Biometrics 简明教程
Biometrics Overview
生物特征识别一词由两个词组成——Bio(希腊语中的生命)和 Metrics(测量)。生物特征识别是信息技术的一个分支,旨在基于个人特征确定一个人的身份。
The term Biometrics is composed of two words − Bio (Greek word for Life) and Metrics (Measurements). Biometrics is a branch of information technology that aims towards establishing one’s identity based on personal traits.
生物特征识别目前是信息安全领域的一个热门术语,因为它能高度准确地识别个人。
Biometrics is presently a buzzword in the domain of information security as it provides high degree of accuracy in identifying an individual.
What is Biometrics?
生物特征识别是一种用于识别、分析和测量个人生理和行为特征的技术。
Biometrics is a technology used to identify, analyze, and measure an individual’s physical and behavioral characteristics.
每个人都是独一无二的,这使他和其他人截然不同。生理特征,如指纹、虹膜颜色、头发颜色、手部几何形状,以及行为特征,如言语的音调和口音、签名或打电脑键盘的方式等,使一个人与众不同。
Each human being is unique in terms of characteristics, which make him or her different from all others. The physical attributes such as finger prints, color of iris, color of hair, hand geometry, and behavioral characteristics such as tone and accent of speech, signature, or the way of typing keys of computer keyboard etc., make a person stand separate from the rest.
个人特征的这些独特性被生物特征识别系统用于:
This uniqueness of a person is then used by the biometric systems to −
-
Identify and verify a person.
-
Authenticate a person to give appropriate rights of system operations.
-
Keep the system safe from unethical handling.
What is a Biometric System?
生物特征识别系统是一种技术,它将个人的生理特征、行为特征或这两者作为输入,进行分析,并将个人识别为真正的用户或恶意用户。
A biometric system is a technology which takes an individual’s physiological, behavioral, or both traits as input, analyzes it, and identifies the individual as a genuine or malicious user.
Evolution of Biometrics
生物特征识别这个概念已经存在好几年了。在 14 世纪,中国就开始对商人及其子女采取指纹识别,以将他们与其他人区分开来。指纹识别至今仍被使用。
The idea of biometrics was present since few years from now. In 14th century, China practiced taking finger prints of merchants and their children to separate them from all others. Fingerprinting is still used today.
-
In the 19th century, an Anthropologist named Alphonse Bertillion developed a method (named Bertillionage) of taking body measurements of persons to identify them. He had realized that even if some features of human body are changed, such as length of hair, weight, etc., some physical traits of body remain unchanged, such as length of fingers. This method diminished quickly as it was found that the persons with same body measurements alone can be falsely taken as one. Subsequently, Richard Edward Henry from Scotland Yard developed a method for fingerprinting.
-
The idea of retinal identification was conceived by Dr. Carleton Simon and Dr. Isadore Goldstein in 1935. In 1976, a research and development effort was put in at EyeDentify Inc. The first commercial retina scanning system was made available in 1981.
-
Iris recognition was invented by John Daugman in 1993 at Cambridge University.
-
In 2001, Biometrics Automated Toolset (BAT) was introduced in Kosovo, which provided a concrete identification means.
今天,生物特征识别已经成为一門独立的研究领域,拥有精确的个人身份识别技术。
Today, biometric has come up as an independent field of study with precise technologies of establishing personal identities.
Why Biometrics is Required?
随着信息技术在银行、科学、医药等领域的应用日益广泛,迫切需要保护系统和数据免遭未经授权的用户侵害。
With increasing use of Information Technology in the field of banking, science, medication, etc., there is an immense need to protect the systems and data from unauthorized users.
生物特征识别用于 authenticating 和 authorizing 个人。尽管这些术语经常配对使用;但它们的意思不同。
Biometrics is used for authenticating and authorizing a person. Though these terms are often coupled; they mean different.
Authentication (Identification)
此过程试图找出问题的答案, “您是否是您自己聲稱的那个人?” 或,“我认识您吗?” 这是将一个人的生物特征识别与整个数据库进行一对多的匹配和比较。
This process tries to find out answer of question, “Are you the same who you are claiming to be?”, or, “Do I know you?” This is one-to-many matching and comparison of a person’s biometrics with the whole database.
Verification
这是匹配的一对一过程,候选人输入的实时样本与数据库中先前存储的模板进行比较。如果两者匹配度超过 70%,则验证成功。
This is the one-to-one process of matching where live sample entered by the candidate is compared with a previously stored template in the database. If both are matching with more than 70% agreeable similarity, then the verification is successful.
Authorization
这是向经过验证的用户分配访问权限的过程。它试图找出问题的答案,“您是否有访问此资源的某些权限?”
It is the process of assigning access rights to the authenticated or verified users. It tries to find out the answer for the question, “Are you eligible to have certain rights to access this resource?”
Shortcomings of Conventional Security Aids
信息系统安全的传统方法使用身份证、密码、个人识别号码 (PIN) 等。它们有以下缺点−
The conventional methods of information system security used ID cards, passwords, Personal Identification Numbers (PINs), etc. They come with the following disadvantages −
-
They all mean recognizing some code associated with the person rather than recognizing the person who actually produced it.
-
They can be forgotten, lost, or stolen.
-
They can be bypassed or easily compromised.
-
They are not precise.
在这种情况下,系统的安全性会受到威胁。当系统需要高水平的可靠保护时,生物识别技术会通过将身份与个人联系得更紧密来提供帮助。
In such cases, the security of the system is threatened. When the systems need high level of reliable protection, biometrics comes to help by binding the identity more oriented to individual.
Basic Components of a Biometric System
通常,生物识别系统可以分为四个基本组成部分。让我们简要查看它们−
In general, a biometric system can be divided into four basic components. Let us see them briefly −
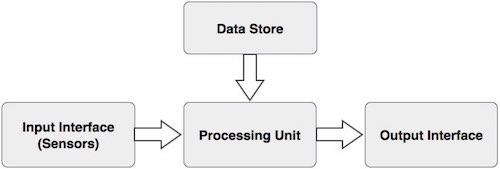
Input Interface (Sensors)
它是将人体生物数据转换成数字形式的生物识别系统的传感组件。
It is the sensing component of a biometrics system that converts human biological data into digital form.
例如,
For example,
-
A Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) imager or a Charge Coupled Device (CCD) in the case of face recognition, handprint recognition, or iris/retinal recognition systems.
-
An optical sensor in case of fingerprint systems.
-
A microphone in case of voice recognition systems.
Processing Unit
处理组件是微处理器、数字信号处理器 (DSP) 或处理从传感器捕获的数据的计算机。
The processing component is a microprocessor, Digital Signal Processor (DSP), or computer that processes the data captured from the sensors.
生物样本的处理包括−
The processing of the biometric sample involves −
-
Sample image enhancement
-
Sample image normalization
-
Feature extraction
-
Comparison of the biometric sample with all stored samples in database.
Database Store
数据库存储注册的样本,在认证时对其进行召回以进行匹配。对于识别,可以是来自随机存取存储器 (RAM)、闪存 EPROM 或数据服务器的任何内存。对于验证,会使用可移动存储元件,如接触式或非接触式智能卡。
The database stores the enrolled sample, which is recalled to perform a match at the time of authentication. For identification, there can be any memory from Random Access Memory (RAM), flash EPROM, or a data server. For verification, a removable storage element like a contact or contactless smart card is used.
