Data Science 简明教程
Data Science - What is Data?
What is Data in Data Science?
数据是数据科学的基础。数据是对指定字符的系统记录、数量或符号,计算机对此执行操作,这些数据可以存储和传输。它是用于特定目的的数据汇编,例如调查或分析。当数据被结构化时,可以将该数据称为信息。数据源(原始数据、次要数据)也是需要考虑的重要因素。
Data is the foundation of data science. Data is the systematic record of a specified characters, quantity or symbols on which operations are performed by a computer, which may be stored and transmitted. It is a compilation of data to be utilised for a certain purpose, such as a survey or an analysis. When structured, data may be referred to as information. The data source (original data, secondary data) is also an essential consideration.
数据有许多形状和形式,但通常可以认为是某种随机实验的结果——一个无法预先确定结果,但其工作原理仍然受分析约束的实验。来自随机实验的数据通常存储在表格或电子表格中。用来表示变量的统计惯例通常称为特征或列,而将单个项目(或单位)称为行。
Data comes in many shapes and forms, but can generally be thought of as being the result of some random experiment - an experiment whose outcome cannot be determined in advance, but whose workings are still subject to analysis. Data from a random experiment are often stored in a table or spreadsheet. A statistical convention to denote variables is often called as features or columns and individual items (or units) as rows.
Types of Data
主要有两类数据,分别是:
There are mainly two types of data, they are −
Qualitative Data
定性数据由无法计算、量化或仅用数字表示的信息组成。它从文本、音频和图片中收集,并使用数据可视化工具进行分布,包括词云、概念图、图形数据库、时间线和信息图表。
Qualitative data consists of information that cannot be counted, quantified, or expressed simply using numbers. It is gathered from text, audio, and pictures and distributed using data visualization tools, including word clouds, concept maps, graph databases, timelines, and infographics.
定性数据分析的目标是回答有关个人活动和动机的问题。收集和分析此类数据可能需要花费很多时间。处理定性数据的研究员或分析师被称为定性研究员或分析师。
The objective of qualitative data analysis is to answer questions about the activities and motivations of individuals. Collecting, and analyzing this kind of data may be time-consuming. A researcher or analyst that works with qualitative data is referred to as a qualitative researcher or analyst.
定性数据可以为任何部门、用户群体或产品提供重要统计信息。
Qualitative data can give essential statistics for any sector, user group, or product.
Types of Qualitative Data
主要有两类定性数据,分别是:
There are mainly two types of Qualitative data, they are −
@[s0}
Nominal Data
在统计中,名义数据(也称为名义标度)用于指定变量,而不提供数值。它是基本测量标度的最基本类型。与序数数据相反,名义数据无法排序或量化。
In statistics, nominal data (also known as nominal scale) is used to designate variables without giving a numerical value. It is the most basic type of measuring scale. In contrast to ordinal data, nominal data cannot be ordered or quantified.
例如,一个人的姓名、头发颜色、国籍等。让我们假设一位名叫 Aby 的女孩头发是棕色的,她来自美国。
For example, The name of the person, the colour of the hair, nationality, etc. Let’s assume a girl named Aby her hair is brown and she is from America.
名义数据既可以是定性的,也可以是定量的。然而,定量标签(例如识别号)没有任何数值或链接与之关联。相反,可以以名义形式表达多个定性数据类别。这些可能包括单词、字母和符号。个人姓名、性别和国籍是最流行的名义数据实例。
Nominal data may be both qualitative and quantitative. Yet, there is no numerical value or link associated with the quantitative labels (e.g., identification number). In contrast, several qualitative data categories can be expressed in nominal form. These might consist of words, letters, and symbols. Names of individuals, gender, and nationality are some of the most prevalent instances of nominal data.
@[s1}
Analyze Nominal Data
可以使用分组方法分析名义数据。变量可以按组排序,并且可以确定每个类别的频率或百分比。此外还可以以图形方式显示数据,例如使用饼图。
Using the grouping approach, nominal data can be analyzed. The variables may be sorted into groups, and the frequency or percentage can be determined for each category. The data may also be shown graphically, for example using a pie chart.
