Mongodb 简明教程
MongoDB - Overview
MongoDB 是一个跨平台文档导向数据库,它提供高性能、高可用性和简单可扩展性。MongoDB 在集合和文档的概念上工作。
MongoDB is a cross-platform, document oriented database that provides, high performance, high availability, and easy scalability. MongoDB works on concept of collection and document.
Database
数据库是集合的物理容器。每个数据库都会在文件系统上获取自己的一组文件。单个 MongoDB 服务器通常具有多个数据库。
Database is a physical container for collections. Each database gets its own set of files on the file system. A single MongoDB server typically has multiple databases.
Collection
集合是一组 MongoDB 文档。它相当于 RDBMS 表。集合存在于单个数据库中。集合不强制执行模式。集合中的文档可以有不同的字段。通常,集合中的所有文档都具有相似或相关用途。
Collection is a group of MongoDB documents. It is the equivalent of an RDBMS table. A collection exists within a single database. Collections do not enforce a schema. Documents within a collection can have different fields. Typically, all documents in a collection are of similar or related purpose.
Document
文档是一组键值对。文档具有动态模式。动态模式意味着同一集合中的文档不必具有相同的字段集或结构,并且集合文档中的常见字段可能保存不同类型的数据。
A document is a set of key-value pairs. Documents have dynamic schema. Dynamic schema means that documents in the same collection do not need to have the same set of fields or structure, and common fields in a collection’s documents may hold different types of data.
下表显示了 RDBMS 术语与 MongoDB 之间的关系。
The following table shows the relationship of RDBMS terminology with MongoDB.
RDBMS |
MongoDB |
Database |
Database |
Table |
Collection |
Tuple/Row |
Document |
column |
Field |
Table Join |
Embedded Documents |
Primary Key |
Primary Key (Default key _id provided by mongodb itself) |
Database Server and Client |
Mysqld/Oracle |
mongod |
mysql/sqlplus |
Sample Document
以下示例显示了博客网站的文档结构,它只是一个逗号分隔的键值对。
Following example shows the document structure of a blog site, which is simply a comma separated key value pair.
{
_id: ObjectId(7df78ad8902c)
title: 'MongoDB Overview',
description: 'MongoDB is no sql database',
by: 'tutorials point',
url: 'http://www.tutorialspoint.com',
tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'],
likes: 100,
comments: [
{
user:'user1',
message: 'My first comment',
dateCreated: new Date(2011,1,20,2,15),
like: 0
},
{
user:'user2',
message: 'My second comments',
dateCreated: new Date(2011,1,25,7,45),
like: 5
}
]
}_id 是一个 12 字节十六进制数字,可确保每份文档的唯一性。你可以在插入文档时提供 _id。如果你不提供,则 MongoDB 会为每份文档提供一个唯一 ID。这 12 个字节的前 4 个字节用于当前时间戳,接下来的 3 个字节用于机器 ID,接下来的 2 个字节用于 MongoDB 服务器的进程 ID,其余 3 个字节是简单的增量 VALUE。
_id is a 12 bytes hexadecimal number which assures the uniqueness of every document. You can provide _id while inserting the document. If you don’t provide then MongoDB provides a unique id for every document. These 12 bytes first 4 bytes for the current timestamp, next 3 bytes for machine id, next 2 bytes for process id of MongoDB server and remaining 3 bytes are simple incremental VALUE.
MongoDB - Advantages
任何关系数据库中都有一个典型的架构设计,用于显示表格数量以及这些表格之间的关系。而在 MongoDB 中,关系的概念不存在。
Any relational database has a typical schema design that shows number of tables and the relationship between these tables. While in MongoDB, there is no concept of relationship.
Advantages of MongoDB over RDBMS
-
Schema less − MongoDB is a document database in which one collection holds different documents. Number of fields, content and size of the document can differ from one document to another.
-
Structure of a single object is clear.
-
No complex joins.
-
Deep query-ability. MongoDB supports dynamic queries on documents using a document-based query language that’s nearly as powerful as SQL.
-
Tuning.
-
Ease of scale-out − MongoDB is easy to scale.
-
Conversion/mapping of application objects to database objects not needed.
-
Uses internal memory for storing the (windowed) working set, enabling faster access of data.
MongoDB - Environment
现在让我们看一下如何在 Windows 上安装 MongoDB。
Let us now see how to install MongoDB on Windows.
