Data Mining 简明教程
Data Mining - Overview
信息产业中有大量可用数据。在转换成有用的信息之前,这些数据毫无用处。有必要分析这些海量数据并从中提取有用信息。
There is a huge amount of data available in the Information Industry. This data is of no use until it is converted into useful information. It is necessary to analyze this huge amount of data and extract useful information from it.
信息提取不是我们需要执行的唯一过程;数据挖掘还涉及其他过程,如数据清理、数据集成、数据转换、数据挖掘、模式评估和数据展示。一旦所有这些过程结束,我们就可以在许多应用程序中使用这些信息,例如欺诈检测、市场分析、生产控制、科学探索等。
Extraction of information is not the only process we need to perform; data mining also involves other processes such as Data Cleaning, Data Integration, Data Transformation, Data Mining, Pattern Evaluation and Data Presentation. Once all these processes are over, we would be able to use this information in many applications such as Fraud Detection, Market Analysis, Production Control, Science Exploration, etc.
What is Data Mining?
数据挖掘被定义为从大量数据中提取信息。换句话说,我们可以说数据挖掘是从小知识中挖掘知识的过程。提取的信息或知识可用于以下任何应用程序 -
Data Mining is defined as extracting information from huge sets of data. In other words, we can say that data mining is the procedure of mining knowledge from data. The information or knowledge extracted so can be used for any of the following applications −
-
Market Analysis
-
Fraud Detection
-
Customer Retention
-
Production Control
-
Science Exploration
Data Mining Applications
数据挖掘在以下领域极有用处 -
Data mining is highly useful in the following domains −
-
Market Analysis and Management
-
Corporate Analysis & Risk Management
-
Fraud Detection
除此之外,数据挖掘还可用于生产控制、客户保留、科学探索、体育、占星术和互联网 Web Surf-Aid 领域
Apart from these, data mining can also be used in the areas of production control, customer retention, science exploration, sports, astrology, and Internet Web Surf-Aid
Market Analysis and Management
以下是数据挖掘使用的各个市场领域 -
Listed below are the various fields of market where data mining is used −
-
Customer Profiling − Data mining helps determine what kind of people buy what kind of products.
-
Identifying Customer Requirements − Data mining helps in identifying the best products for different customers. It uses prediction to find the factors that may attract new customers.
-
Cross Market Analysis − Data mining performs Association/correlations between product sales.
-
Target Marketing − Data mining helps to find clusters of model customers who share the same characteristics such as interests, spending habits, income, etc.
-
Determining Customer purchasing pattern − Data mining helps in determining customer purchasing pattern.
-
Providing Summary Information − Data mining provides us various multidimensional summary reports.
Corporate Analysis and Risk Management
数据挖掘用于企业部门的以下领域 −
Data mining is used in the following fields of the Corporate Sector −
-
Finance Planning and Asset Evaluation − It involves cash flow analysis and prediction, contingent claim analysis to evaluate assets.
-
Resource Planning − It involves summarizing and comparing the resources and spending.
-
Competition − It involves monitoring competitors and market directions.
Fraud Detection
数据挖掘还用于信用卡服务和电信领域以检测欺诈行为。在电话诈骗中,它有助于找到通话目的地、通话时长、一天或一周中的时间等。它还分析了与预期规范不同的模式。
Data mining is also used in the fields of credit card services and telecommunication to detect frauds. In fraud telephone calls, it helps to find the destination of the call, duration of the call, time of the day or week, etc. It also analyzes the patterns that deviate from expected norms.
Data Mining - Tasks
数据挖掘涉及可挖掘的模式类型。根据要挖掘的数据类型,数据挖掘涉及两个类别的功能 −
Data mining deals with the kind of patterns that can be mined. On the basis of the kind of data to be mined, there are two categories of functions involved in Data Mining −
-
Descriptive
-
Classification and Prediction
Descriptive Function
描述功能涉及数据库中数据的常规属性。以下是描述功能列表 −
The descriptive function deals with the general properties of data in the database. Here is the list of descriptive functions −
-
Class/Concept Description
-
Mining of Frequent Patterns
-
Mining of Associations
-
Mining of Correlations
-
Mining of Clusters
Class/Concept Description
类别/概念是指要与类别或概念关联的数据。例如,在一家公司中,销售物品的类别包括计算机和打印机,客户概念包括大额消费者和预算消费者。此类类别或概念的描述称为类别/概念描述。可以通过以下两种方式获取这些描述:
Class/Concept refers to the data to be associated with the classes or concepts. For example, in a company, the classes of items for sales include computer and printers, and concepts of customers include big spenders and budget spenders. Such descriptions of a class or a concept are called class/concept descriptions. These descriptions can be derived by the following two ways −
-
Data Characterization − This refers to summarizing data of class under study. This class under study is called as Target Class.
-
Data Discrimination − It refers to the mapping or classification of a class with some predefined group or class.
Mining of Frequent Patterns
频繁模式是指在交易数据中经常发生的模式。以下是频繁模式的类型列表 −
Frequent patterns are those patterns that occur frequently in transactional data. Here is the list of kind of frequent patterns −
-
Frequent Item Set − It refers to a set of items that frequently appear together, for example, milk and bread.
-
Frequent Subsequence − A sequence of patterns that occur frequently such as purchasing a camera is followed by memory card.
-
Frequent Sub Structure − Substructure refers to different structural forms, such as graphs, trees, or lattices, which may be combined with item-sets or subsequences.
Mining of Association
关联用于零售销售中,以识别经常一起购买的模式。此过程是指揭示数据之间的关系和确定关联规则的过程。
Associations are used in retail sales to identify patterns that are frequently purchased together. This process refers to the process of uncovering the relationship among data and determining association rules.
例如,零售商生成了一条关联规则,表明 70% 的时间牛奶与面包一起出售,而只有 30% 的时间饼干与面包一起出售。
For example, a retailer generates an association rule that shows that 70% of time milk is sold with bread and only 30% of times biscuits are sold with bread.
Mining of Correlations
它是一种附加分析,执行此分析是为了揭示关联属性值对或两个项目集之间的有趣统计关联,以分析它们是否对彼此有正面、负面或无影响。
It is a kind of additional analysis performed to uncover interesting statistical correlations between associated-attribute-value pairs or between two item sets to analyze that if they have positive, negative or no effect on each other.
Classification and Prediction
分类是查找描述数据类别或概念的模型的过程。目的是能够使用此模型来预测类标签未知的对象的类别。此派生模型基于对培训数据集的分析。派生模型可以以下形式呈现:
Classification is the process of finding a model that describes the data classes or concepts. The purpose is to be able to use this model to predict the class of objects whose class label is unknown. This derived model is based on the analysis of sets of training data. The derived model can be presented in the following forms −
-
Classification (IF-THEN) Rules
-
Decision Trees
-
Mathematical Formulae
-
Neural Networks
参与这些过程的函数列表如下:
The list of functions involved in these processes are as follows −
-
Classification − It predicts the class of objects whose class label is unknown. Its objective is to find a derived model that describes and distinguishes data classes or concepts. The Derived Model is based on the analysis set of training data i.e. the data object whose class label is well known.
-
Prediction − It is used to predict missing or unavailable numerical data values rather than class labels. Regression Analysis is generally used for prediction. Prediction can also be used for identification of distribution trends based on available data.
-
Outlier Analysis − Outliers may be defined as the data objects that do not comply with the general behavior or model of the data available.
-
Evolution Analysis − Evolution analysis refers to the description and model regularities or trends for objects whose behavior changes over time.
Data Mining Task Primitives
-
We can specify a data mining task in the form of a data mining query.
-
This query is input to the system.
-
A data mining query is defined in terms of data mining task primitives.
Note − 这些基础函数允许我们以交互方式与数据挖掘系统进行通信。以下为数据挖掘任务基础函数列表 -
Note − These primitives allow us to communicate in an interactive manner with the data mining system. Here is the list of Data Mining Task Primitives −
-
Set of task relevant data to be mined.
-
Kind of knowledge to be mined.
-
Background knowledge to be used in discovery process.
-
Interestingness measures and thresholds for pattern evaluation.
-
Representation for visualizing the discovered patterns.
Set of task relevant data to be mined
这是用户感兴趣的数据库部分。此部分包括以下内容 -
This is the portion of database in which the user is interested. This portion includes the following −
-
Database Attributes
-
Data Warehouse dimensions of interest
Kind of knowledge to be mined
它指要执行的功能类型。这些功能为 -
It refers to the kind of functions to be performed. These functions are −
-
Characterization
-
Discrimination
-
Association and Correlation Analysis
-
Classification
-
Prediction
-
Clustering
-
Outlier Analysis
-
Evolution Analysis
Background knowledge
背景知识允许在多个抽象层级挖掘数据。例如,概念层次是允许在多个抽象层级挖掘数据的背景知识之一。
The background knowledge allows data to be mined at multiple levels of abstraction. For example, the Concept hierarchies are one of the background knowledge that allows data to be mined at multiple levels of abstraction.
Data Mining - Issues
数据挖掘不是一项简单的任务,因为所使用的算法可能非常复杂,而且数据并不总是在一个地方可用。它需要从各种异构数据源进行集成。这些因素还产生了一些问题。在本教程中,我们将讨论有关主要问题 −
Data mining is not an easy task, as the algorithms used can get very complex and data is not always available at one place. It needs to be integrated from various heterogeneous data sources. These factors also create some issues. Here in this tutorial, we will discuss the major issues regarding −
-
Mining Methodology and User Interaction
-
Performance Issues
-
Diverse Data Types Issues
下图描述了主要问题。
The following diagram describes the major issues.

Mining Methodology and User Interaction Issues
它涉及以下类别的问题 −
It refers to the following kinds of issues −
-
Mining different kinds of knowledge in databases − Different users may be interested in different kinds of knowledge. Therefore it is necessary for data mining to cover a broad range of knowledge discovery task.
