示了在对象存储中实现索引 -
The following example shows the implementation of indexes in an object store −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
store.createIndex("branch_db",["branch"],{unique: false});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
const branchIndex = store.index("branch_db");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output
branchIndex:
1
['CSE']
0: "CSE"
length: 1
4
{id: 4, name: 'deevana', branch: 'CSE'}
branch: "CSE"
id: 4
name: "deevana"
2
['EEE']
0: "EEE"
length: 1
3
{id: 3, name: 'palli', branch: 'EEE'}
branch: "EEE"
id: 3
name: "palli"
3
['IT']
0: "IT"
length: 1
1
{id: 1, name: 'jason', branch: 'IT'}
branch: "IT"
id: 1
name: "jason"IndexedDB - Ranges
如果我们不想一次获得全部数据,则使用范围。如果我们只想获得特定范围内的的数据,则使用范围。我们使用 IDBKeyRange 对象来定义范围。此对象具有 4 个方法,分别是 −
When we don’t want to get all the data at once we use ranges. When we want to get data in a specific range only we use ranges. We define the range using the IDBKeyRange object. This object has 4 methods which are −
-
upperBound()
-
lowerBound()
-
bound()
-
only()
Syntax
IDBKeyRange.lowerBound(indexKey);
IDBKeyRange.upperBound(indexKey);
IDBKeyRange.bound(lowerIndexKey, upperIndexKey);下表列出了各种范围代码 −
Following is the list of various range codes −
S.No. |
Range Codes & Description |
1 |
All keys ≥ a DBKeyRange.lowerBound(a) |
2 |
All keys > a IDBKeyRange.lowerBound(a, true) |
3 |
All keys ≤ b IDBKeyRange.upperBound(b) |
4 |
All keys < b IDBKeyRange.upperBound(b, true) |
5 |
All keys ≥ a && ≤ b IDBKeyRange.bound(a, b) |
6 |
All keys > a &&< b IDBKeyRange.bound(a, b, true, true) |
7 |
All keys > a && ≤ b IDBKeyRange.bound(a, b, true, false) |
8 |
All keys ≥ a && < b IDBKeyRange.bound(a, b, false, true) |
9 |
The key = c IDBKeyRange.only(c) |
我们通常使用索引来使用范围,并且在句法中,索引键表示索引键路径值。
We generally use the indexes for using range and in the syntax, the index key represents the indexes keypath value.
Examples
使用 get() 和 getAll() 方法来检索范围代码的各种示例如下所示:
Various examples to retrieve the range codes using get() and getAll() methods is as follows −
class.get(‘student’)
class.getAll(IDBKeyRange.bound(‘science’,’math’)
class.getAll(IDBKeyRange.upperbound(‘science’,true)
class.getAll()
class.getAllKeys(IDBKeyRange.lowerbound(‘student’,true))HTML Example
考虑以下 HTML 示例以获取范围代码:
Consider the HTML example below to obtain the range codes −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
store.createIndex("branch_db",["branch"],{unique: false});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
const branchIndex = store.index("branch_db");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
const upperquery =store.getAll(IDBKeyRange.upperBound('2', true));
upperquery.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("upperquery",upperquery.result);
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output
database opened successfully
upperquery (4) [{...}, {...}, {...}, {...}]
arg1: (4) [{...}, {...}, {...}, {...}]
0: {id: 1, name: 'jason', branch: 'IT'}
1: {id: 2, name: 'praneeth', branch: 'CSE'}
2: {id: 3, name: 'palli', branch: 'EEE'}
3: {id: 4, name: 'deevana', branch: 'CSE'}
length: 4
[[Prototype]]: Array(0)
[[Prototype]]: ObjectIndexedDB - Transactions
事务是一组操作,这些操作要么全部成功,要么全部失败。例如,如果我们通过 UPI 向商家付款,但交易被拒绝,那该笔钱必须退回发送者的帐户。事务维持这种完整性。
A transaction is a group of operations, that should either all succeed, or all fail. For example, if we pay from UPI to a merchant and the transaction declines then the money must fall back to the senders' account. A transaction maintains this integrity.