Output Interface
输出接口将生物识别系统的决策传达给用户,以启用对该用户的访问。这可以是简单的串行通信协议 RS232,或更高带宽的 USB 协议。它也可以是 TCP/IP 协议、射频识别 (RFID)、蓝牙或许多蜂窝协议之一。
The output interface communicates the decision of the biometric system to enable the access to the user. This can be a simple serial communication protocol RS232, or the higher bandwidth USB protocol. It could also be TCP/IP protocol, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Bluetooth, or one of the many cellular protocols.
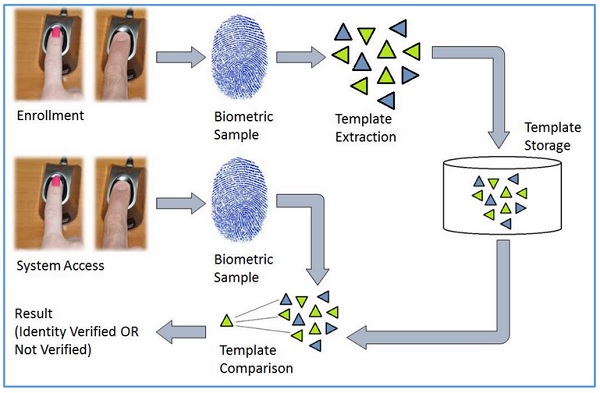
General Working of a Biometric System
生物识别系统执行识别和验证一般需要四个步骤−
There are four general steps a biometric system takes to perform identification and verification −
-
Acquire live sample from candidate. (using sensors)
-
Extract prominent features from sample. (using processing unit)
-
Compare live sample with samples stored in database. (using algorithms)
-
Present the decision. (Accept or reject the candidate.)
生物识别样本从候选用户获取。从样本中提取突出特征,然后将其与存储在数据库中的所有样本进行比较。当输入样本与数据库中某个样本匹配时,生物识别系统将允许该人访问资源;否则拒绝。
The biometric sample is acquired from candidate user. The prominent features are extracted from the sample and it is then compared with all the samples stored in the database. When the input sample matches with one of the samples in the database, the biometric system allows the person to access the resources; otherwise prohibits.
Biometrics Terminology
Biometric Template - 从生物样本中提取的独特特征的数字参考。
Biometric Template − It is a digital reference of the distinct characteristics that are extracted from a biometric sample.
Candidate/Subject - 输入其生物样本的人。
Candidate/Subject − A person who enters his biometric sample.
Closed-Set Identification - 已知数据库中存在那个人。
Closed-Set Identification − The person is known to be existing in the database.
Enrollment - 候选人第一次使用生物识别系统时,将记录基本信息,如姓名、地址等,然后记录候选人的生物特征。
Enrollment − It is when a candidate uses a biometric system for the first time, it records the basic information such as name, address, etc. and then records the candidate’s biometric trait.
False Acceptance Rate (FAR) - 生物识别系统会错误地将未经授权的用户识别为有效用户的可能性度量。
False Acceptance Rate (FAR) − It is the measure of possibility that a biometric system will incorrectly identify an unauthorized user as a valid user.
low FAR ensures high security 提供的生物识别系统。
A biometric system providing low FAR ensures high security.
False Reject Rate (FRR) - 生物识别系统错误地将授权用户拒绝为无效用户的可能性度量。
False Reject Rate (FRR) − It is the measure of possibility that the biometric system will incorrectly reject an authorized user as an invalid user.
Open-Set Identification - 不能保证数据库中存在那个人。
Open-Set Identification − The person is not guaranteed to be existing in the database.
Task - 当生物识别系统搜索数据库以查找匹配样本时。
Task − It is when the biometric system searches the database for matching sample.
Application Areas of Biometrics
生物识别系统有用的应用程序有很多。以下给出其中几个:
There are a number of applications where biometric systems are useful. Few of them are given below −
-
Controlling workplace access.
-
Identity establishment of people for authentic citizenship and immigration systems.
-
Applying access control to sensitive information and systems.
-
Identifying criminals by forensics.
-
Executing online e-commerce transactions.
-
Fraud and theft reduction.
-
Law enforcement.
Biometrics Modalities
生物识别模式只不过是生物识别系统的类别,取决于它作为输入获取的人的特征类型。
A biometric modality is nothing but a category of a biometric system depending upon the type of human trait it takes as input.
生物识别学在很大程度上是统计学。从样本中获取的数据越多,系统就越有可能独特且可靠。它可以针对各种模式进行工作,这些模式与个体的身体测量和特征以及行为模式有关。模式根据个体的生物特征进行分类。
The biometrics is largely statistical. The more the data available from sample, the more the system is likely to be unique and reliable. It can work on various modalities pertaining to measurements of individual’s body and features, and behavioral patterns. The modalities are classified based on the person’s biological traits.
Types of Biometric Modalities
人类存在各种特征,可用作生物识别模式。生物识别模式分为三类:
There are various traits present in humans, which can be used as biometrics modalities. The biometric modalities fall under three types −
-
Physiological
-
Behavioral
-
Combination of physiological and behavioral modality
下表收集了区分这三种模式的要点:
The following table collects the points that differentiate these three modalities −
Physiological Modality |
Behavioral Modality |
Combination of Both Modalities |
This modality pertains to the shape and size of the body. |
This modality is related to change in human behavior over time. |
This modality includes both traits, where the traits are depending upon physical as well as behavioral changes. |
For example − Fingerprint RecognitionHand Geometry Recognition systemFacial Recognition SystemIris Recognition SystemHand Geometry Recognition SystemRetinal Scanning SystemDNA Recognition System |
For example − Gait (the way one walks)Rhythm of typing keysSignature |
For example − Voice Recognition It depends on health, size, and shape of vocal cord, nasal cavities, mouth cavity, shape of lips, etc., and the emotional status, age, illness (behavior) of a person. |
在随后的章节中,我们将更详细地讨论这些模态中的每一个。
In the subsequent chapters, we will discuss each of these modalities in greater detail.
Physiological Modalities
如前所述,生理模态基于对人体部位的直接测量,例如虹膜、指纹、手指的形状和位置等。
As depicted earlier, the physiological modalities are based on the direct measurement of parts of human body such as iris, fingerprint, shape, and position of fingers, etc.
有些身体特征在人的一生中保持不变。它们可以作为识别个人身份的绝佳资源。
There are some physical traits which remain unaltered throughout a person’s life. They can be an excellent resource for identification of an individual.
Fingerprint Recognition System
它是最为人所知和使用的生物识别解决方案,用于对生物识别系统上的个人进行身份验证。它如此受欢迎的原因是,有十个可用的生物识别源以及易于获取。
It is the most known and used biometrics solution to authenticate people on biometric systems. The reasons for it being so popular are there are ten available sources of biometric and ease of acquisition.
每个人都有一个独特的指纹,由脊、沟和线的方向组成。脊有三种基本图案,即 arch, loop 和 whorl 。指纹的唯一性由这些特征以及分叉和斑点(脊端)之类的 minutiae features 决定。
Every person has a unique fingerprint which is composed of ridges, grooves, and direction of the lines. There are three basic patterns of ridges namely, arch, loop, and whorl. The uniqueness of fingerprint is determined by these features as well as minutiae features such as bifurcation and spots (ridge endings).
指纹是最古老、最流行的识别技术之一。指纹匹配技术有三种类型 −
Fingerprint is one of oldest and most popular recognition technique. Fingerprint matching techniques are of three types −
-
Minutiae Based Techniques − In these minutiae points are found and then mapped to their relative position on finger. There are some difficulties such as if image is of low quality, then it is difficult to find minutiae points correctly. Another difficulty is, it considers local position of ridges and furrows; not global.