-
Interactive mining of knowledge at multiple levels of abstraction − The data mining process needs to be interactive because it allows users to focus the search for patterns, providing and refining data mining requests based on the returned results.
-
Incorporation of background knowledge − To guide discovery process and to express the discovered patterns, the background knowledge can be used. Background knowledge may be used to express the discovered patterns not only in concise terms but at multiple levels of abstraction.
-
Data mining query languages and ad hoc data mining − Data Mining Query language that allows the user to describe ad hoc mining tasks, should be integrated with a data warehouse query language and optimized for efficient and flexible data mining.
-
Presentation and visualization of data mining results − Once the patterns are discovered it needs to be expressed in high level languages, and visual representations. These representations should be easily understandable.
-
Handling noisy or incomplete data − The data cleaning methods are required to handle the noise and incomplete objects while mining the data regularities. If the data cleaning methods are not there then the accuracy of the discovered patterns will be poor.
-
Pattern evaluation − The patterns discovered should be interesting because either they represent common knowledge or lack novelty.
Performance Issues
可能存在以下性能相关问题 −
There can be performance-related issues such as follows −
-
Efficiency and scalability of data mining algorithms − In order to effectively extract the information from huge amount of data in databases, data mining algorithm must be efficient and scalable.
-
Parallel, distributed, and incremental mining algorithms − The factors such as huge size of databases, wide distribution of data, and complexity of data mining methods motivate the development of parallel and distributed data mining algorithms. These algorithms divide the data into partitions which is further processed in a parallel fashion. Then the results from the partitions is merged. The incremental algorithms, update databases without mining the data again from scratch.
Diverse Data Types Issues
-
Handling of relational and complex types of data − The database may contain complex data objects, multimedia data objects, spatial data, temporal data etc. It is not possible for one system to mine all these kind of data.
-
Mining information from heterogeneous databases and global information systems − The data is available at different data sources on LAN or WAN. These data source may be structured, semi structured or unstructured. Therefore mining the knowledge from them adds challenges to data mining.
Data Mining - Evaluation
Data Warehouse
数据仓库表现出以下特征以支持管理层决策过程 −
A data warehouse exhibits the following characteristics to support the management’s decision-making process −
-
Subject Oriented − Data warehouse is subject oriented because it provides us the information around a subject rather than the organization’s ongoing operations. These subjects can be product, customers, suppliers, sales, revenue, etc. The data warehouse does not focus on the ongoing operations, rather it focuses on modelling and analysis of data for decision-making.
-
Integrated − Data warehouse is constructed by integration of data from heterogeneous sources such as relational databases, flat files etc. This integration enhances the effective analysis of data.
-
Time Variant − The data collected in a data warehouse is identified with a particular time period. The data in a data warehouse provides information from a historical point of view.
-
Non-volatile − Nonvolatile means the previous data is not removed when new data is added to it. The data warehouse is kept separate from the operational database therefore frequent changes in operational database is not reflected in the data warehouse.
Data Warehousing
数据仓储是构建和使用数据仓库的过程。数据仓库是通过集成来自多个异构源的数据来构建的。它支持分析报告、结构化和/或临时查询以及决策制定。
Data warehousing is the process of constructing and using the data warehouse. A data warehouse is constructed by integrating the data from multiple heterogeneous sources. It supports analytical reporting, structured and/or ad hoc queries, and decision making.
数据仓储涉及数据清理、数据集成和数据合并。为了集成异构数据库,我们采用了以下两种方法:
Data warehousing involves data cleaning, data integration, and data consolidations. To integrate heterogeneous databases, we have the following two approaches −
-
Query Driven Approach
-
Update Driven Approach
Query-Driven Approach
这是集成异构数据库的传统方法。此方法用于在多个异构数据库之上构建包装和集成器。这些集成器也称为“中介器”。
This is the traditional approach to integrate heterogeneous databases. This approach is used to build wrappers and integrators on top of multiple heterogeneous databases. These integrators are also known as mediators.
Process of Query Driven Approach
-
When a query is issued to a client side, a metadata dictionary translates the query into the queries, appropriate for the individual heterogeneous site involved.
-
Now these queries are mapped and sent to the local query processor.
-
The results from heterogeneous sites are integrated into a global answer set.
Update-Driven Approach
当今的数据仓库系统遵循更新驱动方法,而不是前面讨论的传统方法。在更新驱动方法中,来自多个异构源的信息已预先集成并存储在仓库中。此信息可用于直接查询和分析。
Today’s data warehouse systems follow update-driven approach rather than the traditional approach discussed earlier. In the update-driven approach, the information from multiple heterogeneous sources is integrated in advance and stored in a warehouse. This information is available for direct querying and analysis.
Advantages
此方法有以下优点:
This approach has the following advantages −
-
This approach provides high performance.
-
The data can be copied, processed, integrated, annotated, summarized and restructured in the semantic data store in advance.
查询处理不需要与本地源的处理接口。
Query processing does not require interface with the processing at local sources.
From Data Warehousing (OLAP) to Data Mining (OLAM)
在线分析挖掘与在线分析处理通过对多维数据库进行数据挖掘和知识挖掘进行集成。以下是展示了 OLAP 和 OLAM 集成的示意图 −
Online Analytical Mining integrates with Online Analytical Processing with data mining and mining knowledge in multidimensional databases. Here is the diagram that shows the integration of both OLAP and OLAM −

Importance of OLAM
OLAM 出于以下原因很重要 −
OLAM is important for the following reasons −
-
High quality of data in data warehouses − The data mining tools are required to work on integrated, consistent, and cleaned data. These steps are very costly in the preprocessing of data. The data warehouses constructed by such preprocessing are valuable sources of high quality data for OLAP and data mining as well.
-
Available information processing infrastructure surrounding data warehouses − Information processing infrastructure refers to accessing, integration, consolidation, and transformation of multiple heterogeneous databases, web-accessing and service facilities, reporting and OLAP analysis tools.
-
OLAP−based exploratory data analysis − Exploratory data analysis is required for effective data mining. OLAM provides facility for data mining on various subset of data and at different levels of abstraction.
-
Online selection of data mining functions − Integrating OLAP with multiple data mining functions and online analytical mining provide users with the flexibility to select desired data mining functions and swap data mining tasks dynamically.
Data Mining - Terminologies
Data Mining
数据挖掘被定义为从大量数据中提取信息。换句话说,我们可以说数据挖掘是从数据中挖掘知识。此信息可用于以下任意应用程序 −
Data mining is defined as extracting the information from a huge set of data. In other words we can say that data mining is mining the knowledge from data. This information can be used for any of the following applications −
-
Market Analysis
-
Fraud Detection
-
Customer Retention
-
Production Control
-
Science Exploration
Data Mining Engine
数据挖掘引擎对数据挖掘系统至关重要。它由执行以下函数的一组功能模块组成 −
Data mining engine is very essential to the data mining system. It consists of a set of functional modules that perform the following functions −
-
Characterization
-
Association and Correlation Analysis
-
Classification
-
Prediction
-
Cluster analysis
-
Outlier analysis
-
Evolution analysis
Knowledge Base
这是领域知识。这种知识用于指导搜索或评估所得模式的趣味性。
This is the domain knowledge. This knowledge is used to guide the search or evaluate the interestingness of the resulting patterns.
Knowledge Discovery
有些人将数据挖掘与知识发现视为同义词,而另一些人则将数据挖掘视为知识发现过程中必不可少的一步。以下是知识发现过程中涉及的步骤 −
Some people treat data mining same as knowledge discovery, while others view data mining as an essential step in the process of knowledge discovery. Here is the list of steps involved in the knowledge discovery process −
-
Data Cleaning
-
Data Integration
-
Data Selection
-
Data Transformation
-
Data Mining
-
Pattern Evaluation
-
Knowledge Presentation
User interface
用户界面是数据挖掘系统的模块,用于帮助用户和数据挖掘系统之间的通信。用户界面允许以下功能 −
User interface is the module of data mining system that helps the communication between users and the data mining system. User Interface allows the following functionalities −
-
Interact with the system by specifying a data mining query task.
-
Providing information to help focus the search.
-
Mining based on the intermediate data mining results.
-
Browse database and data warehouse schemas or data structures.
-
Evaluate mined patterns.
-
Visualize the patterns in different forms.
Data Integration
数据集成是一种将来自多个异构数据源的数据合并到一个连贯的数据存储中的数据预处理技术。数据集成可能涉及不一致的数据,因此需要数据清理。
Data Integration is a data preprocessing technique that merges the data from multiple heterogeneous data sources into a coherent data store. Data integration may involve inconsistent data and therefore needs data cleaning.
Data Cleaning
数据清理是一种用于清除杂乱数据并更正数据中不一致性的技术。数据清理涉及更正错误数据的转换。数据清理是在为数据仓库准备数据时作为数据预处理步骤执行的。
Data cleaning is a technique that is applied to remove the noisy data and correct the inconsistencies in data. Data cleaning involves transformations to correct the wrong data. Data cleaning is performed as a data preprocessing step while preparing the data for a data warehouse.
Data Selection
数据选择是从数据库中检索与分析任务相关的数据的过程。有时,在数据选择过程之前会执行数据转换和合并。
Data Selection is the process where data relevant to the analysis task are retrieved from the database. Sometimes data transformation and consolidation are performed before the data selection process.
Data Mining - Knowledge Discovery
What is Knowledge Discovery?
有的人不区分数据挖掘和知识发现,而另一些人则将数据挖掘视为知识发现过程中至关重要的一步。以下是知识发现过程中涉及的步骤列表−
Some people don’t differentiate data mining from knowledge discovery while others view data mining as an essential step in the process of knowledge discovery. Here is the list of steps involved in the knowledge discovery process −
-
Data Cleaning − In this step, the noise and inconsistent data is removed.
-
Data Integration − In this step, multiple data sources are combined.
-
Data Selection − In this step, data relevant to the analysis task are retrieved from the database.
-
Data Transformation − In this step, data is transformed or consolidated into forms appropriate for mining by performing summary or aggregation operations.