以下是如何开启事务的语法:
Following is the syntax for opening a transaction −
db.transaction(store[, type]);此处的存储是我们要在其中执行事务的对象存储。事务的类型有两种:
The store here is the object store where we want to do the transaction. The type of the transaction is of 2 types −
-
read-only − can only read, by default it is given.
-
read-write − we can only read and write the data but we cannot create, remove or alter it from object stores.
Transaction life cycle
事务是对象存储之间执行任何操作的连接。每个事务都有一个状态,该状态可以是:
The transaction is a connection between object stores to perform any operations. Each transaction has a state which can be −
-
active − When a transaction is first created. or when a request is associated with a transaction. New requests can be made against the transaction when it is in this state.
-
inactive − A transaction is in this state after control returns to the event after its creation. No requests can be made against the transaction when it is in this state.
-
committing − Once all the requests associated with a transaction are completed then it attempts to commit. During the commit state, no new requests can be made.
-
finished − After a transaction is committed or aborted then it is in the finished state. During the finished state, no new requests can be made.
The lifetime of a transaction
会形成一个具有范围和模式的事务。当事务生成后,其状态最初是激活的。
A transaction with a scope and a mode is formed. A transaction’s state is originally active when it is generated.
-
To begin the transaction, the implementation must queue a task.
-
A success or, error event will be fired when each request connected with a transaction is handled. The transaction state is set to active when the event is sent, allowing subsequent requests to be made against the transaction. The transaction’s status is set to inactive once the event dispatch is completed.
-
A transaction can be canceled at any point before it is completed, even if it isn’t currently active or hasn’t begun.
-
When all requests made against the database are successful, the implementation must attempt to commit the transaction.
-
When a transaction is committed or aborted its state is set to finish.
Transaction scheduling
当事务可以启动时,有一些限制。
When a transaction can be started, there are some limitations.
-
When there is no read or write transactions that: a. were established before transactions tx b. have an overlapping scope with tx c. are not in a final state, a read-only transaction tx can commence.
-
A read/write-only transaction tx can begin when there are no other transactions that − were formed before tx,have an overlapping scope with tx, orare not in a completed state.
Upgrade transactions
模式为 " versionchange " 的事务是升级事务。
A transaction with the mode "versionchange" is an upgrade transaction.
对象存储和数据库中的索引可以使用升级操作进行创建、重命名和删除。
Object stores and indexes in a database can be created, renamed, and deleted using upgrade operations.
如果给出的版本大于当前版本,则在打开与数据库的连接后完成运行升级事务的步骤时自动生成升级事务。在 upgradeneeded 事件处理程序中,此事务将处于活动状态。
If a version greater than the current version is given, an upgrade transaction is automatically produced when completing the steps to run an upgrade transaction after a connection to a database is opened. Within the upgradeneeded event handler, this transaction will be active.
Committing a transaction
必须完成以下步骤才能提交事务 -
The following steps must be completed to commit a transaction −
-
The transaction state is first set to committing.
-
Wait until all of the transaction requests on the list have been processed.
-
Abort the transaction if an error occurs.
-
If the transaction is an upgrade transaction, set the database upgrade transaction’s transactions connections to NULL.
-
Change the transaction state to complete.
-
fire the transaction’s entire event
-
If a transaction is an upgrade transaction, set the request’s transaction to null and make the request that is associated with the transaction.
Syntax
transaction.commit()尝试提交事务。将允许所有挂起请求完成,但不会接受任何新请求。
Attempts to commit the transaction. All pending requests will be allowed to complete, but no new requests will be accepted.
如果挂起的请求失败,则事务将中止。成功请求的成功事件仍将触发,但在事件处理程序中抛出异常不会中止事务,调用 preventDefault() 不会阻止事务中止。
The transaction will abort if a pending request fails. The success events for successful requests will still fire, but throwing an exception in an event handler will not abort the transaction calling preventDefault() will not prevent the transaction from aborting.