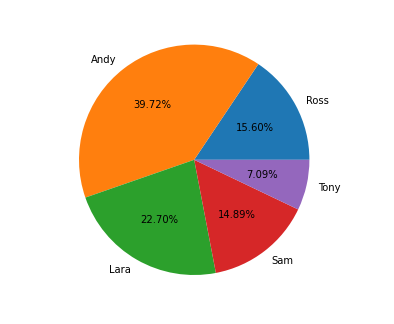
尽管名义数据不能使用数学运算符处理,但仍可以使用统计技术对其进行研究。假设检验是评估和分析数据的其中一种方法。
Although though nominal data cannot be processed using mathematical operators, they may still be studied using statistical techniques. Hypothesis testing is one approach to assess and analyse the data.
使用名义数据,可以使用卡方检验等非参数检验来检验假设。卡方检验的目的是评估给定值的预测频率和实际频率之间是否存在统计上显着的差异。
With nominal data, nonparametric tests such as the chi-squared test may be used to test hypotheses. The purpose of the chi-squared test is to evaluate whether there is a statistically significant discrepancy between the predicted frequency and the actual frequency of the provided values.
@[s2}
Ordinal Data
序数数据是统计数据中的一种数据类型,其中值按自然顺序排列。序数数据最重要的一点是,您无法区分数据值之间的差异。大多数情况下,数据类别的宽度与底层属性的增量不匹配。
Ordinal data is a type of data in statistics where the values are in a natural order. One of the most important things about ordinal data is that you can’t tell what the differences between the data values are. Most of the time, the width of the data categories doesn’t match the increments of the underlying attribute.
在某些情况下,可以通过对数据的值进行分组来找到间隔数据或比率数据的特征。例如,收入范围是序数数据,而实际收入是比率数据。
In some cases, the characteristics of interval or ratio data can be found by grouping the values of the data. For instance, the ranges of income are ordinal data, while the actual income is ratio data.
序数数据不能像间隔或比率数据一样使用数学运算符进行更改。因此,中位数是找出序数数据集中间位置的唯一方法。
Ordinal data can’t be changed with mathematical operators like interval or ratio data can. Because of this, the median is the only way to figure out where the middle of a set of ordinal data is.
此数据类型广泛存在于金融和经济领域。考虑一下一项研究各个国家 GDP 水平的经济研究。如果该报告根据各个国家的 GDP 对其进行评级,则排名就是序数统计数据。
This data type is widely found in the fields of finance and economics. Consider an economic study that examines the GDP levels of various nations. If the report rates the nations based on their GDP, the rankings are ordinal statistics.
@[s3}
Analyzing Ordinal Data
使用可视化工具评估有序数据是最简单的方法。例如,该数据可以显示为一个表格,其中每一行代表一个独立的类别。此外,它们可以使用不同的图表进行图形化表示。条形图是用来显示此类数据最流行的图形样式。
Using visualisation tools to evaluate ordinal data is the easiest method. For example, the data may be displayed as a table where each row represents a separate category. In addition, they may be represented graphically using different charts. The bar chart is the most popular style of graph used to display these types of data.
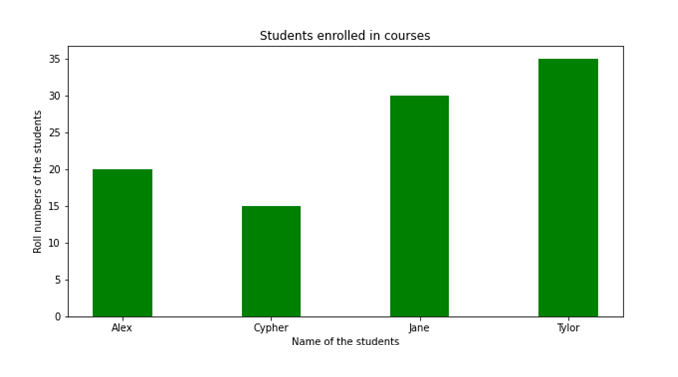
有序数据也可以使用假设检验等复杂的统计分析方法进行研究。需要注意的是,t 检验和 ANOVA 等参数化过程不能用于这些数据集。只有非参数检验(如曼惠特尼 U 检验或威尔科克森配对检验)可以用来评估关于数据的空假设。
Ordinal data may also be studied using sophisticated statistical analysis methods like hypothesis testing. Note that parametric procedures such as the t-test and ANOVA cannot be used to these data sets. Only nonparametric tests, such as the Mann-Whitney U test or Wilcoxon Matched-Pairs test, may be used to evaluate the null hypothesis about the data.