-
Correlation Based Method − It uses richer gray scale information. It overcomes problems of minutiae-based method, by being able to work with bad quality data. But it has some of its own problems like localization of points.
-
Pattern Based (Image Based) Matching − Pattern based algorithms compare the basic fingerprint patterns (arch, whorl, and loop) between a stored template and a candidate fingerprint.

Merits of Finger Recognition System
-
It is the most contemporary method.
-
It is most economical method.
-
It is highly reliable and secure.
-
It works on a small template size, which speeds up the verifying process.
-
It consumes less memory space.
Facial Recognition System
面部识别基于确定下巴、下颌、眼睛、眉毛、鼻子、嘴唇和颧骨的形状和大小。2D 面部扫描仪开始读取面部几何形状并将其记录在网格上。面部几何形状以点的形式传输到数据库中。比较算法执行面部分割并得出结果。面部识别以以下方式执行:
Facial recognition is based on determining shape and size of jaw, chin, shape and location of the eyes, eyebrows, nose, lips, and cheekbones. 2D facial scanners start reading face geometry and recording it on the grid. The facial geometry is transferred to the database in terms of points. The comparison algorithms perform face matching and come up with the results. Facial recognition is performed in the following ways −
-
Facial Metrics − In this type, the distances between pupils or from nose to lip or chin are measured.
-
Eigen faces − It is the process of analyzing the overall face image as a weighted combination of a number of faces.
-
Skin Texture Analysis − The unique lines, patterns, and spots apparent in a person’s skin are located.

Merits of Facial Recognition System
-
It offers easy storage of templates in database.
-
It reduces the statistic complexities to recognize face image.
-
It involves no physical contact with the system.
Iris Recognition System
虹膜识别基于人眼中的虹膜模式。虹膜是一种有色弹性组织,中心有可调节的环形开口。它控制瞳孔的直径。在成年人中,虹膜的纹理在其整个生命周期中都是稳定的。左眼和右眼的虹膜图案不同。虹膜图案和颜色因人而异。
Iris recognition works on the basis of iris pattern in human eye. The iris is the pigmented elastic tissue that has adjustable circular opening in center. It controls the diameter of pupil. In adult humans, the texture of iris is stable throughout their lives. The iris patterns of left and right eyes are different. The iris patterns and colors change from person to person.
它涉及用一枚合格的相机拍摄虹膜图片,存储它,并使用数学算法将它与候选人的眼睛进行比较。
It involves taking the picture of iris with a capable camera, storing it, and comparing the same with the candidate eyes using mathematical algorithms.

Merits of Iris Recognition System
-
It is highly accurate as the chance of matching two irises is 1 in 10 billion people.
-
It is highly scalable as the iris pattern remains same throughout a person’s lifetime.
-
The candidate need not remove glasses or contact lenses; they do not hamper the accuracy of the system.
-
It involves no physical contact with the system.
-
It provides instant verification (2 to 5 seconds) because of its small template size.
Hand Geometry Recognition System
它包括测量手掌的长度和宽度、表面积、手指的长度和位置以及手的整体骨骼结构。每个人的手都是独一无二的,并且可以用来辨别其他人。手掌几何系统有两种−
It includes measuring length and width of palm, surface area, length and position of fingers, and overall bone structure of the hand. A person’s hand is unique and can be used to identify a person from others. There are two Hand Geometry systems −
-
Contact Based − a hand is placed on a scanner’s surface. This placement is positioned by five pins, which guide the candidate hand to position correctly for the camera.
-
Contact Less − In this approach neither pins nor platform are required for hand image acquisition.

Merits of Hand Geometry Recognition System
-
It is sturdy and user friendly.
-
The changes in skin moisture or texture do not affect the result.
Retinal Scanning System
视网膜是眼球后部的内衬层,覆盖了眼球内表面的 65%。它包含 photosensitive 细胞。由于供应血液的血管网络复杂,每个人的视网膜都是独一无二的。
Retina is the lining layer at the back of the eyeball that covers 65% of the eyeball’s inner surface. It contains photosensitive cells. Each person’s retina is unique due to the complex network of blood vessels that supply blood.
它是一种可靠的生物特征,因为视网膜图案在人的一生中保持不变,除了患有糖尿病、青光眼或某些退行性疾病的人的图案除外。
It is a reliable biometric as the retina pattern remains unchanged throughout the person’s life, barring the patterns of persons having diabetes, glaucoma, or some degenerative disorders.
在视网膜扫描过程中,要求一个人取下隐形眼镜或眼镜。将低强度的红外光束投射到某人的眼睛中 10 至 15 秒。红外光被血管吸收,在扫描过程中形成血管图案。然后将此图案数字化并存储在数据库中。
In retinal scanning process, a person is asked to remove lenses or eyeglasses. A low-intensity infrared light beam is casted into a person’s eye for 10 to 15 seconds. This infrared light is absorbed by the blood vessels forming a pattern of blood vessels during the scan. This pattern is then digitized and stored in the database.

Merits of Retinal Scanning System
-
It cannot be forged.
-
It is highly reliable as the error rate is 1 out of a crore samples (which is almost 0%).
Demerits of Retinal Scanning System
-
It is not very user friendly as the user needs to maintain steadiness that can cause discomfort.
-
It tends to reveal some poor health conditions such as hypertension or diabetes, which causes privacy issues.
-
Accuracy of the results is prone to diseases such as cataracts, glaucoma, diabetes, etc.
DNA Recognition System
*D*eoxyribo *N*ucleic *A*cid (DNA) 是人类中的遗传物质。除了同卵双胞胎,每个人都通过其 DNA 中的特征进行唯一识别,该特征位于细胞核中。有多种来源可以收集 DNA 模式,例如血液、唾液、指甲、头发等。
*D*eoxyribo *N*euclic *A*cid (DNA) is the genetic material found in humans. Every human barring identical twins, is uniquely identifiable by the traits found in their DNA, which is located in the nucleus of the cell. There are number of sources from which DNA patterns can be collected such as blood, saliva, nails, hair, etc.
在细胞内,DNA 以称为 chromosomes 的长双螺旋结构组织。人类中有 23 对染色体。在 46 条染色体总数中,后代从每个亲生父母那里继承 23 条染色体。后代的 99.7% DNA 与父母的共享。剩余的 0.3% DNA 包含了个体特有的重复编码。
Within cells, DNA is organized in long double helix structure called chromosomes. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Out of the 46 total chromosomes, the offspring inherits 23 chromosomes from each biological parent. 99.7% of an offspring’s DNA is shared with their parents. The remaining 0.3% DNA contains repetitive coding unique to an individual.
DNA 分析的基本步骤为:
The fundamental steps of DNA profiling are −
-
Separating the DNA from sample acquired from either of blood, saliva, hair, semen, or tissue.
-
Separating the DNA sample into shorter segments.
-
Organizing the DNA segments according to size.
-
Comparing the DNA segments from various samples.
样本越详细,比较就越精确,进而越能识别出该个体。
The more detailed the sample is, the more precise the comparison and in turn the identification of the individual is.

DNA 生物识别在以下方面与其他所有生物识别技术有所不同:
DNA Biometrics differs from all others in the following ways −
-
It needs a tangible physical sample instead of image.
-
DNA matching is done on physical samples. There is no feature extraction or template saving.