Install MongoDB On Windows
要在 Windows 上安装 MongoDB,首先从 https://www.mongodb.org/downloads 下载 MongoDB 的最新版本。务必根据您的 Windows 版本获取正确的 MongoDB 版本。要获取您的 Windows 版本,请打开命令提示符并执行以下命令。
To install MongoDB on Windows, first download the latest release of MongoDB from https://www.mongodb.org/downloads. Make sure you get correct version of MongoDB depending upon your Windows version. To get your Windows version, open command prompt and execute the following command.
C:\>wmic os get osarchitecture
OSArchitecture
64-bit
C:\>32 位版本的 MongoDB 仅支持小于 2GB 的数据库,并且仅适用于测试和评估目的。
32-bit versions of MongoDB only support databases smaller than 2GB and suitable only for testing and evaluation purposes.
现在将下载的文件解压到 c:\ 驱动器或任何其他位置。请确保解压后的文件夹名称为 mongodb-win32-i386-[版本] 或 mongodb-win32-x86_64-[版本]。这里 [版本] 是 MongoDB 下载的版本。
Now extract your downloaded file to c:\ drive or any other location. Make sure the name of the extracted folder is mongodb-win32-i386-[version] or mongodb-win32-x86_64-[version]. Here [version] is the version of MongoDB download.
接下来,打开命令提示符并运行以下命令。
Next, open the command prompt and run the following command.
C:\>move mongodb-win64-* mongodb
1 dir(s) moved.
C:\>如果您在不同的位置解压了 MongoDB,则使用命令 cd FOLDER/DIR 转到该路径,然后运行上述给定的过程。
In case you have extracted the MongoDB at different location, then go to that path by using command cd FOLDER/DIR and now run the above given process.
MongoDB 需要一个数据文件夹来存储其文件。MongoDB 数据目录的默认位置是 c:\data\db。因此,你需要使用命令提示符创建此文件夹,执行以下命令序列。
MongoDB requires a data folder to store its files. The default location for the MongoDB data directory is c:\data\db. So you need to create this folder using the Command Prompt. Execute the following command sequence.
C:\>md data
C:\md data\db如果您必须在不同位置安装 MongoDB,则需要通过在 mongod.exe 中设置路径 dbpath 来为 \data\db 指定备用路径。为此,发出以下命令。
If you have to install the MongoDB at a different location, then you need to specify an alternate path for \data\db by setting the path dbpath in mongod.exe. For the same, issue the following commands.
在命令提示符中,导航到 MongoDB 安装文件夹中存在的 bin 目录。假设我的安装文件夹是 D:\set up\mongodb
In the command prompt, navigate to the bin directory present in the MongoDB installation folder. Suppose my installation folder is D:\set up\mongodb
C:\Users\XYZ>d:
D:\>cd "set up"
D:\set up>cd mongodb
D:\set up\mongodb>cd bin
D:\set up\mongodb\bin>mongod.exe --dbpath "d:\set up\mongodb\data"这将在控制台输出上显示 waiting for connections 消息,表明 mongod.exe 进程正在成功运行。
This will show waiting for connections message on the console output, which indicates that the mongod.exe process is running successfully.
现在,要运行 MongoDB,你需要打开另一个命令提示符并发出以下命令。
Now to run the MongoDB, you need to open another command prompt and issue the following command.
D:\set up\mongodb\bin>mongo.exe
MongoDB shell version: 2.4.6
connecting to: test
>db.test.save( { a: 1 } )
>db.test.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5879b0f65a56a454), "a" : 1 }
>这将显示 MongoDB 已安装且运行成功。下次运行 MongoDB 时,你需要只发出命令即可。
This will show that MongoDB is installed and run successfully. Next time when you run MongoDB, you need to issue only commands.
D:\set up\mongodb\bin>mongod.exe --dbpath "d:\set up\mongodb\data"
D:\set up\mongodb\bin>mongo.exeInstall MongoDB on Ubuntu
运行以下命令以导入 MongoDB 公共 GPG 密钥 −
Run the following command to import the MongoDB public GPG key −
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 7F0CEB10使用以下命令创建 /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb.list 文件。
Create a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb.list file using the following command.
echo 'deb http://downloads-distro.mongodb.org/repo/ubuntu-upstart dist 10gen'
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb.list现在发出以下命令以更新存储库 −
Now issue the following command to update the repository −
sudo apt-get update接下来,使用以下命令安装 MongoDB −
Next install the MongoDB by using the following command −
apt-get install mongodb-10gen = 2.2.3在以上安装中,2.2.3 是当前发布的 MongoDB 版本。确保始终安装最新版本。现在,MongoDB 已成功安装。
In the above installation, 2.2.3 is currently released MongoDB version. Make sure to install the latest version always. Now MongoDB is installed successfully.