Qualitative Data Collection Methods
以下是一些收集定性数据的方法和收集方法——
Below are some approaches and collection methods to collect qualitative data −
-
Data Records − Utilizing data that is already existing as the data source is a best technique to do qualitative research. Similar to visiting a library, you may examine books and other reference materials to obtain data that can be utilised for research.
-
Interviews − Personal interviews are one of the most common ways to get deductive data for qualitative research. The interview may be casual and not have a set plan. It is often like a conversation. The interviewer or researcher gets the information straight from the interviewee.
-
Focus Groups − Focus groups are made up of 6 to 10 people who talk to each other. The moderator’s job is to keep an eye on the conversation and direct it based on the focus questions.
-
Case Studies − Case studies are in-depth analyses of an individual or group, with an emphasis on the relationship between developmental characteristics and the environment.
-
Observation − It is a technique where the researcher observes the object and take down transcript notes to find out innate responses and reactions without prompting.
Quantitative Data
定量数据由数值组成,具有数值特征,并且可以对这种类型的数据执行数学运算,例如加法。定量数据由于其定量特性而具有数学可验证性和可评估性。
Quantitative data consists of numerical values, has numerical features, and mathematical operations can be performed on this type of data such as addition. Quantitative data is mathematically verifiable and evaluable due to its quantitative character.
它们数学导出的简单性使得管理不同参数的测量成为可能。通常,它是通过授予人群一部分的问卷调查、民意调查或调查来收集的,用于统计分析。研究人员能够将收集到的研究结果应用于整个人群。
The simplicity of their mathematical derivations makes it possible to govern the measurement of different parameters. Typically, it is gathered for statistical analysis through surveys, polls, or questionnaires given to a subset of a population. Researchers are able to apply the collected findings to an entire population.
Types of Quantitative Data
定量数据主要有两种类型,它们是——
There are mainly two types of quantitative data, they are −
Discrete Data
Discrete Data
这些是只能采用特定值的数据,而不是范围。例如,有关人群血型或性别的信息被视为离散数据。
These are data that can only take on certain values, as opposed to a range. For instance, data about the blood type or gender of a population is considered discrete data.
离散定量数据的示例可能是您网站的访问者数量;一天可能有 150 次访问,但不可能有 150.6 次访问。通常,饼状图、条形图和饼图用于表示离散数据。
Example of discrete quantitative data may be the number of visitors to your website; you could have 150 visits in one day, but not 150.6 visits. Usually, tally charts, bar charts, and pie charts are used to represent discrete data.
Characteristics of Discrete Data
Characteristics of Discrete Data
由于总结和计算离散数据很简单,因此它通常用于基本的统计分析。让我们检查一下离散数据的一些其他基本特征——
Since it is simple to summarise and calculate discrete data, it is often utilized in elementary statistical analysis. Let’s examine some other essential characteristics of discrete data −
-
Discrete data is made up of discrete variables that are finite, measurable, countable, and can’t be negative (5, 10, 15, and so on).
-
Simple statistical methods, like bar charts, line charts, and pie charts, make it easy to show and explain discrete data.
-
Data can also be categorical, which means it has a fixed number of data values, like a person’s gender.
-
Data that is both time- and space-bound is spread out in a random way. Discrete distributions make it easier to look at discrete values.
Continuous Data
这些数据可能在一定范围内取值,包括最大值和最小值。最大值和最小值之间的差称为数据范围。例如,你学校学生的身高和体重。这被认为是连续数据。连续数据的表格表示称为频数分布。这些可以利用直方图直观地描述。
These are data that may take values between a certain range, including the greatest and lowest possible. The difference between the greatest and least value is known as the data range. For instance, the height and weight of your school’s children. This is considered continuous data. The tabular representation of continuous data is known as a frequency distribution. These may be depicted visually using histograms.