Behavioral Modalities
行为生物识别技术涉及人员的行为或人员执行任务(如走路、签名和键盘输入)的方式。
Behavioral biometrics pertains to the behavior exhibited by people or the manner in which people perform tasks such as walking, signing, and typing on the keyboard.
行为生物识别方式具有更高的差异性,因为它们主要取决于疲劳、情绪等外部因素。与基于生理生物识别技术的解决方案相比,这会导致较高的 FAR 和 FRR。
Behavioral biometrics modalities have higher variations as they primarily depend on the external factors such as fatigue, mood, etc. This causes higher FAR and FRR as compared to solutions based on a physiological biometrics.
Gait Recognition
Gait 是一个人的行走方式。人们在行走时表现出不同的特征,例如身体姿势、行走时两英尺之间的距离、摇摆等,这些特征有助于识别他们。
Gait is the manner of a person’s walking. People show different traits while walking such as body posture, distance between two feet while walking, swaying, etc., which help to recognize them uniquely.
基于对候选人走路视频图像进行分析的步态识别。候选人行走周期的样本由视频记录。然后分析样本以确定膝盖和脚踝等关节的位置,以及在行走时它们之间的角度。
A gait recognition based on the analyzing the video images of candidate’s walk. The sample of candidate’s walk cycle is recorded by Video. The sample is then analyzed for position of joints such as knees and ankles, and the angles made between them while walking.
为每个人员创建一个相应的数学模型并将其存储在数据库中。在验证时,该模型与候选人步态的实时样本进行比较以确定其身份。
A respective mathematical model is created for every candidate person and stored in the database. At the time of verification, this model is compared with the live sample of the candidate walk to determine its identity.

Merits of Gait Recognition System
-
It is non-invasive.
-
It does not need the candidate’s cooperation as it can be used from a distance.
-
It can be used for determining medical disorders by spotting changes in walking pattern of a person in case of Parkinson’s disease.
Signature Recognition System
在这种情况下,签名方式的行为模式比图形形式的签名外观得到更多强调。
In this case, more emphasis is given on the behavioral patterns in which the signature is signed than the way a signature looks in terms of graphics.
行为模式包括书写时间、停顿、压力、笔画方向和签名过程中的速度的变化。复制签名的图形外观可能容易,但要模仿签名的行为模式却不容易。
The behavioral patterns include the changes in the timing of writing, pauses, pressure, direction of strokes, and speed during the course of signing. It could be easy to duplicate the graphical appearance of the signature but it is not easy to imitate the signature with the same behavior the person shows while signing.
此项技术包括一支笔和平板电脑,两者都连接到计算机,用于模板比较和验证。高品质平板电脑可以在签名时捕获速度、压力和时间等行为特征。
This technology consists of a pen and a specialized writing tablet, both connected to a computer for template comparison and verification. A high quality tablet can capture the behavioral traits such as speed, pressure, and timing while signing.

在注册阶段,候选人必须在绘图板上多次签字以获取数据。然后,签名识别算法提取唯一特征,如时间、压力、速度、笔画方向、签名路径上的重要点和签名大小。算法为这些点指定不同的权重值。
During enrollment phase, the candidate must sign on the writing tablet multiple times for data acquisition. The signature recognition algorithms then extracts the unique features such as timing, pressure, speed, direction of strokes, important points on the path of signature, and the size of signature. The algorithm assigns different values of weights to those points.
在识别时,候选人输入签名的实时样本,将其与数据库中的签名进行比较。
At the time of identification, the candidate enters the live sample of the signature, which is compared with the signatures in the database.
Constraints of Signature Recognition System
-
To acquire adequate amount of data, the signature should be small enough to fit on tablet and big enough to be able to deal with.
-
The quality of the writing tablet decides the robustness of signature recognition enrollment template.
-
The candidate must perform the verification processes in the same type of environment and conditions as they were at the time of enrollment. If there is a change, then the enrollment template and live sample template may differ from each other.
Merits of Signature Recognition System
-
Signature recognition process has a high resistance to imposters as it is very difficult to imitate the behavior patterns associated with the signature.
-
It works very well in high amount business transactions. For example, Signature recognition could be used to positively verify the business representatives involved in the transaction before any classified documents are opened and signed.
-
It is a non-invasive tool.
-
We all use our signature in some sort of commerce, and thus there are virtually no privacy rights issues involved.
-
Even if the system is hacked and the template is stolen, it is easy to restore the template.
Keystroke Recognition System
在二战期间,军事情报部门使用一种称为发送者拳头(Fist of the Sender)的技术,根据打字节奏来确定莫尔斯电码是由敌人还是盟军发送的。如今,就硬件而言,击键动力学是最容易实现的生物识别解决方案。
During the World War II, a technique known as Fist of the Sender was used by military intelligence to determine if the Morse code was sent by enemy or ally based on the rhythm of typing. These days, keystroke dynamics the easiest biometric solution to implement in terms of hardware.
此生物识别分析候选人的打字模式、节奏和在键盘上打字的速度。击键识别中使用 dwell time 和 flight time 测量。
This biometric analyzes candidate’s typing pattern, the rhythm, and the speed of typing on a keyboard. The dwell time and flight time measurements are used in keystroke recognition.
Dwell time −它是一个键被按下的持续时间。
Dwell time − It is the duration of time for which a key is pressed.
Flight time −它是在松开一个键和按下下一个键之间经过的时间。
Flight time − It is the time elapsed between releasing a key and pressing the following key.

候选人在键盘上的打字方式有所不同,因为他们找到正确按键所需的时间、飞行时间和停留时间有所不同。他们的打字速度和节奏也根据他们对键盘的熟练程度而异。击键识别系统在一次尝试中每秒监测键盘输入数千次,以根据他们的打字习惯识别用户。
The candidates differ in the way they type on the keyboard as the time they take to find the right key, the flight time, and the dwelling time. Their speed and rhythm of typing also varies according to their level of comfort with the keyboard. Keystroke recognition system monitors the keyboard inputs thousands of times per second in a single attempt to identify users based on their habits of typing.
击键识别有两种类型−
There are two types of keystroke recognition −
-
Static − It is one time recognition at the start of interaction.
-
Continuous − It is throughout the course of interaction.
Application of Keystroke Dynamics
-
Keystroke Recognition is used for identification/verification. It is used with user ID/password as a form of multifactor authentication.
-
It is used for surveillance. Some software solutions track keystroke behavior for each user account without end-user’s knowledge. This tracking is used to analyze if the account was being shared or used by anyone else than the genuine account owner. It is used to verify if some software license is being shared.
Merits of Keystroke Recognition System
-
It needs no special hardware to track this biometric.
-
It is a quick and secure way of identification.
-
A person typing does not have to worry about being watched.
-
Users need no training for enrollment or entering their live samples.
Demerits of Keystroke Recognition System
-
The candidate’s typing rhythm can change between a number of days or within a day itself because of tiredness, sickness, influence of medicines or alcohol, change of keyboard, etc.
-
There are no known features dedicated solely to carry out discriminating information.
Voice Recognition
语音识别生物特征模态是生理模态和行为模态的结合。语音识别只不过是声音识别。它依赖于影响以下因素的特征−
Voice recognition biometric modality is a combination of both physiological and behavioral modalities. Voice recognition is nothing but sound recognition. It relies on features influenced by −
-
Physiological Component − Physical shape, size, and health of a person’s vocal cord, and lips, teeth, tongue, and mouth cavity.
-
Behavioral Component − Emotional status of the person while speaking, accents, tone, pitch, pace of talking, mumbling, etc.