Restart MongoDB
sudo service mongodb restart要使用 MongoDB,请运行以下命令。
To use MongoDB run the following command.
mongo这会将你连接到正在运行的 MongoDB 实例。
This will connect you to running MongoDB instance.
MongoDB Help
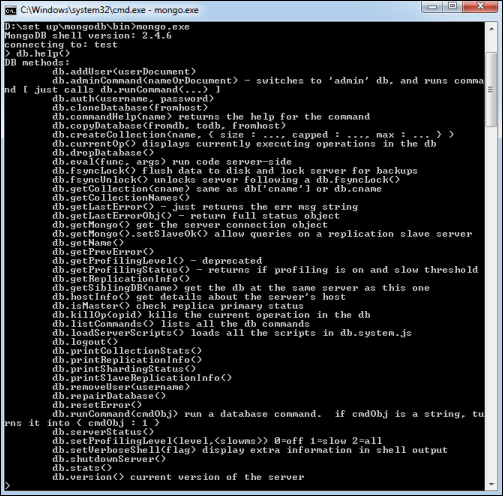
要获取命令列表,请在 MongoDB 客户端中输入 db.help() 。这会给你一个命令列表,如下面的屏幕截图所示。
To get a list of commands, type db.help() in MongoDB client. This will give you a list of commands as shown in the following screenshot.
MongoDB Statistics
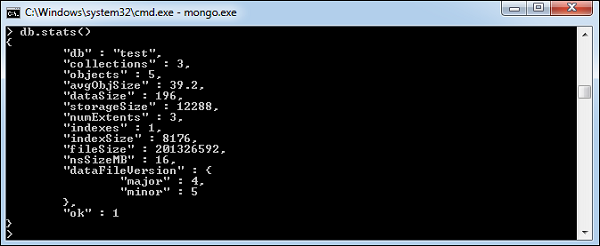
要获取有关 MongoDB 服务器的统计信息,请在 MongoDB 客户端中输入命令 db.stats() 。这会显示数据库名称、集合数量和数据库中的文档。命令的输出显示在下面的屏幕截图中。
To get stats about MongoDB server, type the command db.stats() in MongoDB client. This will show the database name, number of collection and documents in the database. Output of the command is shown in the following screenshot.
MongoDB - Data Modelling
MongoDB 中的数据具有灵活的模式。同一集合中的文档。它们不必具有相同的字段或结构集,并且集合中的普通字段可能包含不同类型的数据。
Data in MongoDB has a flexible schema.documents in the same collection. They do not need to have the same set of fields or structure, and common fields in a collection’s documents may hold different types of data.
Some considerations while designing Schema in MongoDB
-
Design your schema according to user requirements.
-
Combine objects into one document if you will use them together. Otherwise separate them (but make sure there should not be need of joins).
-
Duplicate the data (but limited) because disk space is cheap as compare to compute time.
-
Do joins while write, not on read.
-
Optimize your schema for most frequent use cases.
-
Do complex aggregation in the schema.
Example
假设一个客户需要一个数据库设计,用于他的博客/网站,并查看 RDBMS 和 MongoDB 架构设计之间的区别。该网站有以下要求。
Suppose a client needs a database design for his blog/website and see the differences between RDBMS and MongoDB schema design. Website has the following requirements.
-
Every post has the unique title, description and url.
-
Every post can have one or more tags.
-
Every post has the name of its publisher and total number of likes.
-
Every post has comments given by users along with their name, message, data-time and likes.
-
On each post, there can be zero or more comments.
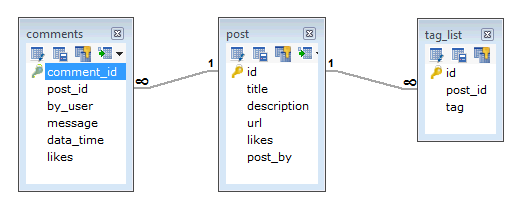
在 RDBMS 架构中,上述要求的设计将至少有三个表。
In RDBMS schema, design for above requirements will have minimum three tables.
而在 MongoDB 架构中,设计将有一个集合类和以下结构 −
While in MongoDB schema, design will have one collection post and the following structure −
{
_id: POST_ID
title: TITLE_OF_POST,
description: POST_DESCRIPTION,
by: POST_BY,
url: URL_OF_POST,
tags: [TAG1, TAG2, TAG3],
likes: TOTAL_LIKES,
comments: [
{
user:'COMMENT_BY',
message: TEXT,
dateCreated: DATE_TIME,
like: LIKES
},
{
user:'COMMENT_BY',
message: TEXT,
dateCreated: DATE_TIME,
like: LIKES
}
]
}因此在显示数据时,在 RDBMS 中你需要连接三个表,而在 MongoDB 中,数据只将从一个集合中显示。
So while showing the data, in RDBMS you need to join three tables and in MongoDB, data will be shown from one collection only.