-
Data Mining − In this step, intelligent methods are applied in order to extract data patterns.
-
Pattern Evaluation − In this step, data patterns are evaluated.
-
Knowledge Presentation − In this step, knowledge is represented.
下图显示了知识发现的过程 −
The following diagram shows the process of knowledge discovery −

Data Mining - Systems
各种数据挖掘系统中可供选择。数据挖掘系统可能集成以下技术 −
There is a large variety of data mining systems available. Data mining systems may integrate techniques from the following −
-
Spatial Data Analysis
-
Information Retrieval
-
Pattern Recognition
-
Image Analysis
-
Signal Processing
-
Computer Graphics
-
Web Technology
-
Business
-
Bioinformatics
Data Mining System Classification
根据以下条件可以对数据挖掘系统进行分类 −
A data mining system can be classified according to the following criteria −
-
Database Technology
-
Statistics
-
Machine Learning
-
Information Science
-
Visualization
-
Other Disciplines

除此之外,还可以根据所挖掘的(a)数据库、所挖掘的(b)知识、所利用的(c)技术和所适应的(d)应用程序对数据挖掘系统进行分类。
Apart from these, a data mining system can also be classified based on the kind of (a) databases mined, (b) knowledge mined, (c) techniques utilized, and (d) applications adapted.
Classification Based on the Databases Mined
我们可以根据所挖掘的数据库类型对数据挖掘系统进行分类。可以根据数据模型、数据类型等不同条件对数据库系统进行分类。相应地,数据挖掘系统也进行分类。
We can classify a data mining system according to the kind of databases mined. Database system can be classified according to different criteria such as data models, types of data, etc. And the data mining system can be classified accordingly.
例如,如果我们根据数据模型对数据库进行分类,则可能有一个关系、事务、对象关系或数据仓库挖掘系统。
For example, if we classify a database according to the data model, then we may have a relational, transactional, object-relational, or data warehouse mining system.
Classification Based on the kind of Knowledge Mined
我们还可以根据所挖掘的知识类型对数据挖掘系统进行分类。这意味着根据诸如以下功能对数据挖掘系统进行分类−
We can classify a data mining system according to the kind of knowledge mined. It means the data mining system is classified on the basis of functionalities such as −
-
Characterization
-
Discrimination
-
Association and Correlation Analysis
-
Classification
-
Prediction
-
Outlier Analysis
-
Evolution Analysis
Classification Based on the Techniques Utilized
我们可以根据所用技术的类型对数据挖掘系统进行分类。我们可以根据涉及的用户交互程度或所采用的分析方法描述这些技术。
We can classify a data mining system according to the kind of techniques used. We can describe these techniques according to the degree of user interaction involved or the methods of analysis employed.
Integrating a Data Mining System with a DB/DW System
如果数据挖掘系统未与数据库或数据仓库系统集成,则将没有要通信的系统。此方案称为非耦合方案。在这个方案中,重点放在数据挖掘设计以及为挖掘可用数据集开发高效且有效的算法上。
If a data mining system is not integrated with a database or a data warehouse system, then there will be no system to communicate with. This scheme is known as the non-coupling scheme. In this scheme, the main focus is on data mining design and on developing efficient and effective algorithms for mining the available data sets.
集成方案如下列出 −
The list of Integration Schemes is as follows −
-
No Coupling − In this scheme, the data mining system does not utilize any of the database or data warehouse functions. It fetches the data from a particular source and processes that data using some data mining algorithms. The data mining result is stored in another file.
-
Loose Coupling − In this scheme, the data mining system may use some of the functions of database and data warehouse system. It fetches the data from the data respiratory managed by these systems and performs data mining on that data. It then stores the mining result either in a file or in a designated place in a database or in a data warehouse.
-
Semi−tight Coupling − In this scheme, the data mining system is linked with a database or a data warehouse system and in addition to that, efficient implementations of a few data mining primitives can be provided in the database.
-
Tight coupling − In this coupling scheme, the data mining system is smoothly integrated into the database or data warehouse system. The data mining subsystem is treated as one functional component of an information system.
Data Mining - Query Language
数据挖掘查询语言 (DMQL) 由 Han、Fu、Wang 提议用于 DBMiner 数据挖掘系统。数据挖掘查询语言实际上基于结构化查询语言 (SQL)。可以设计数据挖掘查询语言来支持特设和交互式数据挖掘。此 DMQL 提供用于指定原始元素的命令。DMQL 可以与数据库和数据仓库配合使用。DMQL 可用于定义数据挖掘任务。我们特别检查如何在 DMQL 中定义数据仓库和数据市集。
The Data Mining Query Language (DMQL) was proposed by Han, Fu, Wang, et al. for the DBMiner data mining system. The Data Mining Query Language is actually based on the Structured Query Language (SQL). Data Mining Query Languages can be designed to support ad hoc and interactive data mining. This DMQL provides commands for specifying primitives. The DMQL can work with databases and data warehouses as well. DMQL can be used to define data mining tasks. Particularly we examine how to define data warehouses and data marts in DMQL.
Syntax for Task-Relevant Data Specification
以下是用于指定任务相关数据的 DMQL 语法 −
Here is the syntax of DMQL for specifying task-relevant data −
use database database_name
or
use data warehouse data_warehouse_name
in relevance to att_or_dim_list
from relation(s)/cube(s) [where condition]
order by order_list
group by grouping_listSyntax for Specifying the Kind of Knowledge
我们在此将讨论表征、辨别、关联、分类和预测的语法。
Here we will discuss the syntax for Characterization, Discrimination, Association, Classification, and Prediction.
Characterization
表征语法如下 −
The syntax for characterization is −
mine characteristics [as pattern_name]
analyze {measure(s) }analyze 子句,指定聚合测量值,例如 count、sum 或 count%。
The analyze clause, specifies aggregate measures, such as count, sum, or count%.
例如 -
For example −
Description describing customer purchasing habits.
mine characteristics as customerPurchasing
analyze count%Discrimination
辨别语法如下 −
The syntax for Discrimination is −
mine comparison [as {pattern_name]}
For {target_class } where {t arget_condition }
{versus {contrast_class_i }
where {contrast_condition_i}}
analyze {measure(s) }例如,用户可能会将大额挥霍者定义为平均购买 100 美元或更多商品的客户;而将预算挥霍者定义为平均购买低于 100 美元商品的客户。可以通过 DMQL 将从每个此类别的客户中挖掘的辨别描述指定为 −
For example, a user may define big spenders as customers who purchase items that cost $100 or more on an average; and budget spenders as customers who purchase items at less than $100 on an average. The mining of discriminant descriptions for customers from each of these categories can be specified in the DMQL as −
mine comparison as purchaseGroups
for bigSpenders where avg(I.price) ≥$100
versus budgetSpenders where avg(I.price)< $100
analyze countAssociation
关联语法如下 −
The syntax for Association is−
mine associations [ as {pattern_name} ]
{matching {metapattern} }例如 −
For Example −
mine associations as buyingHabits
matching P(X:customer,W) ^ Q(X,Y) ≥ buys(X,Z)其中 X 是客户关系的关键;P 和 Q 是谓词变量;W、Y 和 Z 是对象变量。
where X is key of customer relation; P and Q are predicate variables; and W, Y, and Z are object variables.
Classification
分类语法如下 −
The syntax for Classification is −
mine classification [as pattern_name]
analyze classifying_attribute_or_dimension例如,要挖掘模式,将客户信用评级分类,其中这些类别由属性 credit_rating 确定,并且将挖掘分类确定为 classifyCustomerCreditRating。
For example, to mine patterns, classifying customer credit rating where the classes are determined by the attribute credit_rating, and mine classification is determined as classifyCustomerCreditRating.
analyze credit_ratingSyntax for Concept Hierarchy Specification
要指定概念层次结构,请使用以下语法 −
To specify concept hierarchies, use the following syntax −
use hierarchy <hierarchy> for <attribute_or_dimension>我们使用不同的语法来定义不同类型的层次结构,例如 −
We use different syntaxes to define different types of hierarchies such as−
-schema hierarchies
define hierarchy time_hierarchy on date as [date,month quarter,year]
-
set-grouping hierarchies
define hierarchy age_hierarchy for age on customer as
level1: {young, middle_aged, senior} < level0: all
level2: {20, ..., 39} < level1: young
level3: {40, ..., 59} < level1: middle_aged
level4: {60, ..., 89} < level1: senior
-operation-derived hierarchies
define hierarchy age_hierarchy for age on customer as
{age_category(1), ..., age_category(5)}
:= cluster(default, age, 5) < all(age)
-rule-based hierarchies
define hierarchy profit_margin_hierarchy on item as
level_1: low_profit_margin < level_0: all
if (price - cost)< $50
level_1: medium-profit_margin < level_0: all
if ((price - cost) > $50) and ((price - cost) ≤ $250))
level_1: high_profit_margin < level_0: allSyntax for Interestingness Measures Specification
用户可以使用该语句指定有趣性测量和阈值 −
Interestingness measures and thresholds can be specified by the user with the statement −
with <interest_measure_name> threshold = threshold_value例如 −
For Example −
with support threshold = 0.05
with confidence threshold = 0.7Syntax for Pattern Presentation and Visualization Specification
我们有一个语法,允许用户指定一种或多种形式中发现的模式的显示方式。
We have a syntax, which allows users to specify the display of discovered patterns in one or more forms.
display as <result_form>例如 −
For Example −
display as tableFull Specification of DMQL
作为一名公司的市场经理,您希望对购买价格不少于 100 美元的商品的顾客的购买习惯进行表征;根据顾客的年龄、购买商品的类型以及购买商品的地点。您希望知道具有该特征的顾客的百分比。特别是,您只对在加拿大进行的,并使用美国运通信用卡支付的购买感兴趣。您希望以表格的形式查看结果说明。
As a market manager of a company, you would like to characterize the buying habits of customers who can purchase items priced at no less than $100; with respect to the customer’s age, type of item purchased, and the place where the item was purchased. You would like to know the percentage of customers having that characteristic. In particular, you are only interested in purchases made in Canada, and paid with an American Express credit card. You would like to view the resulting descriptions in the form of a table.
use database AllElectronics_db
use hierarchy location_hierarchy for B.address
mine characteristics as customerPurchasing
analyze count%
in relevance to C.age,I.type,I.place_made
from customer C, item I, purchase P, items_sold S, branch B
where I.item_ID = S.item_ID and P.cust_ID = C.cust_ID and
P.method_paid = "AmEx" and B.address = "Canada" and I.price ≥ 100
with noise threshold = 5%
display as tableData Mining Languages Standardization
标准化数据挖掘语言将服务以下目的 −
Standardizing the Data Mining Languages will serve the following purposes −
-
Helps systematic development of data mining solutions.