Event Handlers
各种事件处理程序属性如下所示
Various event handler attributes are as follows
attribute EventHandler onabort;
attribute EventHandler oncomplete;
attribute EventHandler onerror;Transactions Example
下面给出了一个简单的 JavaScript 程序来演示事务的使用 -
A simple JavaScript program to demonstrate the usage of a transaction is given below −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
document.write("transaction complete");
db.close;
};
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output
database opened successfully
transaction complete在这里创建事务,只有在创建事务时才能将数据添加到对象存储中,最终在事务完成后,我们关闭数据库。
Here a transaction is created, only when a transaction is created can we add data into the object store and finally after the transaction is complete we close the database.
Example
以下示例演示了一个事务属性 oncomplete 的用法 -
The following example shows the usage of a transaction attribute oncomplete −
function student(db, names) {
let transaction = db.transaction(['names'], 'readwrite');
let store = transaction.objectStore('names');
for (let i = 0; i < messages.length; i++) {
store.add({text: names[i]});
}
transaction.oncomplete = function()
{document.write('transaction complete')};
}Abort transactions
要中止事务,请按照以下步骤操作 -
To abort a transaction, follow these steps −
-
All transaction-related modifications to the database are undone.
-
Changes in object stores, indexes, and versions are likewise reverted during upgrade transactions.
-
Complete the transaction state.
-
Set transactions error to error if the error is not null.
-
Set the request processed flag to true for each request in the transactions request list.
-
Set the requests done flag to true and the results to define.
-
If the transaction is an upgrade transaction, set the upgrade transaction associated with the transaction’s connection to null.
-
Create an abort at transaction event with the bubbles attribute set to true.
-
If the transaction is an upgrade transaction, assume that request is the transaction’s open request.
IndexedDB - Error Handling
我们编写的并非所有请求都会返回输出。这可能是由于 -
Not all requests we write will return an output. This may happen due to −
-
possible errors while writing the code.
-
If the storage limit has been exceeded.
-
If transactions have failed etc.
在失败的请求中,事务被取消,并且所有更改都被恢复。但有时我们希望在不恢复所有更改的情况下处理失败,为此可使用 request.onerror 处理程序。它可以通过调用 event.preventDefault() 来防止事务中止。
In a failed request the transaction is canceled, and all the changes are reverted. But sometimes we want to handle the failure without reverting all the changes to do that we use the request.onerror handler. It can prevent the transaction abort by calling event.preventDefault().
Example
以下给出了在 IndexedDB 中显示错误处理的一个示例:
An example to show error handling in IndexedDB is given below −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>IndexedDB</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("DATABASE", 1);
request.onsuccess = function (){
document.write("database creation success")
}
request.onerror = function(event){
document.write("Database not created " + event.target.errorCode);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output
Database not created undefined我们可以通过为此使用 db.onerror 处理程序来捕获错误。
We can catch errors using the db.onerror handler for it.
db.onerror = function(event) {
let request = event.target;
document.write("Error is found", request.error);
};当具有相同 id 的对象已存在时,会发生约束错误。但有时,如果一个错误得到完全处理,并且我们不想报告该错误,则可以通过在 request.onerror 中使用 event.stopPropagation() 来阻止冒泡。
The constraint error is occured when an object with the same id already exists. But sometimes if any of an error is fully handled and we don’t want to report it we can stop the bubbling by using event.stopPropagation() in request.onerror.
request.onerror = function(event) {
if (request.error.name == "ConstraintError") {
document.write("id already exists");
event.preventDefault();
event.stopPropagation();
}
}IndexedDB - Searching
我们遇到许多情况,需要在对象存储中搜索值。对象存储在内部进行排序。可以通过以下方式完成:
We encounter many situations where we need to search for values in an object store. Object stores are sorted internally. It can be done by −
-
Searching by a key value or a key range.
-
Searching based on another object field.