MongoDB - Create Database
在本章中,我们将看到如何在 MongoDB 中创建一个数据库。
In this chapter, we will see how to create a database in MongoDB.
The use Command
MongoDB use DATABASE_NAME 用于创建数据库。如果数据库不存在,该命令将创建一个新数据库,否则将返回现有数据库。
MongoDB use DATABASE_NAME is used to create database. The command will create a new database if it doesn’t exist, otherwise it will return the existing database.
Example
如果您想使用名为 <mydb> 的数据库,则 use DATABASE 语句如下 −
If you want to use a database with name <mydb>, then use DATABASE statement would be as follows −
>use mydb
switched to db mydb要检查您当前选择的数据库,请使用命令 db
To check your currently selected database, use the command db
>db
mydb如果您想查看数据库列表,请使用命令 show dbs 。
If you want to check your databases list, use the command show dbs.
>show dbs
local 0.78125GB
test 0.23012GB您创建的数据库 (mydb) 不存在列表中。要显示数据库,您需要向其中至少插入一个文档。
Your created database (mydb) is not present in list. To display database, you need to insert at least one document into it.
>db.movie.insert({"name":"tutorials point"})
>show dbs
local 0.78125GB
mydb 0.23012GB
test 0.23012GB在 MongoDB 中,默认数据库为 test。如果您未创建任何数据库,则集合将存储在 test 数据库中。
In MongoDB default database is test. If you didn’t create any database, then collections will be stored in test database.
MongoDB - Drop Database
在本章中,我们将看到如何使用 MongoDB 命令删除数据库。
In this chapter, we will see how to drop a database using MongoDB command.
The dropDatabase() Method
MongoDB db.dropDatabase() 命令用于删除现有数据库。
MongoDB db.dropDatabase() command is used to drop a existing database.
Syntax
dropDatabase() 命令的基本语法如下 −
Basic syntax of dropDatabase() command is as follows −
db.dropDatabase()这会删除所选的数据库。如果你没有选定任何数据库,那么它会删除默认的「test」数据库。
This will delete the selected database. If you have not selected any database, then it will delete default 'test' database.
Example
首先,通过使用命令检查可用数据库的列表, show dbs 。
First, check the list of available databases by using the command, show dbs.
>show dbs
local 0.78125GB
mydb 0.23012GB
test 0.23012GB
>如果你想删除新数据库 <mydb> ,那么 dropDatabase() 命令如下 −
If you want to delete new database <mydb>, then dropDatabase() command would be as follows −
>use mydb
switched to db mydb
>db.dropDatabase()
>{ "dropped" : "mydb", "ok" : 1 }
>现在检查数据库列表。
Now check list of databases.
>show dbs
local 0.78125GB
test 0.23012GB
>MongoDB - Create Collection
在本章中,我们将介绍如何使用 MongoDB 创建集合。
In this chapter, we will see how to create a collection using MongoDB.
The createCollection() Method
MongoDB db.createCollection(name, options) 用于创建集合。
MongoDB db.createCollection(name, options) is used to create collection.
Syntax
createCollection() 命令的基本语法如下:
Basic syntax of createCollection() command is as follows −
db.createCollection(name, options)在命令中, name 是要创建的集合的名称。 Options 是一个文档,用于指定集合的配置。
In the command, name is name of collection to be created. Options is a document and is used to specify configuration of collection.
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
Name |
String |
Name of the collection to be created |
Options |
Document |
(Optional) Specify options about memory size and indexing |
“选项”参数是可选的,因此您只需要指定集合的名称。以下是您可以使用的选项列表:
Options parameter is optional, so you need to specify only the name of the collection. Following is the list of options you can use −
Field |
Type |
Description |
capped |
Boolean |
(Optional) If true, enables a capped collection. Capped collection is a fixed size collection that automatically overwrites its oldest entries when it reaches its maximum size. If you specify true, you need to specify size parameter also. |
autoIndexId |
Boolean |
(Optional) If true, automatically create index on _id field.s Default value is false. |
size |
number |
(Optional) Specifies a maximum size in bytes for a capped collection. If capped is true, then you need to specify this field also. |
max |
number |
(Optional) Specifies the maximum number of documents allowed in the capped collection. |
在插入文档时,MongoDB 首先会检查带上限的集合的 size 域,然后检查 max 域。
While inserting the document, MongoDB first checks size field of capped collection, then it checks max field.