-
Improves interoperability among multiple data mining systems and functions.
-
Promotes education and rapid learning.
-
Promotes the use of data mining systems in industry and society.
Data Mining - Classification & Prediction
有两种形式的数据分析可以用于提取描述重要类别的模型或预测未来的数据趋势。这两种形式如下 −
There are two forms of data analysis that can be used for extracting models describing important classes or to predict future data trends. These two forms are as follows −
-
Classification
-
Prediction
分类模型预测分类类别标签;预测模型预测连续的值函数。例如,我们可以构建一个分类模型,将银行贷款申请归类为安全或有风险,或构建一个预测模型,根据潜在客户的收入和职业来预测他们在计算机设备上的支出(以美元为单位)。
Classification models predict categorical class labels; and prediction models predict continuous valued functions. For example, we can build a classification model to categorize bank loan applications as either safe or risky, or a prediction model to predict the expenditures in dollars of potential customers on computer equipment given their income and occupation.
What is classification?
以下是数据分析任务是分类的案例示例 −
Following are the examples of cases where the data analysis task is Classification −
-
A bank loan officer wants to analyze the data in order to know which customer (loan applicant) are risky or which are safe.
-
A marketing manager at a company needs to analyze a customer with a given profile, who will buy a new computer.
在上述两个示例中,构造了一个模型或分类器来预测分类标签。对于贷款申请数据,这些标签是“有风险”或“安全”,对于市场数据,这些标签是“是”或“否”。
In both of the above examples, a model or classifier is constructed to predict the categorical labels. These labels are risky or safe for loan application data and yes or no for marketing data.
What is prediction?
以下是数据分析任务是预测的案例示例 −
Following are the examples of cases where the data analysis task is Prediction −
假设营销经理需要预测给定客户在他公司的一次促销中会花费多少钱。在这个示例中,我们很乐意预测一个数字值。因此,数据分析任务是数字预测的示例。在这种情况下,将构造一个模型或预测器来预测连续值函数或有序值。
Suppose the marketing manager needs to predict how much a given customer will spend during a sale at his company. In this example we are bothered to predict a numeric value. Therefore the data analysis task is an example of numeric prediction. In this case, a model or a predictor will be constructed that predicts a continuous-valued-function or ordered value.
Note − 回归分析是一种最常用于数字预测的统计方法。
Note − Regression analysis is a statistical methodology that is most often used for numeric prediction.
How Does Classification Works?
借助我们上面讨论的银行贷款申请,让我们了解分类的工作原理。数据分类过程包括两个步骤 −
With the help of the bank loan application that we have discussed above, let us understand the working of classification. The Data Classification process includes two steps −
-
Building the Classifier or Model
-
Using Classifier for Classification
Building the Classifier or Model
-
This step is the learning step or the learning phase.
-
In this step the classification algorithms build the classifier.
-
The classifier is built from the training set made up of database tuples and their associated class labels.
-
Each tuple that constitutes the training set is referred to as a category or class. These tuples can also be referred to as sample, object or data points.

Using Classifier for Classification
在此步骤中,分类器用于分类。这里使用测试数据来评估分类规则的准确度。如果准确度被认为可以接受,则可以将分类规则应用于新数据元组。
In this step, the classifier is used for classification. Here the test data is used to estimate the accuracy of classification rules. The classification rules can be applied to the new data tuples if the accuracy is considered acceptable.

Classification and Prediction Issues
主要问题是为分类和预测准备数据。准备数据包含以下活动:
The major issue is preparing the data for Classification and Prediction. Preparing the data involves the following activities −
-
Data Cleaning − Data cleaning involves removing the noise and treatment of missing values. The noise is removed by applying smoothing techniques and the problem of missing values is solved by replacing a missing value with most commonly occurring value for that attribute.
-
Relevance Analysis − Database may also have the irrelevant attributes. Correlation analysis is used to know whether any two given attributes are related.
-
Data Transformation and reduction − The data can be transformed by any of the following methods. Normalization − The data is transformed using normalization. Normalization involves scaling all values for given attribute in order to make them fall within a small specified range. Normalization is used when in the learning step, the neural networks or the methods involving measurements are used. Generalization − The data can also be transformed by generalizing it to the higher concept. For this purpose we can use the concept hierarchies.
Note − 还可以通过其他一些方法来减少数据,例如小波变换、分箱、直方图分析和聚类。
Note − Data can also be reduced by some other methods such as wavelet transformation, binning, histogram analysis, and clustering.
Comparison of Classification and Prediction Methods
以下是比较分类和预测方法的标准:
Here is the criteria for comparing the methods of Classification and Prediction −
-
Accuracy − Accuracy of classifier refers to the ability of classifier. It predict the class label correctly and the accuracy of the predictor refers to how well a given predictor can guess the value of predicted attribute for a new data.
-
Speed − This refers to the computational cost in generating and using the classifier or predictor.
-
Robustness − It refers to the ability of classifier or predictor to make correct predictions from given noisy data.
-
Scalability − Scalability refers to the ability to construct the classifier or predictor efficiently; given large amount of data.
-
Interpretability − It refers to what extent the classifier or predictor understands.
Data Mining - Decision Tree Induction
决策树是一个包含根节点、分支和叶节点的结构。每个内部节点表示对属性的测试,每个分支表示测试结果,每个叶节点包含一个类标签。树中最高级别的节点是根节点。
A decision tree is a structure that includes a root node, branches, and leaf nodes. Each internal node denotes a test on an attribute, each branch denotes the outcome of a test, and each leaf node holds a class label. The topmost node in the tree is the root node.
以下决策树用于表示 buy_computer 概念,它表示一家公司的客户是否可能会购买计算机。每个内部节点表示对属性的测试。每个叶节点表示一个类。
The following decision tree is for the concept buy_computer that indicates whether a customer at a company is likely to buy a computer or not. Each internal node represents a test on an attribute. Each leaf node represents a class.

拥有决策树的好处如下−
The benefits of having a decision tree are as follows −
-
It does not require any domain knowledge.
-
It is easy to comprehend.
-
The learning and classification steps of a decision tree are simple and fast.
Decision Tree Induction Algorithm
一位名叫 J. Ross Quinlan 的机器研究人员在 1980 年开发了一种名为 ID3(迭代二分器)的决策树算法。随后,他提出了 ID3 的继任者 C4.5。ID3 和 C4.5 采用贪婪方法。在这种演算法中,不存在回溯;以自顶向下的递归分而治之的方式构建树。
A machine researcher named J. Ross Quinlan in 1980 developed a decision tree algorithm known as ID3 (Iterative Dichotomiser). Later, he presented C4.5, which was the successor of ID3. ID3 and C4.5 adopt a greedy approach. In this algorithm, there is no backtracking; the trees are constructed in a top-down recursive divide-and-conquer manner.
Generating a decision tree form training tuples of data partition D
Algorithm : Generate_decision_tree
Input:
Data partition, D, which is a set of training tuples
and their associated class labels.
attribute_list, the set of candidate attributes.
Attribute selection method, a procedure to determine the
splitting criterion that best partitions that the data
tuples into individual classes. This criterion includes a
splitting_attribute and either a splitting point or splitting subset.
Output:
A Decision Tree
Method
create a node N;
if tuples in D are all of the same class, C then
return N as leaf node labeled with class C;
if attribute_list is empty then
return N as leaf node with labeled
with majority class in D;|| majority voting
apply attribute_selection_method(D, attribute_list)
to find the best splitting_criterion;
label node N with splitting_criterion;
if splitting_attribute is discrete-valued and
multiway splits allowed then // no restricted to binary trees
attribute_list = splitting attribute; // remove splitting attribute
for each outcome j of splitting criterion
// partition the tuples and grow subtrees for each partition
let Dj be the set of data tuples in D satisfying outcome j; // a partition
if Dj is empty then
attach a leaf labeled with the majority
class in D to node N;
else
attach the node returned by Generate
decision tree(Dj, attribute list) to node N;
end for
return N;Data Mining - Bayesian Classification
贝叶斯分类基于贝叶斯定理。贝叶斯分类器是统计分类器。贝叶斯分类器可以预测类成员身份概率,例如给定元组属于特定类的概率。
Bayesian classification is based on Bayes' Theorem. Bayesian classifiers are the statistical classifiers. Bayesian classifiers can predict class membership probabilities such as the probability that a given tuple belongs to a particular class.
Baye’s Theorem
贝叶斯定理是以托马斯·贝叶斯命名的。有两种类型的概率 -
Bayes' Theorem is named after Thomas Bayes. There are two types of probabilities −
-
Posterior Probability [P(H/X)]
-
Prior Probability [P(H)]
其中 X 是数据元组,H 是一些假设。
where X is data tuple and H is some hypothesis.
根据贝叶斯定理,
According to Bayes' Theorem,
Bayesian Belief Network
贝叶斯信念网络指定了联合条件概率分布。它们也被称为信念网络、贝叶斯网络或概率网络。
Bayesian Belief Networks specify joint conditional probability distributions. They are also known as Belief Networks, Bayesian Networks, or Probabilistic Networks.