Searching by Key
我们可以通过对一个可接受的键范围使用 IDBKeyRange 对象,来搜索精确的键值或键值范围。IDBKeyRange 对象具有以下调用:
We can search for exact key values or a range of key values by using IDBKeyRange objects with an acceptable key Range. IDBKeyRange object has the following calls −
-
IDBKeyRange.lowerBound(lower, [open]) for >=lower
-
IDBKeyRange.upperBound(upper, [open]) for >=upper
-
IDBKeyRange.bound(lower, upper, [lowerOpen] , [upperOpen]) between lower and upper
-
IDBKeyRange.only(key) if the range contains only one key.
为了执行实际搜索,我们在对象存储上使用查询参数。用于执行这些操作的不同类型的函数是:
To perform the actual search we use the query argument on the object store. The different types of methods to perform these operations are
-
store.get(query) − Search for the first value in the store by a key or a range
-
store.getAll([query],[count]) − Search for all values in the store till the limit of the count mentioned.
-
store.getKey(query) − search for the first key for which the query is satisfied.
-
store.getAllKeys([query],[count]) − search for all the keys for which the query is satisfied till the limit of the count is completed.
-
store.count([query]) − get the total count of the keys for which the query is satisfied.
Example
在此示例中,我们使用 getAll() 方法检索所有对象,并按其键来搜索对象:
In this example, we are retrieving all the objects using the getAll() method and searching for objects by their key −
class.get(‘student’)
class.getAll(IDBKeyRange.bound(‘science’,’math’)
class.getAll(IDBKeyRange.upperbound(‘science’,true)
class.getAll()
class.getAllKeys(IDBKeyRange.lowerbound(‘student’,true))Searching by a field or index
为了根据其他对象字段进行搜索,我们需要使用索引。索引存储具有所需值的对象的键列表。索引在内部也像对象存储一样进行排序。
To search based on other object fields we need to use indexes. An index stores a list of keys for objects that have the value required. Indexes are also internally sorted like object stores.
Syntax
objectStore.createIndex(name, keyPath, [options]);name - 索引名称
name − Index Name
keyPath - 将在对象字段的路径上进行搜索
keyPath − Searching will be done on the path to the object field
options - 选项分为 2 类
options − options are of 2 types
-
unique − Objects in the store with a unique value will be present at the key path and duplicates cannot be made of them.
-
multi−entry − if the value on the keypath is an array then by default the index will treat the whole array as a key but if we use multi-entry the array members will become index keys.
Example
如果我们想要根据价格搜索电话,则示例程序如下所示:
If we want to search for phones based on price, the example program is as follows −
openRequest.onupgradeneeded = function() {
let books = db.createObjectStore('phone', {keyPath: 'id'});
let index = books.createIndex('pricephone', 'price');
};要创建索引,我们需要使用升级项。
To create an index we need to use the upgrade needed.
-
the index will track the price field.
-
If the price is not unique we can’t set the unique option.
-
If the price is not an array then multiEntry is not applicable.
Example
在以下示例中,我们创建一个事务,并使用 getAll() 函数检索所有对象。检索这些对象后,我们搜索该事务中的对象值。如果找到,则返回该对象;如果没有,则返回 false。
In the following example, we create a transaction and retrieve all the objects using the getAll() function. Once they are retrieved, we search for object values in that transaction. If found, return the object; if not, return false.
let transaction = db.transaction("phones");
let books = transaction.objectStore("phones");
let priceIndex = books.index("price_index");
let request = priceIndex.getAll(7);
request.onsuccess = function() {
if (request.result !== undefined) {
document.write("Phones", request.result);
} else {
document.write("There are no such phones");
}
};HTML Example
搜索对象存储中值的 HTML 脚本实现如下:
The HTML script implementation to search for values in object store is given below −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
store.createIndex("branch_db",["branch"],{unique: false});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
const branchIndex = store.index("branch_db");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
const req = branchIndex.getAll(["CSE"]);
req.onsuccess = function(){
if(req.result!==undefined){
document.write("bots",req.result);
} else{
document.write("There are no such bots");
}
};
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>IndexedDB - Cursors
在检索数据时,当我们知道想要检索哪个键时,我们使用了 get() 函数,但如果我们想要逐个浏览对象存储的所有值,我们可以使用游标。
In retrieving data we used the get() function when we knew what key we wanted to retrieve but if we want to step through all the values of the object store we can use cursors.