Examples
createCollection() 方法基本语法(无选项):
Basic syntax of createCollection() method without options is as follows −
>use test
switched to db test
>db.createCollection("mycollection")
{ "ok" : 1 }
>您可以使用命令 show collections 检查创建的集合。
You can check the created collection by using the command show collections.
>show collections
mycollection
system.indexes以下示例显示 createCollection() 方法的语法,包括几个重要选项 −
The following example shows the syntax of createCollection() method with few important options −
>db.createCollection("mycol", { capped : true, autoIndexId : true, size :
6142800, max : 10000 } )
{ "ok" : 1 }
>在 MongoDB 中,您无需创建集合。当您插入某个文档时,MongoDB 会自动创建集合。
In MongoDB, you don’t need to create collection. MongoDB creates collection automatically, when you insert some document.
>db.tutorialspoint.insert({"name" : "tutorialspoint"})
>show collections
mycol
mycollection
system.indexes
tutorialspoint
>MongoDB - Drop Collection
在本章中,我们将看到如何通过 MongoDB 删除集合。
In this chapter, we will see how to drop a collection using MongoDB.
The drop() Method
MongoDB 的 db.collection.drop() 用于从数据库删除集合。
MongoDB’s db.collection.drop() is used to drop a collection from the database.
Example
首先,检查你数据库中可用的集合 mydb 。
First, check the available collections into your database mydb.
>use mydb
switched to db mydb
>show collections
mycol
mycollection
system.indexes
tutorialspoint
>现在删除具有名称 mycollection 的集合。
Now drop the collection with the name mycollection.
>db.mycollection.drop()
true
>再次检查数据库中的集合列表。
Again check the list of collections into database.
>show collections
mycol
system.indexes
tutorialspoint
>drop() 方法将返回 true,如果所选的集合已成功删除,否则它将返回 false。
drop() method will return true, if the selected collection is dropped successfully, otherwise it will return false.
MongoDB - Datatypes
MongoDB 支持多种数据类型。其中一些是: −
MongoDB supports many datatypes. Some of them are −
-
String − This is the most commonly used datatype to store the data. String in MongoDB must be UTF-8 valid.
-
Integer − This type is used to store a numerical value. Integer can be 32 bit or 64 bit depending upon your server.
-
Boolean − This type is used to store a boolean (true/ false) value.
-
Double − This type is used to store floating point values.
-
Min/ Max keys − This type is used to compare a value against the lowest and highest BSON elements.
-
Arrays − This type is used to store arrays or list or multiple values into one key.
-
Timestamp − ctimestamp. This can be handy for recording when a document has been modified or added.
-
Object − This datatype is used for embedded documents.
-
Null − This type is used to store a Null value.
-
Symbol − This datatype is used identically to a string; however, it’s generally reserved for languages that use a specific symbol type.
-
*Date * − This datatype is used to store the current date or time in UNIX time format. You can specify your own date time by creating object of Date and passing day, month, year into it.
-
Object ID − This datatype is used to store the document’s ID.
-
Binary data − This datatype is used to store binary data.
-
Code − This datatype is used to store JavaScript code into the document.
-
Regular expression − This datatype is used to store regular expression.
MongoDB - Insert Document
在本教程中,我们将学习如何将文档插入到 MongoDB 集合中。
In this chapter, we will learn how to insert document in MongoDB collection.
The insert() Method
要将数据插入到 MongoDB 集合中,需要使用 MongoDB 的 insert() 或 save() 方法。
To insert data into MongoDB collection, you need to use MongoDB’s insert() or save() method.
Syntax
insert() 命令的基本语法如下:
The basic syntax of insert() command is as follows −
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.insert(document)Example
>db.mycol.insert({
_id: ObjectId(7df78ad8902c),
title: 'MongoDB Overview',
description: 'MongoDB is no sql database',
by: 'tutorials point',
url: 'http://www.tutorialspoint.com',
tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'],
likes: 100
})此处的 mycol 名称是我们在前一章中创建的集合名称。如果集合在数据库中不存在,则 MongoDB 将创建该集合,然后向其中插入文档。
Here mycol is our collection name, as created in the previous chapter. If the collection doesn’t exist in the database, then MongoDB will create this collection and then insert a document into it.
在已插入的文档中,如果我们不指定 _id 参数,则 MongoDB 将为该文档分配一个唯一的 ObjectId。
In the inserted document, if we don’t specify the _id parameter, then MongoDB assigns a unique ObjectId for this document.