-
A Belief Network allows class conditional independencies to be defined between subsets of variables.
-
It provides a graphical model of causal relationship on which learning can be performed.
-
We can use a trained Bayesian Network for classification.
定义贝叶斯推理网络的两个组件为:
There are two components that define a Bayesian Belief Network −
-
Directed acyclic graph
-
A set of conditional probability tables
Directed Acyclic Graph
-
Each node in a directed acyclic graph represents a random variable.
-
These variable may be discrete or continuous valued.
-
These variables may correspond to the actual attribute given in the data.
Directed Acyclic Graph Representation
下图给出了六个布尔变量的有向无环图。
The following diagram shows a directed acyclic graph for six Boolean variables.
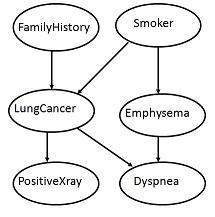
图中的弧表示因果关系。例如,肺癌受个人的家族肺癌史和是否为吸烟者的影响。值得注意的是,已知患者患有肺癌,则变量 PositiveXray 与患者是否有家族肺癌史或是否为吸烟者无关。
The arc in the diagram allows representation of causal knowledge. For example, lung cancer is influenced by a person’s family history of lung cancer, as well as whether or not the person is a smoker. It is worth noting that the variable PositiveXray is independent of whether the patient has a family history of lung cancer or that the patient is a smoker, given that we know the patient has lung cancer.
Conditional Probability Table
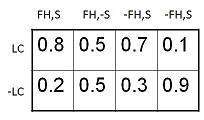
变量 LungCancer (LC) 的条件概率表显示了其父节点 FamilyHistory (FH) 和 Smoker (S) 的值的每种可能组合,如下所示:
The conditional probability table for the values of the variable LungCancer (LC) showing each possible combination of the values of its parent nodes, FamilyHistory (FH), and Smoker (S) is as follows −
Data Mining - Rule Based Classification
IF-THEN Rules
基于规则的分类器使用了一系列的 IF-THEN 规则来进行分类。我们可以使用下面的方式表达规则:
Rule-based classifier makes use of a set of IF-THEN rules for classification. We can express a rule in the following from −
让我们考虑规则 R1,
Let us consider a rule R1,
R1: IF age = youth AND student = yes
THEN buy_computer = yesPoints to remember −
Points to remember −
-
The IF part of the rule is called rule antecedent or precondition.
-
The THEN part of the rule is called rule consequent.
-
The antecedent part the condition consist of one or more attribute tests and these tests are logically ANDed.
-
The consequent part consists of class prediction.
Note − 我们还可以将规则 R1 写成:
Note − We can also write rule R1 as follows −
R1: (age = youth) ^ (student = yes))(buys computer = yes)如果一个给定的元组的条件成立,则前件得到满足。
If the condition holds true for a given tuple, then the antecedent is satisfied.
Rule Extraction
这里我们将学习如何通过从决策树中提取 IF-THEN 规则来构建基于规则的分类器。
Here we will learn how to build a rule-based classifier by extracting IF-THEN rules from a decision tree.
Points to remember −
Points to remember −
从决策树中提取规则的步骤:
To extract a rule from a decision tree −
-
One rule is created for each path from the root to the leaf node.
-
To form a rule antecedent, each splitting criterion is logically ANDed.
-
The leaf node holds the class prediction, forming the rule consequent.
Rule Induction Using Sequential Covering Algorithm
顺序覆盖算法可用于提取 IF-THEN 规则形成训练数据。我们不需要首先生成决策树。在此算法中,给定类的每个规则都涵盖了该类的许多元组。
Sequential Covering Algorithm can be used to extract IF-THEN rules form the training data. We do not require to generate a decision tree first. In this algorithm, each rule for a given class covers many of the tuples of that class.
一些顺序覆盖算法是 AQ、CN2 和 RIPPER。根据一般策略,规则是一次学到的。每次规则被学到时,规则所覆盖的元组都会被移除并继续处理剩余的元组。这是因为决策树中到每个叶子的路径都对应一条规则。
Some of the sequential Covering Algorithms are AQ, CN2, and RIPPER. As per the general strategy the rules are learned one at a time. For each time rules are learned, a tuple covered by the rule is removed and the process continues for the rest of the tuples. This is because the path to each leaf in a decision tree corresponds to a rule.
Note - 决策树归纳可以被认为是同时学习一组规则。
Note − The Decision tree induction can be considered as learning a set of rules simultaneously.
以下是用于一次为一个类学习规则的顺序学习算法。当从类 Ci 中学习规则时,我们希望规则仅涵盖类 C 中的所有元组,而不涵盖其他类的元组。
The Following is the sequential learning Algorithm where rules are learned for one class at a time. When learning a rule from a class Ci, we want the rule to cover all the tuples from class C only and no tuple form any other class.
Algorithm: Sequential Covering
Input:
D, a data set class-labeled tuples,
Att_vals, the set of all attributes and their possible values.
Output: A Set of IF-THEN rules.
Method:
Rule_set={ }; // initial set of rules learned is empty
for each class c do
repeat
Rule = Learn_One_Rule(D, Att_valls, c);
remove tuples covered by Rule form D;
until termination condition;
Rule_set=Rule_set+Rule; // add a new rule to rule-set
end for
return Rule_Set;Rule Pruning
由于以下原因,对规则进行剪枝 -
The rule is pruned is due to the following reason −
-
The Assessment of quality is made on the original set of training data. The rule may perform well on training data but less well on subsequent data. That’s why the rule pruning is required.
-
The rule is pruned by removing conjunct. The rule R is pruned, if pruned version of R has greater quality than what was assessed on an independent set of tuples.
FOIL 是用于规则剪枝的一种简单有效的方法。对于给定的规则 R,
FOIL is one of the simple and effective method for rule pruning. For a given rule R,
其中 pos 和 neg 分别是 R 涵盖的正元组的数量。
where pos and neg is the number of positive tuples covered by R, respectively.
Note - 此值将随着 R 在剪枝集上的准确性而增加。因此,如果剪枝后的版本 R 的 FOIL_Prune 值较高,则剪枝 R。
Note − This value will increase with the accuracy of R on the pruning set. Hence, if the FOIL_Prune value is higher for the pruned version of R, then we prune R.
Miscellaneous Classification Methods
此处我们将讨论其他分类方法,如遗传算法、粗糙集方法和模糊集方法。
Here we will discuss other classification methods such as Genetic Algorithms, Rough Set Approach, and Fuzzy Set Approach.
Genetic Algorithms
遗传算法的思想源自自然进化。在遗传算法中,首先创建初始种群。这个初始种群由随机生成的规则组成。我们可以用一串位来表示每条规则。
The idea of genetic algorithm is derived from natural evolution. In genetic algorithm, first of all, the initial population is created. This initial population consists of randomly generated rules. We can represent each rule by a string of bits.
例如,在给定的训练集中,样本由两个布尔属性描述,例如 A1 和 A2。而给定的训练集包含两个类,例如 C1 和 C2。
For example, in a given training set, the samples are described by two Boolean attributes such as A1 and A2. And this given training set contains two classes such as C1 and C2.
我们可以将规则 IF A1 AND NOT A2 THEN C2 编码为位串 100 。在此位表示中,最左边的两位分别代表属性 A1 和 A2。
We can encode the rule IF A1 AND NOT A2 THEN C2 into a bit string 100. In this bit representation, the two leftmost bits represent the attribute A1 and A2, respectively.
同样,规则 IF NOT A1 AND NOT A2 THEN C1 可编码为 001 。
Likewise, the rule IF NOT A1 AND NOT A2 THEN C1 can be encoded as 001.
Note - 如果属性有 K 个值,其中 K>2,则我们可以使用 K 位对属性值进行编码。类也以相同的方式编码。
Note − If the attribute has K values where K>2, then we can use the K bits to encode the attribute values. The classes are also encoded in the same manner.
要点 -
Points to remember −
-
Based on the notion of the survival of the fittest, a new population is formed that consists of the fittest rules in the current population and offspring values of these rules as well.
-
The fitness of a rule is assessed by its classification accuracy on a set of training samples.
-
The genetic operators such as crossover and mutation are applied to create offspring.
-
In crossover, the substring from pair of rules are swapped to form a new pair of rules.
-
In mutation, randomly selected bits in a rule’s string are inverted.
Rough Set Approach
我们可以使用粗糙集方法来发现不精确和噪声数据中的结构关系。
We can use the rough set approach to discover structural relationship within imprecise and noisy data.
Note - 此方法只能应用于离散值属性。因此,连续值属性必须在使用之前离散化。
Note − This approach can only be applied on discrete-valued attributes. Therefore, continuous-valued attributes must be discretized before its use.
粗糙集理论基于在给定的训练数据中建立等价类。形成等价类的元组是不可辨别的。这意味着样本相对于描述数据的属性是相同的。
The Rough Set Theory is based on the establishment of equivalence classes within the given training data. The tuples that forms the equivalence class are indiscernible. It means the samples are identical with respect to the attributes describing the data.
在给定的真实世界数据中,有些类不能用可用属性来区分。我们可以使用粗糙集来 roughly 定义这样的类。
There are some classes in the given real world data, which cannot be distinguished in terms of available attributes. We can use the rough sets to roughly define such classes.
对于给定的类 C,粗糙集定义近似为以下两个集合 -
For a given class C, the rough set definition is approximated by two sets as follows −
-
Lower Approximation of C − The lower approximation of C consists of all the data tuples, that based on the knowledge of the attribute, are certain to belong to class C.
-
Upper Approximation of C − The upper approximation of C consists of all the tuples, that based on the knowledge of attributes, cannot be described as not belonging to C.