Voice Recognition System
语音识别也被称为说话人识别。在注册时,用户需要对麦克风说出单词或短语。这对于获取候选人的语音样本是必要的。
Voice Recognition is also called Speaker Recognition. At the time of enrollment, the user needs to speak a word or phrase into a microphone. This is necessary to acquire speech sample of a candidate.
来自麦克风的电信号由模数转换器 (ADC) 转换成数字信号。它以数字化样本的形式记录在计算机内存中。然后,计算机比较并尝试将候选人的输入语音与存储的数字化语音样本进行匹配,并识别出候选人。
The electrical signal from the microphone is converted into digital signal by an Analog to Digital (ADC) converter. It is recorded into the computer memory as a digitized sample. The computer then compares and attempts to match the input voice of candidate with the stored digitized voice sample and identifies the candidate.

Voice Recognition Modalities
语音识别有两种变体− speaker dependent 和 speaker independent 。
There are two variants of voice recognition − speaker dependent and speaker independent.
说话者相关的语音识别依赖于候选人的特定语音特征的知识。此系统通过语音训练(或注册)学习这些特征。
Speaker dependent voice recognition relies on the knowledge of candidate’s particular voice characteristics. This system learns those characteristics through voice training (or enrollment).
-
The system needs to be trained on the users to accustom it to a particular accent and tone before employing to recognize what was said.
-
It is a good option if there is only one user going to use the system.
说话者无关系统能够通过限制单词和短语等语音环境识别不同用户的语音。这些系统用于自动电话界面。
Speaker independent systems are able to recognize the speech from different users by restricting the contexts of the speech such as words and phrases. These systems are used for automated telephone interfaces.
-
They do not require training the system on each individual user.
-
They are a good choice to be used by different individuals where it is not required to recognize each candidate’s speech characteristics.
Difference between Voice and Speech Recognition
说话者识别和语音识别很容易被误认为是同一技术;但它们是不同的技术。让我们看看原因:
Speaker recognition and Speech recognition are mistakenly taken as same; but they are different technologies. Let us see, how −
Speaker Recognition (Voice Recognition) |
Speech Recognition |
The objective of voice recognition is to recognize WHO is speaking. |
The speech recognition aims at understanding and comprehending WHAT was spoken. |
It is used to identify a person by analyzing its tone, voice pitch, and accent. |
It is used in hand-free computing, map, or menu navigation. |
Multimodal Biometric Systems
迄今为止我们讨论的所有生物识别系统都是单模态的,它们采用单一信息来源进行验证。顾名思义,多模态生物识别系统可以接受两个或更多生物识别输入的信息。
All the biometric systems we discussed till now were unimodal, which take single source of information for authentication. As the name depicts, multimodal biometric systems work on accepting information from two or more biometric inputs.
多模态生物识别系统增加了系统从用户处获取的输入信息范围和种类,用于验证信息。
A multimodal biometric system increases the scope and variety of input information the system takes from the users for authentication.
Why Multimodal Biometrics is Required?
单模态系统需要应对各种挑战,例如缺乏隐秘性、样本的非普遍性、用户在使用系统时的舒适度和自由程度、存储数据的欺骗攻击等。
The unimodal systems have to deal with various challenges such as lack of secrecy, non-universality of samples, extent of user’s comfort and freedom while dealing with the system, spoofing attacks on stored data, etc.
采用多模态生物识别系统可以解决其中一些挑战。
Some of these challenges can be addressed by employing a multimodal biometric system.
需要它还有许多其他原因,例如 -
There are several more reasons for its requirement, such as −
-
Availability of multiple traits makes the multimodal system more reliable.
-
A multimodal biometric system increases security and secrecy of user data.
-
A multimodal biometric system conducts fusion strategies to combine decisions from each subsystem and then comes up with a conclusion. This makes a multimodal system more accurate.
-
If any of the identifiers fail to work for known or unknown reasons, the system still can provide security by employing the other identifier.
-
Multimodal systems can provide knowledge about “liveliness” of the sample being entered by applying liveliness detection techniques. This makes them capable to detect and handle spoofing.
Working of Multimodal Biometric System
多模式生物识别系统具有单模式系统所具有的所有常规模块 -
Multimodal biometric system has all the conventional modules a unimodal system has −
-
Capturing module
-
Feature extraction module
-
Comparison module
-
Decision making module
此外,它还具有融合技术,以整合来自两个不同认证系统的的信息。融合可以在以下任何级别完成 -
In addition, it has a fusion technique to integrate the information from two different authentication systems. The fusion can be done at any of the following levels −
-
During feature extraction.
-
During comparison of live samples with stored biometric templates.
-
During decision making.
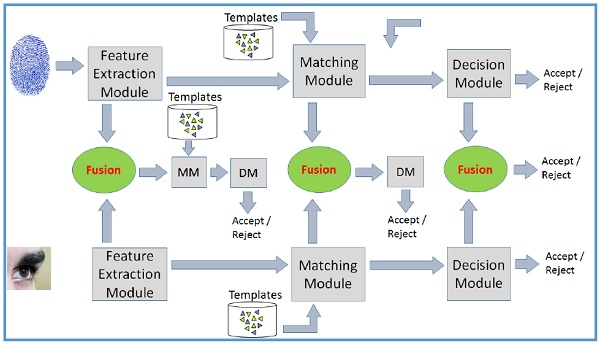
在初始阶段集成或融合信息的多分系统被认为比在后期集成信息的系统更有效。原因很明显,早期阶段比比较模块的匹配分数包含更准确的信息。
The multimodal biometric systems that integrate or fuse the information at initial stage are considered to be more effective than the systems those integrate the information at the later stages. The obvious reason to this is, the early stage contains more accurate information than the matching scores of the comparison modules.
Fusion Scenarios in Multimodal Biometric System
在多分身生物特征识别系统中,特征和组件的数量可能会有所不同。它们可能是以下形式 -
Within a multimodal biometric system, there can be variety in number of traits and components. They can be as follows −
-
Single biometric trait, multiple sensors.
-
Single biometric trait, multiple classifiers (say, minutiae-based matcher and texture-based matcher).
-
Single biometric trait, multiple units (say, multiple fingers).
-
Multiple biometric traits of an individual (say, iris, fingerprint, etc.)
然后对这些特质进行操作以确认用户的身份。
These traits are then operated upon to confirm user’s identity.
Design Issues with Multimodal Biometric Systems
在设计多分身生物特征识别系统时,您需要考虑许多因素 -
You need to consider a number of factors while designing a multimodal biometric system −
-
Level of security you need to bring in.
-
The number of users who will use the system.
-
Types of biometric traits you need to acquire.
-
The number of biometric traits from the users.
-
The level at which multiple biometric traits need integration.
-
The technique to be adopted to integrate the information.
-
The trade-off between development cost versus system performance.
Biometric Modality Selection
要能够选择合适的生物特征系统,您需要在各个方面对其进行比较。您需要根据方便性、系统规范和性能以及您的预算来评估系统是否适合您的要求。
To be able to select a proper biometric system, you need to compare them on various aspects. You need to assess the suitability of the systems to your requirements in terms of convenience, system specifications and performance, and your budget.
您可以通过研究各种有效性标准来选择最合适的生物特征系统。
You can select best suitable biometric system by studying various criteria for their effectiveness.
Criteria for Effective Biometric System
衡量生物特征系统有效性的七个基本标准 −
There are seven basic criteria for measuring effectiveness of a biometric system −
-
Uniqueness − It determines how uniquely a biometric system can recognize a user from a group of users. It is a primary criterion.