_id 是 12 字节十六进制数字,对集合中的每个文档都是唯一的。12 字节的划分如下:
_id is 12 bytes hexadecimal number unique for every document in a collection. 12 bytes are divided as follows −
_id: ObjectId(4 bytes timestamp, 3 bytes machine id, 2 bytes process id,
3 bytes incrementer)要在单个查询中插入多个文档,你可以在 insert() 命令中传递文档的数组。
To insert multiple documents in a single query, you can pass an array of documents in insert() command.
Example
>db.post.insert([
{
title: 'MongoDB Overview',
description: 'MongoDB is no sql database',
by: 'tutorials point',
url: 'http://www.tutorialspoint.com',
tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'],
likes: 100
},
{
title: 'NoSQL Database',
description: "NoSQL database doesn't have tables",
by: 'tutorials point',
url: 'http://www.tutorialspoint.com',
tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'],
likes: 20,
comments: [
{
user:'user1',
message: 'My first comment',
dateCreated: new Date(2013,11,10,2,35),
like: 0
}
]
}
])要插入该文档,您也可以使用 db.post.save(document) 。如果您未在文档中指定 _id ,则 save() 方法将与 insert() 方法相同。如果您指定 _id,它将替换包含 _id 的文档的所有数据,如 save() 方法中所指定的那样。
To insert the document you can use db.post.save(document) also. If you don’t specify _id in the document then save() method will work same as insert() method. If you specify _id then it will replace whole data of document containing _id as specified in save() method.
MongoDB - Query Document
在本章中,我们将学习如何从 MongoDB 集合查询文档。
In this chapter, we will learn how to query document from MongoDB collection.
The find() Method
要从 MongoDB 集合中查询数据,你需要使用 MongoDB 的 find() 方法。
To query data from MongoDB collection, you need to use MongoDB’s find() method.
The pretty() Method
要以格式化的方式显示结果,可以使用 pretty() 方法。
To display the results in a formatted way, you can use pretty() method.
Example
>db.mycol.find().pretty()
{
"_id": ObjectId(7df78ad8902c),
"title": "MongoDB Overview",
"description": "MongoDB is no sql database",
"by": "tutorials point",
"url": "http://www.tutorialspoint.com",
"tags": ["mongodb", "database", "NoSQL"],
"likes": "100"
}
>除了 find() 方法外,还有 findOne() 方法,它只返回一个文档。
Apart from find() method, there is findOne() method, that returns only one document.
RDBMS Where Clause Equivalents in MongoDB
要根据某个条件查询文档,可以使用以下操作。
To query the document on the basis of some condition, you can use following operations.
Operation |
Syntax |
Example |
RDBMS Equivalent |
Equality |
{<key>:<value>} |
db.mycol.find({"by":"tutorials point"}).pretty() |
where by = 'tutorials point' |
Less Than |
{<key>:{$lt:<value>}} |
db.mycol.find({"likes":{$lt:50}}).pretty() |
where likes < 50 |
Less Than Equals |
{<key>:{$lte:<value>}} |
db.mycol.find({"likes":{$lte:50}}).pretty() |
where likes ⇐ 50 |
Greater Than |
{<key>:{$gt:<value>}} |
db.mycol.find({"likes":{$gt:50}}).pretty() |
where likes > 50 |
Greater Than Equals |
{<key>:{$gte:<value>}} |
db.mycol.find({"likes":{$gte:50}}).pretty() |
where likes >= 50 |
Not Equals |
{<key>:{$ne:<value>}} |
db.mycol.find({"likes":{$ne:50}}).pretty() |
where likes != 50 |
AND in MongoDB
Syntax
在 find() 方法中,如果你通过用逗号分隔的方式传递多个键,那么 MongoDB 将其视为 AND 条件。以下是 AND 的基本语法 −
In the find() method, if you pass multiple keys by separating them by ',' then MongoDB treats it as AND condition. Following is the basic syntax of AND −
>db.mycol.find(
{
$and: [
{key1: value1}, {key2:value2}
]
}
).pretty()Example
以下示例将显示所有由“教程点”编写的教程,其标题为“MongoDB 概述”。
Following example will show all the tutorials written by 'tutorials point' and whose title is 'MongoDB Overview'.
>db.mycol.find({$and:[{"by":"tutorials point"},{"title": "MongoDB Overview"}]}).pretty() {
"_id": ObjectId(7df78ad8902c),
"title": "MongoDB Overview",
"description": "MongoDB is no sql database",
"by": "tutorials point",
"url": "http://www.tutorialspoint.com",
"tags": ["mongodb", "database", "NoSQL"],
"likes": "100"
}对于给出的示例,等效的 where 子句将是 ' where by = 'tutorials point' AND title = 'MongoDB Overview' ' 。您可以在 find 子句中传递任意数量的键值对。
For the above given example, equivalent where clause will be ' where by = 'tutorials point' AND title = 'MongoDB Overview' '. You can pass any number of key, value pairs in find clause.