首先我们使用 open cursor 函数,然后我们可以向其中添加我们的参数。我们可以在 openCursor() 函数中插入的参数如下:
Firstly we use the open cursor function and then we can add our arguments to it. The arguments which we can insert in openCursor() function are −
-
Limit the range of objects by using a key range
-
The direction in which we want to iterate
以下是游标的语法
Following is the syntax of cursors
Syntax
ObjectStore.openCursor(optionalKeyRange, optionalDirection);对于对象存储,我们使用 openCursor()
For the object store, we use the openCursor()
-
optionalKeyRange − we can limit the range of how many objects we need to retrieve.
-
optionalDirection − we can specify the direction we want to iterate.
Example 1
在此示例中,我们了解如何使用 JavaScript 打开游标函数:
In this example, we learn how to open a cursor function using JavaScript −
var objectStore = db.transaction("student").objectStore("student”);
objectStore.openCursor().onsuccess = event => {
var cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
document.write("Name" + cursor.key + cursor.value.name);
cursor.continue();
} else {
document.write("entries closed");
}
};Example 2
当我们想从对象存储中检索所有对象并将其放置到数组中时。
When we want to retrieve all objects from the object store and place them in an array.
var student = [];
objectStore.openCursor().onsuccess = event => {
var cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
student.push(cursor.value);
cursor.continue();
} else {
document.write(student);
}
};Example 3
下面是另一个使用 JavaScript 中的 openCursor() 函数的示例 −
Given below is another example to implement the openCursor() function in JavaScript −
var singleKeyRange = IDBKeyRange.only("Jason");
var lowerBoundKeyRange = IDBKeyRange.lowerBound("Praneeth");
var lowerBoundOpenKeyRange = IDBKeyRange.lowerBound("jason", true);
var upperBoundOpenKeyRange = IDBKeyRange.upperBound("praneeth", true);
var boundKeyRange = IDBKeyRange.bound("jason", "praneeth", false, true);
index.openCursor(boundKeyRange).onsuccess = event => {
var cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
cursor.continue();
}
};或者如果我们想给出方向 −
or else if we want to give the direction −
objectStore.openCursor(boundKeyRange, "prev").onsuccess = event => {
var cursor = event.target.result;
if (cursor) {
cursor.continue();
}
};HTML Example
按照如下内容实现游标函数使用情况的 HTML 脚本 −
The HTML script to implement the usage of cursor function is given as follows −
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const request = indexedDB.open("botdatabase",1);
request.onupgradeneeded = function(){
const db = request.result;
const store = db.createObjectStore("bots",{ keyPath: "id"});
store.createIndex("branch_db",["branch"],{unique: false});
}
request.onsuccess = function(){
document.write("database opened successfully");
const db = request.result;
const transaction=db.transaction("bots","readwrite");
const store = transaction.objectStore("bots");
const branchIndex = store.index("branch_db");
store.add({id: 1, name: "jason",branch: "IT"});
store.add({id: 2, name: "praneeth",branch: "CSE"});
store.add({id: 3, name: "palli",branch: "EEE"});
store.add({id: 4, name: "abdul",branch: "IT"});
store.put({id: 4, name: "deevana",branch: "CSE"});
const req = store.openCursor();
req.onsuccess = function(){
const cursor = req.result;
if(cursor){
const key = cursor.key;
const value = cursor.value;
document.write(key,value);
cursor.continue();
} else {
document.write("bots completed");
}
}
transaction.oncomplete = function(){
db.close;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>IndexedDB - Promise Wrapper
Promises ,就像回调函数一样,是一种在不对 javascript 的运行时线程停止的情况下告知你的代码完成异步操作时要执行什么操作的技术。
Promises, like callbacks, are a technique of telling what you want your code to perform once an asynchronous operation completes without stopping the runtime’s thread of javascript.