下图显示了类 C 的上近似和下近似 -
The following diagram shows the Upper and Lower Approximation of class C −

Fuzzy Set Approaches
模糊集理论也称为可能性理论。该理论是由 Lotfi Zadeh 在 1965 年提出的,作为 two-value logic 和 probability theory 的替代品。该理论允许我们在高层次的抽象中工作。它还为我们提供了处理数据不精确测量的方法。
Fuzzy Set Theory is also called Possibility Theory. This theory was proposed by Lotfi Zadeh in 1965 as an alternative the two-value logic and probability theory. This theory allows us to work at a high level of abstraction. It also provides us the means for dealing with imprecise measurement of data.
模糊集理论还允许我们处理模糊或不确切的事实。例如,成为高收入人群的成员是不确切的(例如,如果 50,000 美元很高,那么 49,000 美元和 48,000 美元呢)。与传统的 CRISP 集不同,在传统的 CRISP 集中,元素要么属于 S 或其补集,但在模糊集理论中,元素可以属于多个模糊集。
The fuzzy set theory also allows us to deal with vague or inexact facts. For example, being a member of a set of high incomes is in exact (e.g. if $50,000 is high then what about $49,000 and $48,000). Unlike the traditional CRISP set where the element either belong to S or its complement but in fuzzy set theory the element can belong to more than one fuzzy set.
例如,收入值 49,000 美元属于中等和高模糊集,但程度不同。该收入值的模糊集表示如下 -
For example, the income value $49,000 belongs to both the medium and high fuzzy sets but to differing degrees. Fuzzy set notation for this income value is as follows −
mmedium_income($49k)=0.15 and mhigh_income($49k)=0.96其中“m”是分别对 medium_income 和 high_income 的模糊集进行操作的隶属函数。该符号可以用图表表示如下 -
where ‘m’ is the membership function that operates on the fuzzy sets of medium_income and high_income respectively. This notation can be shown diagrammatically as follows −

Data Mining - Cluster Analysis
簇是属于同一类的对象组。换句话说,相似对象被归入一个簇中,而不相似对象被归入另一个簇中。
Cluster is a group of objects that belongs to the same class. In other words, similar objects are grouped in one cluster and dissimilar objects are grouped in another cluster.
What is Clustering?
聚类是将一组抽象对象变成相似对象类的过程。
Clustering is the process of making a group of abstract objects into classes of similar objects.
Points to Remember
Points to Remember
-
A cluster of data objects can be treated as one group.
-
While doing cluster analysis, we first partition the set of data into groups based on data similarity and then assign the labels to the groups.
-
The main advantage of clustering over classification is that, it is adaptable to changes and helps single out useful features that distinguish different groups.
Applications of Cluster Analysis
-
Clustering analysis is broadly used in many applications such as market research, pattern recognition, data analysis, and image processing.
-
Clustering can also help marketers discover distinct groups in their customer base. And they can characterize their customer groups based on the purchasing patterns.
-
In the field of biology, it can be used to derive plant and animal taxonomies, categorize genes with similar functionalities and gain insight into structures inherent to populations.
-
Clustering also helps in identification of areas of similar land use in an earth observation database. It also helps in the identification of groups of houses in a city according to house type, value, and geographic location.
-
Clustering also helps in classifying documents on the web for information discovery.
-
Clustering is also used in outlier detection applications such as detection of credit card fraud.
-
As a data mining function, cluster analysis serves as a tool to gain insight into the distribution of data to observe characteristics of each cluster.
Requirements of Clustering in Data Mining
以下要点阐明了为什么需要在数据挖掘中进行聚类 −
The following points throw light on why clustering is required in data mining −
-
Scalability − We need highly scalable clustering algorithms to deal with large databases.
-
Ability to deal with different kinds of attributes − Algorithms should be capable to be applied on any kind of data such as interval-based (numerical) data, categorical, and binary data.
-
Discovery of clusters with attribute shape − The clustering algorithm should be capable of detecting clusters of arbitrary shape. They should not be bounded to only distance measures that tend to find spherical cluster of small sizes.
-
High dimensionality − The clustering algorithm should not only be able to handle low-dimensional data but also the high dimensional space.
-
Ability to deal with noisy data − Databases contain noisy, missing or erroneous data. Some algorithms are sensitive to such data and may lead to poor quality clusters.
-
Interpretability − The clustering results should be interpretable, comprehensible, and usable.
Clustering Methods
聚类方法可归类为以下类别−
Clustering methods can be classified into the following categories −
-
Partitioning Method
-
Hierarchical Method
-
Density-based Method
-
Grid-Based Method
-
Model-Based Method
-
Constraint-based Method
Partitioning Method
假设我们给定一个由“n”个对象组成的数据库,并且划分法构建了“k”个数据分区。每个分区都将表示一个簇,并且k ≤ n。这意味着它会将数据分成k个组,满足以下要求−
Suppose we are given a database of ‘n’ objects and the partitioning method constructs ‘k’ partition of data. Each partition will represent a cluster and k ≤ n. It means that it will classify the data into k groups, which satisfy the following requirements −
-
Each group contains at least one object.
-
Each object must belong to exactly one group.
Points to remember −
Points to remember −
-
For a given number of partitions (say k), the partitioning method will create an initial partitioning.
-
Then it uses the iterative relocation technique to improve the partitioning by moving objects from one group to other.
Hierarchical Methods
这种方法对给定的数据对象集创建了一种分层分解。我们可以根据分层分解的形成方式对分层方法进行分类。这里有两种方法−
This method creates a hierarchical decomposition of the given set of data objects. We can classify hierarchical methods on the basis of how the hierarchical decomposition is formed. There are two approaches here −
-
Agglomerative Approach
-
Divisive Approach
Agglomerative Approach
这种方法也称为自下而上的方法。在这种方法中,我们从每个对象形成一个单独的组开始。其不断合并彼此接近的对象或组。其会不断这样做,直到所有组都合并为一个或直到终止条件成立。
This approach is also known as the bottom-up approach. In this, we start with each object forming a separate group. It keeps on merging the objects or groups that are close to one another. It keep on doing so until all of the groups are merged into one or until the termination condition holds.
Divisive Approach
这种方法也称为自上而下的方法。在这种方法中,我们从同一个簇中的所有对象开始。在连续迭代中,将一个簇分成较小的簇。其会进行此操作,直到一个簇中的每个对象或终止条件成立。该方法是严格的,即一旦合并或分裂完成,则永远无法撤消。
This approach is also known as the top-down approach. In this, we start with all of the objects in the same cluster. In the continuous iteration, a cluster is split up into smaller clusters. It is down until each object in one cluster or the termination condition holds. This method is rigid, i.e., once a merging or splitting is done, it can never be undone.
Approaches to Improve Quality of Hierarchical Clustering
以下是用于提高分层聚类质量的两种方法−
Here are the two approaches that are used to improve the quality of hierarchical clustering −
-
Perform careful analysis of object linkages at each hierarchical partitioning.
-
Integrate hierarchical agglomeration by first using a hierarchical agglomerative algorithm to group objects into micro-clusters, and then performing macro-clustering on the micro-clusters.
Density-based Method
此方法基于密度的概念。基本想法是在邻域密度超过一定阈值时继续扩展给定簇,即对于给定簇中的每个数据点,给定簇的半径至少要包含最少数量的点。
This method is based on the notion of density. The basic idea is to continue growing the given cluster as long as the density in the neighborhood exceeds some threshold, i.e., for each data point within a given cluster, the radius of a given cluster has to contain at least a minimum number of points.
Grid-based Method
在此当中,对象共同形成一个网格。对象空间被量子化成有限数量的单元格,形成了网格结构。
In this, the objects together form a grid. The object space is quantized into finite number of cells that form a grid structure.
Advantages
Advantages
-
The major advantage of this method is fast processing time.
-
It is dependent only on the number of cells in each dimension in the quantized space.
Model-based methods
在此方法中,假设每个簇一个模型,以找到给定模型的最佳数据拟合。此方法通过对密度函数进行聚类来定位簇。它反映了数据点的空间分布。
In this method, a model is hypothesized for each cluster to find the best fit of data for a given model. This method locates the clusters by clustering the density function. It reflects spatial distribution of the data points.
此方法还提供了一种基于标准统计数据自动确定簇数量的方法,将离群点或噪声考虑在内。因此,它产生了鲁棒的聚类方法。
This method also provides a way to automatically determine the number of clusters based on standard statistics, taking outlier or noise into account. It therefore yields robust clustering methods.
Constraint-based Method
在此方法中,聚类是通过纳入用户或面向应用程序的约束执行的。约束指的是用户期望或所需聚类结果的属性。约束为我们提供了一种与聚类过程进行交互的方式。约束可以由用户或应用程序要求指定。
In this method, the clustering is performed by the incorporation of user or application-oriented constraints. A constraint refers to the user expectation or the properties of desired clustering results. Constraints provide us with an interactive way of communication with the clustering process. Constraints can be specified by the user or the application requirement.
Data Mining - Mining Text Data
文本数据库包含大量的文档集合。它们从多种来源收集这些信息,例如新闻文章、书籍、数字图书馆、电子邮件、网页等。由于信息量的增加,文本数据库正在迅速增长。在许多文本数据库中,数据是半结构化的。
Text databases consist of huge collection of documents. They collect these information from several sources such as news articles, books, digital libraries, e-mail messages, web pages, etc. Due to increase in the amount of information, the text databases are growing rapidly. In many of the text databases, the data is semi-structured.
例如,一个文档可能包含一些结构化字段,例如标题、作者、出版日期等。但除了结构数据之外,文档还包含非结构化文本组件,例如摘要和内容。在不知道文档中可能包含什么的情况下,很难制定有效的查询来分析和提取数据中有用的信息。用户需要工具来比较文档并对其重要性和相关性进行排名。因此,文本挖掘已变得流行,并成为数据挖掘中的一个基本主题。
For example, a document may contain a few structured fields, such as title, author, publishing_date, etc. But along with the structure data, the document also contains unstructured text components, such as abstract and contents. Without knowing what could be in the documents, it is difficult to formulate effective queries for analyzing and extracting useful information from the data. Users require tools to compare the documents and rank their importance and relevance. Therefore, text mining has become popular and an essential theme in data mining.