OR in MongoDB
Syntax
要基于 OR 条件查询文档,您需要使用 $or 关键字。以下是 OR 的基本语法 −
To query documents based on the OR condition, you need to use $or keyword. Following is the basic syntax of OR −
>db.mycol.find(
{
$or: [
{key1: value1}, {key2:value2}
]
}
).pretty()Example
以下示例将显示所有由“教程点”编写的教程,或其标题为“MongoDB 概述”的教程。
Following example will show all the tutorials written by 'tutorials point' or whose title is 'MongoDB Overview'.
>db.mycol.find({$or:[{"by":"tutorials point"},{"title": "MongoDB Overview"}]}).pretty()
{
"_id": ObjectId(7df78ad8902c),
"title": "MongoDB Overview",
"description": "MongoDB is no sql database",
"by": "tutorials point",
"url": "http://www.tutorialspoint.com",
"tags": ["mongodb", "database", "NoSQL"],
"likes": "100"
}
>Using AND and OR Together
Example
以下示例将显示喜欢次数大于 10,且其标题为“MongoDB 概述”或作者为“教程点”的文档。等效的 SQL where 子句是 'where likes>10 AND (by = 'tutorials point' OR title = 'MongoDB Overview')'
The following example will show the documents that have likes greater than 10 and whose title is either 'MongoDB Overview' or by is 'tutorials point'. Equivalent SQL where clause is 'where likes>10 AND (by = 'tutorials point' OR title = 'MongoDB Overview')'
>db.mycol.find({"likes": {$gt:10}, $or: [{"by": "tutorials point"},
{"title": "MongoDB Overview"}]}).pretty()
{
"_id": ObjectId(7df78ad8902c),
"title": "MongoDB Overview",
"description": "MongoDB is no sql database",
"by": "tutorials point",
"url": "http://www.tutorialspoint.com",
"tags": ["mongodb", "database", "NoSQL"],
"likes": "100"
}
>MongoDB - Update Document
MongoDB 的 update() 和 save() 方法用于更新集合中的文档。update() 方法更新现有文档中的值,而 save() 方法用 save() 方法传递的文档替换现有文档。
MongoDB’s update() and save() methods are used to update document into a collection. The update() method updates the values in the existing document while the save() method replaces the existing document with the document passed in save() method.
MongoDB Update() Method
update() 方法更新现有文档中的值。
The update() method updates the values in the existing document.
Syntax
update() 方法的基本语法如下:
The basic syntax of update() method is as follows −
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.update(SELECTION_CRITERIA, UPDATED_DATA)Example
考虑 mycol 集合具有以下数据。
Consider the mycol collection has the following data.
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec5), "title":"MongoDB Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec6), "title":"NoSQL Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec7), "title":"Tutorials Point Overview"}以下示例将设置标题为“MongoDB 概述”的文档的新标题“新 MongoDB 教程”。
Following example will set the new title 'New MongoDB Tutorial' of the documents whose title is 'MongoDB Overview'.
>db.mycol.update({'title':'MongoDB Overview'},{$set:{'title':'New MongoDB Tutorial'}})
>db.mycol.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec5), "title":"New MongoDB Tutorial"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec6), "title":"NoSQL Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec7), "title":"Tutorials Point Overview"}
>默认情况下,MongoDB 将仅更新单个文档。要更新多个文档,你需要将参数“multi”设置为 true。
By default, MongoDB will update only a single document. To update multiple documents, you need to set a parameter 'multi' to true.
>db.mycol.update({'title':'MongoDB Overview'},
{$set:{'title':'New MongoDB Tutorial'}},{multi:true})MongoDB Save() Method
save() 方法用 save() 方法中传递的新文档替换现有文档。
The save() method replaces the existing document with the new document passed in the save() method.
Syntax
MongoDB save() 方法的基本语法如下所示:
The basic syntax of MongoDB save() method is shown below −
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.save({_id:ObjectId(),NEW_DATA})Example
以下示例将用 _id“5983548781331adf45ec5”替换文档。
Following example will replace the document with the _id '5983548781331adf45ec5'.