与在异步函数完成后提供回调函数来运行的方式不同,可以使用 promise 代替。
Instead of supplying a callback to an asynchronous function to run after it completes, promises can be used instead.
Promise 库是 Jake Archibald 创建的,它使用 promise 而不是事件。
Promise library was created by Jake Archibald and it uses promises rather than events.
使用起来比传统的 IndexedDB 更加容易。它简化了 API,同时仍然保留了 API 的结构。
It is easier to use than the traditional IndexedDB. It simplifies the API while still maintaining its structure.
这里我们仅展示了为什么我们可以使用 Promise 库的原因,要了解关于它的更多信息,您可以访问以下网站 −
Here we are showing the enhancements only as to why we can use the Promised library to know more about it you can visit the following website −
它有一些增强功能 −
It has a few enhancements −
-
IDBDatabase
-
IDBTransaction
-
IDBCursor
IDBDatabase
从对象存储获取或设置的快捷方式
Shortcuts to get or set from an object store
const value = await db.get(storeName, key);
await db.put(storeName, value, key);从索引获取的快捷方式
Shortcuts to get from an Index
const value = await db.getFromIndex(storeName, indexName, key);IDBTransaction
tx.store
如果事务是一个单个存储,则存储属性引用存储,否则未定义,那么我们使用
If a transaction is a single store the store property references the store or else it is undefined then we use
const tx = db.transaction('any transaction');
const store = tx.store;
tx.objectStore(storeName);tx.done
当事务成功完成时,.done promise 解决,否则会因事务错误拒绝。
The .done promise resolves when a transaction is completed successfully else it rejects with a transaction error.
const tx = db.transaction(storeName, 'readwrite');
await Promise.all([
tx.store.add('one', 'two'),
tx.store.put('three', 'four'),
tx.done,
]);IDBCursor
游标推进的方法为 −
The cursor advance methods are −
-
Advance
-
Continue
-
ContinuePrimaryKey
它们返回对 cursor 的 promise,否则返回 null。
They return a promise to cursor or else it returns null.
let cursor = await db.transaction(storeName).store.openCursor();
while (cursor) {
document.write(cursor.key, cursor.value);
cursor = await cursor.continue();
}IndexedDB - ECMAScript Binding
Firstly, what is ECMAScript?
ECMAScript(欧洲计算机制造商协会脚本)是一种基于 JavaScript 的脚本语言。
ECMAScript (European Computer Manufacturers Association Script) is a scripting language based on JavaScript.
JavaScript ES6 添加了新的语法和功能,以便更容易读取代码,并且我们可以为相同的功能编写更少的代码。ES6 有许多新功能,例如箭头函数、模板字符串、类分解等。
JavaScript ES6 adds new syntaxes and features so that the code is more easily readable and we can write less code for the same functionality. ES6 has many new features like arrow functions, template strings, class destruction, etc.
绑定 - 使用“this”关键字将对象绑定到函数并引用它。
Binding - Bind an object to a function and reference it using the ‘this’ keyword.
ECMAScript 处理键、值和键路径。
ECMAScript deals with keys, values, and keypaths.
它定义了此规范中定义的键值如何转换为 ECMAScript 值以及如何从 ECMAScript 值转换。
It defines how key values defined in this specification are converted to and from ECMAScript values.
Extract a key from a value
若要使用包含值、键路径和可选的多条目标志的键路径从值中提取键,我们需要执行以下步骤。结果可以是键、无效、失败,甚至异常。
To extract a key from a value using a key path with value, keyPath, and an optional multi-entry flag we need to follow the following steps. The results can be a key, invalid, failure, or even an exception.
-
Where r is the result of evaluating a keypath on a value with value and keypath. Rethrow any exceptions. If r is a failure return failure.
-
key be the result of converting a value to a key with r if the multi-entry flag is false, and the result of converting a value to a multi-entry key with r otherwise. Rethrow any exceptions.
-
If the key is invalid, return invalid.
-
Return key.