-
Universality − It indicates requirement for unique characteristics of each person in the world, which cannot be reproduced. It is a secondary criterion.
-
Permanence − It indicates that a personal trait recorded needs to be constant in the database for a certain time period.
-
Collectability − It is the ease at which a person’s trait can be acquired, measured, or processed further.
-
Performance − It is the efficiency of system in terms of accuracy, speed, fault handling, and robustness.
-
Acceptability − It is the user-friendliness, or how good the users accept the technology such that they are cooperative to let their biometric trait captured and assessed.
-
Circumvention − It is the ease with which a trait is possibly imitated using an artifact or substitute.
Comparison of Various Biometric Modalities
让我们从以下方面比较所有生物识别系统 −
Let us compare all the biometric system in the following terms −
Biometric Characteristic |
Universality |
Uniqueness |
Permanence |
Collect-Ability |
Performance |
Accept-ability |
Circum-vention |
Finger Print |
Medium |
High |
High |
Medium |
High |
Medium |
High |
Face Recognition |
High |
Low |
Medium |
High |
Low |
High |
Low |
Hand Geometry |
Medium |
Medium |
Medium |
High |
Medium |
Medium |
Medium |
Iris Recognition |
High |
High |
High |
Medium |
High |
Low |
High |
Retinal Scan |
High |
High |
Medium |
Low |
High |
Low |
High |
DNA |
High |
High |
Medium |
High |
High |
Low |
Low |
Keystroke |
High |
Low |
Low |
High |
Medium |
High |
High |
Signature |
Low |
Low |
Low |
High |
Low |
High |
Low |
Voice |
Medium |
Low |
Low |
Medium |
Low |
High |
Low |
您可以根据需要处理的标准选择合适的生物特征系统,如表所示。
You can select an appropriate biometric system depending upon the criteria you need to deal with as shown in the table.
Biometric System Performance
生物特征识别系统制造商声称系统性能很高,而在实际操作环境中实际上很难实现这一点。可能的原因是,在受控的环境设置、硬件的限制等条件下进行的测试。
Biometric system manufacturers claim high system performance which is practically difficult to achieve in actual operating environments. The possible reasons are, tests conducted in controlled environment setups, limitations on hardware, etc.
例如,语音识别系统只能在安静的环境中有效工作,面部识别系统如果照明条件受到控制,并且受试者接受过适当清洗和放置手指的训练,则可以正常工作。
For example, a voice recognition system can work efficiently only in quiet environment, a facial recognition system can work fine if lighting conditions are controlled, and candidates can be trained to clean and place their fingers properly on the fingerprint scanners.
然而,在实践中,在目标操作环境中可能无法获得这样的理想条件。
However, in practice, such ideal conditions may not be available in the target operating environment.
Performance Measurements
生物特征识别系统的性能测量与拒绝错误率 (FRR) 和接受错误率 (FAR) 密切相关。
The performance measurements of a biometric system are closely tied to False Reject Rate (FRR) and False Accept Rate (FAR).
FRR 也称为 Type-I error 或假不匹配率 (FNMR),它表示合法用户被系统拒绝的可能性。
FRR is also known as Type-I error or False Non Match Rate (FNMR) which states the likelihood of a legitimate user being rejected by the system.
FAR 被称为 Type-II error 或错误匹配率 (FMR),它表明系统接受虚假身份声明的可能性。
FAR is referred to as Type-II error or False Match Rate (FMR) which states the likelihood of a false identity claim being accepted by the system.
理想的生物特征系统预计对 FAR 和 FRR 都产生零值。这意味着它应该接受所有真正用户并拒绝所有虚假身份声明,但这实际上是无法实现的。
An ideal biometric system is expected to produce zero value for both FAR and FRR. Means it should accept all genuine users and reject all fake identity claims, which is practically not achievable.
FAR 和 FRR 成反比。如果 FAR 得到改善,则 FRR 会下降。 high FRR ensures high security 的生物特征系统。如果 FRR 过高,则系统需要多次输入活体样本,这会降低效率。
FAR and FRR are inversely proportional to each other. If FAR is improved, then the FRR declines. A biometric system providing high FRR ensures high security. If the FRR is too high, then the system requires to enter the live sample a number of times, which makes it less efficient.
当前生物特征技术的性能远未达到理想状态。因此,系统开发人员需要根据安全要求在这两个因素之间保持良好的平衡。
The performance of current biometrics technologies is far from the ideal. Hence the system developers need to keep a good balance between these two factors depending on the security requirements.
Pattern Recognition & Biometrics
模式识别涉及识别模式并再次确认。通常,模式可以是指纹图像、手写的草书单词、人脸、语音信号、条形码或互联网上的网页。
Pattern recognition deals with identifying a pattern and confirming it again. In general, a pattern can be a fingerprint image, a handwritten cursive word, a human face, a speech signal, a bar code, or a web page on the Internet.
各个模式通常根据其属性分为不同的类别。当具有相同属性的模式组合在一起时,结果组也是一个模式,通常称为模式 class 。
The individual patterns are often grouped into various categories based on their properties. When the patterns of same properties are grouped together, the resultant group is also a pattern, which is often called a pattern class.
模式识别是观察、区分感兴趣模式并对模式或模式类别做出正确判断的科学。因此,生物识别系统通过将一个人的特征与存储的模板进行比较来识别和分类 individuals。
Pattern recognition is the science for observing, distinguishing the patterns of interest, and making correct decisions about the patterns or pattern classes. Thus, a biometric system applies pattern recognition to identify and classify the individuals, by comparing it with the stored templates.
Pattern Recognition in Biometrics
模式识别技术执行以下任务 −
The pattern recognition technique conducts the following tasks −
-
Classification − Identifying handwritten characters, CAPTCHAs, distinguishing humans from computers.
-
Segmentation − Detecting text regions or face regions in images.
-
Syntactic Pattern Recognition − Determining how a group of math symbols or operators are related, and how they form a meaningful expression.
下表突出显示了模式识别在生物特征识别中的作用 −
The following table highlights the role of pattern recognition in biometrics −
Pattern Recognition Task |
Input |
Output |
Character Recognition (Signature Recognition) |
Optical signals or Strokes |
Name of the character |
Speaker Recognition |
Voice |
Identity of the speaker |
Fingerprint, Facial image, hand geometry image |
Image |
Identity of the user |
Components of Pattern Recognition
模式识别技术将人类特征的随机模式提取成紧凑的数字签名,该数字签名可充当生物标识符。生物识别系统使用模式识别技术对用户进行分类并单独识别。
Pattern recognition technique extracts a random pattern of human trait into a compact digital signature, which can serve as a biological identifier. The biometric systems use pattern recognition techniques to classify the users and identify them separately.
模式识别的组成部分如下 −
The components of pattern recognition are as follows −

Popular Algorithms in Pattern Recognition
最流行的模式生成算法如下 −
The most popular pattern generation algorithms are −
Signal Processing & Biometrics
在现实世界中,我们可以获得各种信号,例如声音、光、无线电信号、来自人体的生物医学信号等。所有这些信号都以连续的信息流(称为模拟信号)的形式出现。人声是我们从现实世界中获得的信号,并用作生物特征输入。
There are various signals we can get in the real world such as sound, light, radio signals, biomedical signals from human body, etc. All these signals are in the form of a continuous stream of information, called analog signals. Human voice is a kind of signal we get from the real world and use as biometric input.