Characteristics of continuous data
Characteristics of continuous data
另一方面,连续数据可以是数字,或者随时间和日期变化。由于可能的值是无限的,所以此数据类型使用高级的统计分析方法。连续数据的以下重要特征 −
Continuous data, on the other hand, can be either numbers or spread out over time and date. This data type uses advanced statistical analysis methods because there are an infinite number of possible values. The important characteristics about continuous data are −
-
Continuous data changes over time, and at different points in time, it can have different values.
-
Random variables, which may or may not be whole numbers, make up continuous data.
-
Data analysis tools like line graphs, skews, and so on are used to measure continuous data.
-
One type of continuous data analysis that is often used is regression analysis.
Quantitative Data Collection Methods
下面是一些用于收集定量数据的方法和采集方法 −
Below are some approaches and collection methods to collect quantitative data −
-
Surveys and Questionnaires − These types of research are good for getting detailed feedback from users and customers, especially about how people feel about a product, service, or experience.
-
Open-source Datasets − There are a lot of public datasets that can be found online and analysed for free. Researchers sometimes look at data that has already been collected and try to figure out what it means in a way that fits their own research project.
-
Experiments − A common method is an experiment, which usually has a control group and an experimental group. The experiment is set up so that it can be controlled and the conditions can be changed as needed.
-
Sampling − When there are a lot of data points, it may not be possible to survey each person or data point. In this case, quantitative research is done with the help of sampling. Sampling is the process of choosing a sample of data that is representative of the whole. The two types of sampling are Random sampling (also called probability sampling), and non-random sampling.
Types of Data Collection
根据来源,数据收集可以分为两类 −
Data collection can be classified into two types according to the source −
-
Primary Data − These are the data that are acquired for the first time for a particular purpose by an investigator. Primary data are 'pure' in the sense that they have not been subjected to any statistical manipulations and are authentic. Examples of primary data include the Census of India.
-
Secondary Data − These are the data that were initially gathered by a certain entity. This indicates that this kind of data has already been gathered by researchers or investigators and is accessible in either published or unpublished form. This data is impure because statistical computations may have previously been performed on it. For example, Information accessible on the website of the Government of India or the Department of Finance, or in other archives, books, journals, etc.
Big Data
大数据被定义为具有更大数据量的数据,需要克服后勤方面的挑战来处理它们。大数据指的是更大、更复杂的数据集合,特别是来自新型数据源的数据。一些数据集非常庞大,以至于传统的的数据处理软件无法处理它们。然而,这些海量数据可以用来解决以前无法解决的业务难题。
Big data is defined as data with a larger volume and require overcoming logistical challenges to deal with them. Big data refers to bigger, more complicated data collections, particularly from novel data sources. Some data sets are so extensive that conventional data processing software is incapable of handling them. But, these vast quantities of data can be use to solve business challenges that were previously unsolvable.
数据科学是关于如何分析巨量数据并从中获取信息的研究。你可以将大数据和数据科学比作原油和炼油厂。数据科学和大数据源于统计学和传统的数据管理方式,但现在被视为独立的领域。
Data Science is the study of how to analyse huge amount of data and get the information from them. You can compare big data and data science to crude oil and an oil refinery. Data Science and big data grew out of statistics and traditional ways of managing data, but they are now seen as separate fields.
人们常常使用三个 V 来描述大数据的特性 −
People often use the three Vs to describe the characteristics of big data −
-
Volume − How much information is there?
-
Variety − How different are the different kinds of data?
-
Velocity − How fast do new pieces of information get made?
How do we use Data in Data Science?
每条数据都必须经过预处理。这是一系列将原始数据转换为更易理解且有价值的格式以供进一步处理的基本流程。常见流程为−
Every data must undergo pre-processing. This is an essential series of processes that converts raw data into a more comprehensible and valuable format for further processing. Common procedures are −
-
Collect and Store the Dataset
-
Data Cleaning
-
Data Integration
-
Data Transformation
我们将在接下来的章节中详细讨论这些流程。
We will discuss these processes in detail in upcoming chapters.