Information Retrieval
信息检索涉及从大量文本文档中检索信息。一些数据库系统通常不存在于信息检索系统中,因为两者处理不同类型的数据。信息检索系统示例包括 −
Information retrieval deals with the retrieval of information from a large number of text-based documents. Some of the database systems are not usually present in information retrieval systems because both handle different kinds of data. Examples of information retrieval system include −
-
Online Library catalogue system
-
Online Document Management Systems
-
Web Search Systems etc.
Note − 信息检索系统的主要问题是根据用户的查询在文档集合中定位相关文档。这种类型的用户查询由一些描述信息需求的关键词组成。
Note − The main problem in an information retrieval system is to locate relevant documents in a document collection based on a user’s query. This kind of user’s query consists of some keywords describing an information need.
在这种搜索问题中,用户主动从集合中提取相关信息。当用户临时需要信息时,即短期需要时,这种方法比较合适。但是,如果用户长期需要信息,那么检索系统还可以主动将新到达的信息项目推送到用户。
In such search problems, the user takes an initiative to pull relevant information out from a collection. This is appropriate when the user has ad-hoc information need, i.e., a short-term need. But if the user has a long-term information need, then the retrieval system can also take an initiative to push any newly arrived information item to the user.
这种访问信息的方式称为信息过滤。相应的系统称为过滤系统或推荐系统。
This kind of access to information is called Information Filtering. And the corresponding systems are known as Filtering Systems or Recommender Systems.
Basic Measures for Text Retrieval
当系统根据用户的输入检索大量文档时,我们需要检查系统的准确性。将与查询相关的文档集表示为 {Relevant},而将检索到的文档集表示为 {Retrieved}。既相关又检索到的文档集可以表示为 {Relevant} ∩ {Retrieved}。这可以通过以下韦恩图的形式展示 −
We need to check the accuracy of a system when it retrieves a number of documents on the basis of user’s input. Let the set of documents relevant to a query be denoted as {Relevant} and the set of retrieved document as {Retrieved}. The set of documents that are relevant and retrieved can be denoted as {Relevant} ∩ {Retrieved}. This can be shown in the form of a Venn diagram as follows −

评估文本检索质量有三个基本度量 −
There are three fundamental measures for assessing the quality of text retrieval −
-
Precision
-
Recall
-
F-score
Precision
准确率是检索到的文档中实际上与查询相关的文档的百分比。准确率可以定义为 −
Precision is the percentage of retrieved documents that are in fact relevant to the query. Precision can be defined as −
Precision= |{Relevant} ∩ {Retrieved}| / |{Retrieved}|Recall
召回率是与查询相关且实际上已检索到的文档的百分比。召回率定义为 −
Recall is the percentage of documents that are relevant to the query and were in fact retrieved. Recall is defined as −
Recall = |{Relevant} ∩ {Retrieved}| / |{Relevant}|F-score
F 分数是常用的折衷方案。信息检索系统通常需要在准确度和召回率之间折衷。F 分数定义为召回率或准确率的调和平均值,如下所示 −
F-score is the commonly used trade-off. The information retrieval system often needs to trade-off for precision or vice versa. F-score is defined as harmonic mean of recall or precision as follows −
F-score = recall x precision / (recall + precision) / 2Data Mining - Mining World Wide Web
万维网包含大量的信息,为数据挖掘提供了丰富的来源。
The World Wide Web contains huge amounts of information that provides a rich source for data mining.
Challenges in Web Mining
根据以下观察,网络对资源和知识发现提出了巨大挑战 −
The web poses great challenges for resource and knowledge discovery based on the following observations −
-
The web is too huge − The size of the web is very huge and rapidly increasing. This seems that the web is too huge for data warehousing and data mining.
-
Complexity of Web pages − The web pages do not have unifying structure. They are very complex as compared to traditional text document. There are huge amount of documents in digital library of web. These libraries are not arranged according to any particular sorted order.
-
Web is dynamic information source − The information on the web is rapidly updated. The data such as news, stock markets, weather, sports, shopping, etc., are regularly updated.
-
Diversity of user communities − The user community on the web is rapidly expanding. These users have different backgrounds, interests, and usage purposes. There are more than 100 million workstations that are connected to the Internet and still rapidly increasing.
-
Relevancy of Information − It is considered that a particular person is generally interested in only small portion of the web, while the rest of the portion of the web contains the information that is not relevant to the user and may swamp desired results.
Mining Web page layout structure
网页的基本结构基于文档对象模型 (DOM)。DOM 结构是指树状结构,其中页面中的 HTML 标记对应于 DOM 树中的节点。我们可以使用 HTML 中的预定义标记对网页进行分割。HTML 语法很灵活,因此网页不会遵循 W3C 规范。不遵循 W3C 规范可能会导致 DOM 树结构出错。
The basic structure of the web page is based on the Document Object Model (DOM). The DOM structure refers to a tree like structure where the HTML tag in the page corresponds to a node in the DOM tree. We can segment the web page by using predefined tags in HTML. The HTML syntax is flexible therefore, the web pages does not follow the W3C specifications. Not following the specifications of W3C may cause error in DOM tree structure.
DOM 结构最初是为了在浏览器中展示而引入的,而不是为了描述网页的语义结构。DOM 结构无法正确识别网页不同部分之间的语义关系。
The DOM structure was initially introduced for presentation in the browser and not for description of semantic structure of the web page. The DOM structure cannot correctly identify the semantic relationship between the different parts of a web page.
Vision-based page segmentation (VIPS)
-
The purpose of VIPS is to extract the semantic structure of a web page based on its visual presentation.
-
Such a semantic structure corresponds to a tree structure. In this tree each node corresponds to a block.
-
A value is assigned to each node. This value is called the Degree of Coherence. This value is assigned to indicate the coherent content in the block based on visual perception.
-
The VIPS algorithm first extracts all the suitable blocks from the HTML DOM tree. After that it finds the separators between these blocks.
-
The separators refer to the horizontal or vertical lines in a web page that visually cross with no blocks.
-
The semantics of the web page is constructed on the basis of these blocks.
下图显示了 VIPS 算法的过程 −
The following figure shows the procedure of VIPS algorithm −

Data Mining - Applications & Trends
数据挖掘在不同领域被广泛使用。现如今有许多可用的商业数据挖掘系统,但该领域仍面临许多挑战。在本教程中,我们将讨论数据挖掘的应用和趋势。
Data mining is widely used in diverse areas. There are a number of commercial data mining system available today and yet there are many challenges in this field. In this tutorial, we will discuss the applications and the trend of data mining.
Data Mining Applications
以下列举了数据挖掘被广泛使用的领域 −
Here is the list of areas where data mining is widely used −
-
Financial Data Analysis
-
Retail Industry
-
Telecommunication Industry
-
Biological Data Analysis
-
Other Scientific Applications
-
Intrusion Detection
Financial Data Analysis
银行和金融业中的财务数据通常可靠且质量上乘,可促成系统化的数据分析和数据挖掘。一些典型情况如下 −
The financial data in banking and financial industry is generally reliable and of high quality which facilitates systematic data analysis and data mining. Some of the typical cases are as follows −
-
Design and construction of data warehouses for multidimensional data analysis and data mining.
-
Loan payment prediction and customer credit policy analysis.
-
Classification and clustering of customers for targeted marketing.
-
Detection of money laundering and other financial crimes.
Retail Industry
数据挖掘在零售业有很大的应用空间,因为它从销售、客户购买历史记录、货物运输、消费和服务中收集了大量数据。由于网络越来越方便、可用,并且越来越受欢迎,收集的数据量会继续快速增长,这是理所当然的。
Data Mining has its great application in Retail Industry because it collects large amount of data from on sales, customer purchasing history, goods transportation, consumption and services. It is natural that the quantity of data collected will continue to expand rapidly because of the increasing ease, availability and popularity of the web.
零售业的数据挖掘有助于识别客户购买模式和趋势,从而提高客户服务质量,提升客户保留率和满意度。以下列举了零售业中数据挖掘的示例 −
Data mining in retail industry helps in identifying customer buying patterns and trends that lead to improved quality of customer service and good customer retention and satisfaction. Here is the list of examples of data mining in the retail industry −
-
Design and Construction of data warehouses based on the benefits of data mining.
-
Multidimensional analysis of sales, customers, products, time and region.
-
Analysis of effectiveness of sales campaigns.
-
Customer Retention.
-
Product recommendation and cross-referencing of items.
Telecommunication Industry
如今,电信行业是提供各种服务的最蓬勃发展的行业之一,例如传真、寻呼机、蜂窝电话、互联网信使、图像、电子邮件、网络数据传输等。由于新计算机和通信技术的发展,电信行业正在迅速扩张。这就是数据挖掘变得非常重要的原因,有助于业务的理解和开展。
Today the telecommunication industry is one of the most emerging industries providing various services such as fax, pager, cellular phone, internet messenger, images, e-mail, web data transmission, etc. Due to the development of new computer and communication technologies, the telecommunication industry is rapidly expanding. This is the reason why data mining is become very important to help and understand the business.
电信行业的数据挖掘有助于识别电信模式、捕捉欺诈活动、更好地利用资源以及提高服务质量。以下列出了数据挖掘改善电信服务的一些示例:
Data mining in telecommunication industry helps in identifying the telecommunication patterns, catch fraudulent activities, make better use of resource, and improve quality of service. Here is the list of examples for which data mining improves telecommunication services −
-
Multidimensional Analysis of Telecommunication data.
-
Fraudulent pattern analysis.
-
Identification of unusual patterns.
-
Multidimensional association and sequential patterns analysis.
-
Mobile Telecommunication services.
-
Use of visualization tools in telecommunication data analysis.