What is a Signal?
信号是可以传达、显示、记录或修改的,包含某些信息的可测量物理量。
A signal is a measurable physical quantity containing some information, which can be conveyed, displayed, recorded, or modified.
Signal Processing in Biometrics
处理信号的原因有很多。生物特征系统需要进行语音处理出于多种原因——
There are various reasons for processing signals. The biometric systems, require voice processing for various reasons −
-
To extract meaningful information from the candidate’s sample.
-
To remove noise from the sample.
-
To make the sample transmittable.
-
To remove distortion of sample.
模拟信号处理模块将现实世界中的信息(例如声波)转换为 0 和 1 的形式,使其易于现代数字系统(例如生物识别系统)理解和使用。击键、手部几何形状、签名和语音属于信号处理和模式识别的领域。
The analog signal processing module converts real world information such as sound wave in the form of 0s and 1s to make it understandable and usable by the contemporary digital systems such as biometric systems. The keystrokes, hand geometry, signature, and speech fall into the domains of signal processing and pattern recognition.
Digital Signal Processing Systems (DSPs)
有两种类型的信号——模拟和数字。模拟信号是信息的不间断连续流,而数字信号是 0 和 1 的流。
There are two types of signals − analog and digital. The analog signals are uninterrupted, continuous stream of information whereas digital signal is a stream of 0s and 1s.
DSP 系统是生物特征系统的重要组成部分之一,它通过使用模数转换器 (ADC) 采样和数字化,将模拟信号转换为离散数字值的流。
DSP systems are one of the important components of biometric systems, which convert analog signals into a stream of discrete digital values by sampling and digitizing using an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC).
DSP 是单芯片数字微型计算机,处理来自摄像头、指纹传感器、麦克风等的电子传感器产生的电信号。
DSPs are single-chip digital microcomputers, which process electrical signals generated by electronic sensors from cameras, fingerprint sensors, microphones, etc.
DSP in Biometrics
DSP 使生物识别系统小巧便携,运行高效,整体成本更低。
A DSP allows the biometric system to be small and easily portable, to perform efficiently and to be overall less costly.
DSP 架构旨在支持复杂的数学算法,其中涉及大量的乘法和加法。DSP 可以借助算术逻辑单元 (ALU) 中的乘累加 (MAC) 硬件在一个周期内执行乘/加。
The DSP architecture is built to support complex mathematical algorithms that involve a significant amount of multiplication and addition. The DSP can execute multiply/add in a single cycle with the help of the multiply/accumulate (MAC) hardware inside its Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU).
它还可以使用二维快速傅里叶变换 (FFT) 和有限 IR 滤波器来提高捕获图像的分辨率。
It can also enhance the resolution of the captured image with the use of two-dimensional Fast Fourier Transforms (FFT) and finite IR filters.
Biometrics & Image Processing
在信息时代,图像占据了很大份额。在生物特征识别中,需要图像处理才能识别在数据库中存储的生物特征图像的个人。面部,指纹,虹膜等是基于图像的生物特征识别,需要图像处理和模式识别技术。
Images have a huge share in this era of information. In biometrics, image processing is required for identifying an individual whose biometric image is stored in the database previously. Faces, fingerprints, irises, etc., are image-based biometrics, which require image processing and pattern recognition techniques.
为了使基于图像的生物识别系统准确工作,它需要以非常清晰且未经篡改的形式获得用户生物特征的样本图像。
For an image based biometric system to work accurately, it needs to have the sample image of user’s biometric in a very clear and non-adulterated form.
Requirement of Image Processing in Biometrics
用户生物特征的图像被输入到生物识别系统中。该系统被编程为使用方程式来处理图像,然后存储每个像素的计算结果。
The image of user’s biometric is fed into the biometric system. The system is programmed to manipulate the image using equations, and then store the results of the computation for each pixel.
为了选择性地增强数据中的某些精细特征并消除某些噪声,数字数据要经过各种图像处理操作。
To selectively enhance certain fine features in the data and to remove certain noise, the digital data is subjected to various image processing operations.
图像处理方法可以分为三类功能 −
Image processing methods can be grouped into three functional categories −
Image Restoration
图像复原主要包括 −
Image restoration mainly includes −
-
Reducing noise introduced in the image at the time of acquiring sample.
-
Removing distortions appeared during enrollment of biometric.
图像平滑可以降低图像中的噪声。平滑过程是通过将每个像素替换为与相邻像素的平均值来进行的。生物识别系统使用各种滤波算法和降噪技术,例如中值滤波、自适应滤波、统计直方图、小波变换等。
Image smoothing reduces noise in the image. Smoothing is carried out by replacing each pixel by the average value with the neighboring pixel. The biometric system uses various filtering algorithms and noise reduction techniques such as Median Filtering, Adaptive Filtering, Statistical Histogram, Wavelet Transforms, etc.
Image Enhancement
图像增强技术可以改善图像的任何部分或特征的可见性并抑制其他部分的信息。它仅在还原完成后才会进行操作。它包括提高亮度、锐化、调整对比度等,以便图像可用于进一步处理。
Image enhancement techniques improve the visibility of any portion or feature of the image and suppress the information in other parts. It is done only after restoration is completed. It includes brightening, sharpening, adjusting contrast, etc., so that the image is usable for further processing.
Feature Extraction
从图像中可以提取两种类型的特征,即:
Two types of features are extracted from image, namely −
-
General features − The features such as shape, texture, color, etc., which are used to describe content of the image.
-
Domain-specific features − They are application dependent features such as face, iris, fingerprint, etc. Gabor filters are used to extract features.
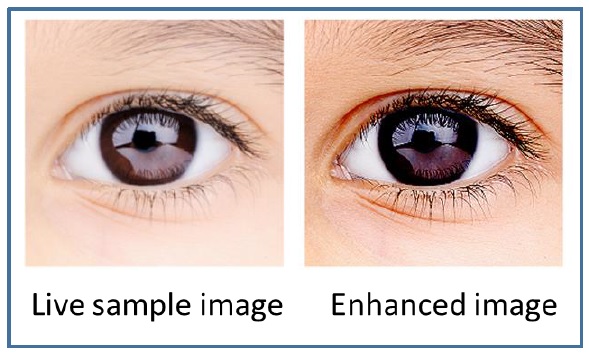
当从图像中提取特征时,你需要选择一个合适的分类器。广泛使用的分类器 Nearest Neighbor classifier ,它将候选图像的特征矢量与存储在数据库中的图像矢量进行比较。
When the features are extracted from the image, you need to choose a suitable classifier. The widely used classifier Nearest Neighbor classifier, which compares the feature vector of the candidate image with the vector of the image stored in the database.
B-Splines 是用于描述指纹生物识别系统中曲线模式的近似值。B 样条的系数用作特征。在虹膜识别系统的情况下,虹膜图像使用离散小波变换 (DWT) 分解,然后 DWT 系数用作特征。
B-Splines are approximations applied to describe curve patterns in fingerprint biometric systems. The coefficients of B-Splines are used as features. In case of iris recognition system, the images of iris are decomposed using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and the DWT coefficients are then used as features.
Biometric System Security
生物识别系统的工作在很大程度上取决于受操作限制的输入设备。有时,设备本身可能无法捕获必要的输入样本。它们可能无法充分捕获样本。这使得系统不可靠且脆弱。
The operations of a biometric system depend heavily on the input devices that are subjected to operational limitations. At times, the devices themselves may fail to capture the necessary input samples. They may not capture the sample sufficiently. This makes the system unreliable and vulnerable.