Biological Data Analysis
近来,我们在生物学领域取得了巨大的发展,如基因组学、蛋白质组学、功能基因组学和生物医学研究。生物数据挖掘是生物信息学的重要组成部分。以下列出了数据挖掘在生物数据分析中发挥作用的方面:
In recent times, we have seen a tremendous growth in the field of biology such as genomics, proteomics, functional Genomics and biomedical research. Biological data mining is a very important part of Bioinformatics. Following are the aspects in which data mining contributes for biological data analysis −
-
Semantic integration of heterogeneous, distributed genomic and proteomic databases.
-
Alignment, indexing, similarity search and comparative analysis multiple nucleotide sequences.
-
Discovery of structural patterns and analysis of genetic networks and protein pathways.
-
Association and path analysis.
-
Visualization tools in genetic data analysis.
Other Scientific Applications
上述讨论的应用程序倾向于处理相对较小和同质的数据集,统计技术适合这些数据集。从地球科学、天文学等科学领域收集到了大量数据。由于气候和生态系统建模、化学工程、流体动力学等各个领域中的快速数值模拟,正在生成大量的数据集。以下是数据挖掘在科学应用领域的应用:
The applications discussed above tend to handle relatively small and homogeneous data sets for which the statistical techniques are appropriate. Huge amount of data have been collected from scientific domains such as geosciences, astronomy, etc. A large amount of data sets is being generated because of the fast numerical simulations in various fields such as climate and ecosystem modeling, chemical engineering, fluid dynamics, etc. Following are the applications of data mining in the field of Scientific Applications −
-
Data Warehouses and data preprocessing.
-
Graph-based mining.
-
Visualization and domain specific knowledge.
Intrusion Detection
入侵是指任何威胁网络资源的完整性、机密性或可用性的行为。在当今这个互联的世界里,安全性已成为主要问题。随着互联网使用的增加以及用于入侵和攻击网络的工具和技巧的可用性,入侵检测已成为网络管理的关键组成部分。以下是数据挖掘技术可应用于入侵检测的领域列表:
Intrusion refers to any kind of action that threatens integrity, confidentiality, or the availability of network resources. In this world of connectivity, security has become the major issue. With increased usage of internet and availability of the tools and tricks for intruding and attacking network prompted intrusion detection to become a critical component of network administration. Here is the list of areas in which data mining technology may be applied for intrusion detection −
-
Development of data mining algorithm for intrusion detection.
-
Association and correlation analysis, aggregation to help select and build discriminating attributes.
-
Analysis of Stream data.
-
Distributed data mining.
-
Visualization and query tools.
Data Mining System Products
有许多数据挖掘系统产品和特定领域的数据挖掘应用程序。新的数据挖掘系统和应用程序正在添加到以前系统中。此外,我们正在努力对数据挖掘语言进行标准化。
There are many data mining system products and domain specific data mining applications. The new data mining systems and applications are being added to the previous systems. Also, efforts are being made to standardize data mining languages.
Choosing a Data Mining System
数据挖掘系统取决于以下特性:
The selection of a data mining system depends on the following features −
-
Data Types − The data mining system may handle formatted text, record-based data, and relational data. The data could also be in ASCII text, relational database data or data warehouse data. Therefore, we should check what exact format the data mining system can handle.
-
System Issues − We must consider the compatibility of a data mining system with different operating systems. One data mining system may run on only one operating system or on several. There are also data mining systems that provide web-based user interfaces and allow XML data as input.
-
Data Sources − Data sources refer to the data formats in which data mining system will operate. Some data mining system may work only on ASCII text files while others on multiple relational sources. Data mining system should also support ODBC connections or OLE DB for ODBC connections.
-
Data Mining functions and methodologies − There are some data mining systems that provide only one data mining function such as classification while some provides multiple data mining functions such as concept description, discovery-driven OLAP analysis, association mining, linkage analysis, statistical analysis, classification, prediction, clustering, outlier analysis, similarity search, etc.
-
Coupling data mining with databases or data warehouse systems − Data mining systems need to be coupled with a database or a data warehouse system. The coupled components are integrated into a uniform information processing environment. Here are the types of coupling listed below − No couplingLoose CouplingSemi tight CouplingTight Coupling
-
Scalability − There are two scalability issues in data mining − Row (Database size) Scalability − A data mining system is considered as row scalable when the number or rows are enlarged 10 times. It takes no more than 10 times to execute a query. Column (Dimension) Salability − A data mining system is considered as column scalable if the mining query execution time increases linearly with the number of columns.
-
Visualization Tools − Visualization in data mining can be categorized as follows − Data VisualizationMining Results VisualizationMining process visualizationVisual data mining
-
Data Mining query language and graphical user interface − An easy-to-use graphical user interface is important to promote user-guided, interactive data mining. Unlike relational database systems, data mining systems do not share underlying data mining query language.
Trends in Data Mining
数据挖掘的概念仍在不断发展,以下是我们在这个领域看到的最新趋势−
Data mining concepts are still evolving and here are the latest trends that we get to see in this field −
-
Application Exploration.
-
Scalable and interactive data mining methods.
-
Integration of data mining with database systems, data warehouse systems and web database systems.
-
SStandardization of data mining query language.
-
Visual data mining.
-
New methods for mining complex types of data.
-
Biological data mining.
-
Data mining and software engineering.
-
Web mining.
-
Distributed data mining.
-
Real time data mining.
-
Multi database data mining.
-
Privacy protection and information security in data mining.
Data Mining - Themes
Theoretical Foundations of Data Mining
数据挖掘的理论基础包括以下概念 −
The theoretical foundations of data mining includes the following concepts −
-
Data Reduction − The basic idea of this theory is to reduce the data representation which trades accuracy for speed in response to the need to obtain quick approximate answers to queries on very large databases. Some of the data reduction techniques are as follows − Singular value Decomposition Wavelets Regression Log-linear models Histograms Clustering Sampling Construction of Index Trees
-
Data Compression − The basic idea of this theory is to compress the given data by encoding in terms of the following − Bits Association Rules Decision Trees Clusters
-
Pattern Discovery − The basic idea of this theory is to discover patterns occurring in a database. Following are the areas that contribute to this theory − Machine Learning Neural Network Association Mining Sequential Pattern Matching Clustering
-
Probability Theory − This theory is based on statistical theory. The basic idea behind this theory is to discover joint probability distributions of random variables.
-
Probability Theory − According to this theory, data mining finds the patterns that are interesting only to the extent that they can be used in the decision-making process of some enterprise.
-
Microeconomic View − As per this theory, a database schema consists of data and patterns that are stored in a database. Therefore, data mining is the task of performing induction on databases.
-
Inductive databases − Apart from the database-oriented techniques, there are statistical techniques available for data analysis. These techniques can be applied to scientific data and data from economic and social sciences as well.
Statistical Data Mining
以下是一些统计数据挖掘技术:
Some of the Statistical Data Mining Techniques are as follows −
-
Regression − Regression methods are used to predict the value of the response variable from one or more predictor variables where the variables are numeric. Listed below are the forms of Regression − Linear Multiple Weighted Polynomial Nonparametric Robust
-
Generalized Linear Models − Generalized Linear Model includes − Logistic Regression Poisson Regression The model’s generalization allows a categorical response variable to be related to a set of predictor variables in a manner similar to the modelling of numeric response variable using linear regression.
-
Analysis of Variance − This technique analyzes − Experimental data for two or more populations described by a numeric response variable. One or more categorical variables (factors).
-
Mixed-effect Models − These models are used for analyzing grouped data. These models describe the relationship between a response variable and some co-variates in the data grouped according to one or more factors.
-
Factor Analysis − Factor analysis is used to predict a categorical response variable. This method assumes that independent variables follow a multivariate normal distribution.
-
Time Series Analysis − Following are the methods for analyzing time-series data − Auto-regression Methods. Univariate ARIMA (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average) Modeling. Long-memory time-series modeling.
Visual Data Mining
可视化数据挖掘使用数据和/或知识可视化技术从大型数据集发现隐含知识。可视化数据挖掘可以看作以下学科的整合:
Visual Data Mining uses data and/or knowledge visualization techniques to discover implicit knowledge from large data sets. Visual data mining can be viewed as an integration of the following disciplines −
-
Data Visualization
-
Data Mining
可视化数据挖掘与以下内容密切相关:
Visual data mining is closely related to the following −
-
Computer Graphics
-
Multimedia Systems
-
Human Computer Interaction
-
Pattern Recognition
-
High-performance Computing
通常,数据可视化和数据挖掘可以通过以下方式整合:
Generally data visualization and data mining can be integrated in the following ways −
-
Data Visualization − The data in a database or a data warehouse can be viewed in several visual forms that are listed below − Boxplots 3-D Cubes Data distribution charts Curves Surfaces Link graphs etc.
-
Data Mining Result Visualization − Data Mining Result Visualization is the presentation of the results of data mining in visual forms. These visual forms could be scattered plots, boxplots, etc.
-
Data Mining Process Visualization − Data Mining Process Visualization presents the several processes of data mining. It allows the users to see how the data is extracted. It also allows the users to see from which database or data warehouse the data is cleaned, integrated, preprocessed, and mined.
Audio Data Mining
音频数据挖掘利用音频信号来指示数据模式或数据挖掘结果的特征。通过将模式转换成声音并进行沉思,我们可以聆听音调和曲调(而不是观看图像)来识别任何有趣的内容。
Audio data mining makes use of audio signals to indicate the patterns of data or the features of data mining results. By transforming patterns into sound and musing, we can listen to pitches and tunes, instead of watching pictures, in order to identify anything interesting.
Data Mining and Collaborative Filtering
如今,消费者在购物时会遇到各种各样的商品和服务。在实时客户交易中,推荐系统会向消费者提供产品推荐,从而帮助消费者。协同过滤方法通常用于向消费者推荐产品。这些推荐基于其他消费者的意见。
Consumers today come across a variety of goods and services while shopping. During live customer transactions, a Recommender System helps the consumer by making product recommendations. The Collaborative Filtering Approach is generally used for recommending products to customers. These recommendations are based on the opinions of other customers.