生物识别系统越脆弱,就越不安全。
The more vulnerable a biometric system is, the more insecure it is.
Biometric System Vulnerability
这有生物识别系统脆弱性的两个主要原因:
There are the two major causes of biometric system vulnerability −
System Failures
生物识别系统无法工作的有两种方式:
There are two ways in which a biometric system can fail to work −
-
Intrinsic failures − They are failures such as non-working sensors, failure of feature extraction, matching, or decision making modules, etc.
-
Failures due to attacks − They are due to loopholes in the biometric system design, availability of any computations to the attackers, insider attacks from unethical system administrators, etc.
Risks with Biometric System Security
生物识别系统的安全性很重要,因为生物识别数据不容易撤销或替换。关于生物识别系统安全性的重要风险如下:
The security of a biometric system is important as the biometric data is not easy to revoke or replace. There are following prominent risks regarding security of biometric systems −
Risk of User Data Being Stolen
如果生物识别系统很脆弱,黑客可以破坏其安全性并收集记录在数据库中的用户数据。它对隐私构成了更大的威胁。
If the biometric system is vulnerable, the hacker can breach the security of it and collect the user data recorded in the database. It creates more hazards to privacy.
Risk of User Data Getting Compromised
在获取生物识别样本后,黑客可以向系统提供一个虚假样本。如果用户数据遭到破坏,它将永远遭到破坏。显而易见的原因是,用户只有有限数量的生物识别数据,并且它们很难被替换,这与密码或身份证不同。
After acquiring the biometric sample, the hacker can present a fake sample to the system. If user data is compromised, it remains compromised forever. The obvious reason is, user has only a limited number of biometrics and they are difficult to replace, unlike passwords or ID cards.
尽管生物识别数据经过加密和存储,但它需要解密才能进行匹配。在匹配时,黑客可能会破坏安全性。
Though biometric data is encrypted and stored, it needs to be decrypted for matching purpose. At the time of matching a hacker may breach the security.
Biometric System Security
已提出多种解决方案来解决生物特征系统安全问题。永远不要以原始形式存储生物特征模板。它们已加密,有时甚至两次加密。
A number of solutions are proposed to address the biometric system security issue. Biometric templates are never stored in the raw form. They are encrypted; sometimes even twice.
对于生物特征,涉及各种资源,例如人员(受试者或候选人)、实体(系统组件或流程)和生物特征数据(信息)。 confidentiality, integrity, authenticity, non-repudiation 和 availability 的安全要求在生物特征领域至关重要。让我们简要回顾一下它们 -
In the case of biometrics, there are various resources involved such as humans (subjects or candidates), entities (system components or processes), and biometric data (information). The security requirements of confidentiality, integrity, authenticity, non-repudiation, and availability are essential in biometrics. Let us go through them briefly −
Authenticity
它是纯净、真实或原始的品质或状态,而不是复制品。信息在其创建、存储或传输时的状态和品质保持不变时即为真实。
It is the quality or the state of being pure, genuine, or original, rather than being reproduced. Information is authentic when it is in the same state and quality when it was created, stored, or transferred.
生物特征系统中有两种真实性 - entity authenticity 和 data origin authenticity 。实体真实性确认参与整体处理的所有实体都是他们声称的那样。数据来源真实性确保数据的真实性和原创性。例如,生物特征数据是通过传感器设备采集的。来自真实传感器的捕获数据未从先前的记录中伪造。
There are two authenticities in a biometric system − entity authenticity and data origin authenticity. Entity authenticity confirms that all entities involved in the overall processing are the ones they claim to be. Data origin authenticity ensures genuineness and originality of data. For example, the biometrics data is captured with sensor devices. The captured data that came from a genuine sensor is not spoofed from a previous recording.
Confidentiality
它限制信息访问和向授权用户披露,并防止未经授权的人员访问或披露。在生物特征系统的情况下,它主要指生物特征和相关身份验证信息,当它被捕获和存储时,需要对其保密,以防止未经授权的实体获取。
It is limiting information access and disclosure to authorized users and preventing access by or disclosure to unauthorized people. In cases of a biometric system, it mainly refers to biometric and related authentication information when it is captured and stored, which needs to be kept secret from unauthorized entities.
生物特征信息只应完全可供其所属的人员访问。在识别和变化期间,需要采取适当的安全措施对访问候选人进行限制。
The biometric information should only be accessible completely to the person it belongs. During identification and variation, the accessing candidate needs to be restricted with appropriate security measures.
Integrity
它是完整且未经改动,涉及到其一致性、准确性和正确性。对于生物特征系统,完整性应很高。应通过纳入其通知和更正,防止或最早检测到操作和存储期间的任何恶意操作。
It is the condition of being complete and unaltered that refers to its consistency, accuracy, and correctness. For a biometric system, the integrity should be high. Any malicious manipulations during operation and storage should be kept away or detected earliest by including its notification and correction.
Non-repudiation
它是识别所涉及的资源,如实体和组件。它也被视为责任。例如,它禁止生物特征信息的发件人或收件人否认发送或接收生物特征信息。
It is identification of involved resources such as entities and components. It is also seen as accountability. For example, it prohibits a sender or a recipient of biometric information from denying having sent or received biometric information.
Availability
如果集合中的所有成员都可以访问资源,则资源相对于该集合具有可用性属性。一个称为 reachability 的方面确保人或系统流程可以或不能被联系,具体取决于用户兴趣。
A resource has the property of availability with respect to a set of entities if all members of the set can access the resource. An aspect called reachability ensures that the humans or system processes either can or cannot be contacted, depending on user interests.
攻击者可能使系统对真实用户不可用,从而阻止他们使用经过身份验证的应用程序。这些攻击者以信息的可用性为目标。
Attackers can make the system unusable for genuine users, thus preventing them from using authenticated applications. These attackers target the availability of the information.
Criteria for Generating Biometric Templates
以下是生成生物特征模板的标准 -
Here are the criteria for generating biometric templates −
-
Ensuring that the template comes from a human candidate and is captured by a genuine sensor and software.
-
Securing a biometric template by encryption with irreversibility properties. This makes it difficult for hackers to compute the original biometric information from secure template.
-
Creating an unlikable (unique) biometric template. A biometric system should not be able to access the template of the same candidate recorded into another biometric system. In case if a hacker manages to retrieve a biometric template from one biometric system, he should not be able to use this template to gain access through another biometric system even though both verifications may be based on the same biometric template of the candidate. Further, an unlinkable biometric system should make it impossible to derive any information based on the relation between two templates.
-
Creating a cancellable and renewable template. It emphasizes on the ability to cancel or deactivate the compromised template and reproduce another one, in a similar manner that a lost or stolen smartcard can be reproduced.
-
The ‘renewable’ and ‘unlinkable’ characteristics are achieved through salting techniques. Salting adds randomly generated unique data known as ‘salt’ to the original information to make it distinct from the others.
-
Designing a biometric system accuracy with respect to both FAR and FRR.
-
Selecting a suitable encryption algorithm carefully. Some algorithms may amplify even small variations inherent in an individual’s biometric data, which can lead to higher FRR.
-
Using an important encryption technique such as hashing method, which is effective when a different permutation is applied with each template generation. Different permutations ensure the uniqueness of each template despite using the same input biometric data.
-
Employing an effective protection scheme to elevate the performance of the system.
已经在生物特征数据安全性与隐私方面做了大量的研发。
A lot of research and development is being done towards the security and privacy of biometric data.