>db.mycol.save(
{
"_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec5), "title":"Tutorials Point New Topic",
"by":"Tutorials Point"
}
)
>db.mycol.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec5), "title":"Tutorials Point New Topic",
"by":"Tutorials Point"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec6), "title":"NoSQL Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec7), "title":"Tutorials Point Overview"}
>MongoDB - Delete Document
在本章中,我们将了解如何通过 MongoDB 删除文档。
In this chapter, we will learn how to delete a document using MongoDB.
The remove() Method
MongoDB 的 remove() 方法用于从集合中移除文档。remove() 方法接受两个参数。一个是删除条件,第二个是 justOne 标志。
MongoDB’s remove() method is used to remove a document from the collection. remove() method accepts two parameters. One is deletion criteria and second is justOne flag.
-
deletion criteria − (Optional) deletion criteria according to documents will be removed.
-
justOne − (Optional) if set to true or 1, then remove only one document.
Syntax
remove() 方法的基本语法如下 -
Basic syntax of remove() method is as follows −
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.remove(DELLETION_CRITTERIA)Example
考虑 mycol 集合具有以下数据。
Consider the mycol collection has the following data.
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec5), "title":"MongoDB Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec6), "title":"NoSQL Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec7), "title":"Tutorials Point Overview"}以下示例将移除所有标题为“MongoDB Overview” 的文档。
Following example will remove all the documents whose title is 'MongoDB Overview'.
>db.mycol.remove({'title':'MongoDB Overview'})
>db.mycol.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec6), "title":"NoSQL Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec7), "title":"Tutorials Point Overview"}
>MongoDB - Projection
在 MongoDB 中,投影是指仅选择必要的数据,而不选择文档的全部数据。如果某个文档有 5 个字段,并且你只需要显示 3 个,那么只从中选择 3 个字段即可。
In MongoDB, projection means selecting only the necessary data rather than selecting whole of the data of a document. If a document has 5 fields and you need to show only 3, then select only 3 fields from them.
The find() Method
MongoDB 的 find() 方法(在 MongoDB Query Document 中进行了说明)接受第二个可选参数,即希望检索的字段列表。在 MongoDB 中,执行 find() 方法时,它会显示文档的所有字段。要限制此行为,需要设置一个带有值 1 或 0 的字段列表。1 用于显示字段,0 用于隐藏字段。
MongoDB’s find() method, explained in MongoDB Query Document accepts second optional parameter that is list of fields that you want to retrieve. In MongoDB, when you execute find() method, then it displays all fields of a document. To limit this, you need to set a list of fields with value 1 or 0. 1 is used to show the field while 0 is used to hide the fields.
Syntax
find() 方法与投影结合起来的基本语法如下:
The basic syntax of find() method with projection is as follows −
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.find({},{KEY:1})Example
考虑集合 mycol 具有以下数据:
Consider the collection mycol has the following data −
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec5), "title":"MongoDB Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec6), "title":"NoSQL Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec7), "title":"Tutorials Point Overview"}下面的示例将在查询文档时显示文档的标题。
Following example will display the title of the document while querying the document.
>db.mycol.find({},{"title":1,_id:0})
{"title":"MongoDB Overview"}
{"title":"NoSQL Overview"}
{"title":"Tutorials Point Overview"}
>请注意,在执行 find() 方法时始终会显示 _id 字段,如果你不想要此字段,那么需要将其设置为 0。
Please note _id field is always displayed while executing find() method, if you don’t want this field, then you need to set it as 0.
MongoDB - Limit Records
在本节中,我们将了解如何使用 MongoDB 限制记录。
In this chapter, we will learn how to limit records using MongoDB.
The Limit() Method
要限制 MongoDB 中的记录,你需要使用 limit() 方法。该方法接受一个数字类型参数,即要显示的文档数。
To limit the records in MongoDB, you need to use limit() method. The method accepts one number type argument, which is the number of documents that you want to be displayed.
Syntax
limit() 方法的基本语法如下 −
The basic syntax of limit() method is as follows −
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.find().limit(NUMBER)Example
考虑集合 myycol 具有以下数据。
Consider the collection myycol has the following data.
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec5), "title":"MongoDB Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec6), "title":"NoSQL Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec7), "title":"Tutorials Point Overview"}以下示例在查询文档时仅显示两个文档。
Following example will display only two documents while querying the document.
>db.mycol.find({},{"title":1,_id:0}).limit(2)
{"title":"MongoDB Overview"}
{"title":"NoSQL Overview"}
>如果你未在 limit() 方法中指定数字参数,那么它将显示集合中的所有文档。
If you don’t specify the number argument in limit() method then it will display all documents from the collection.
MongoDB Skip() Method
除 limit() 方法外,还有另一个方法 skip() ,该方法也接受数字类型参数,用于跳过指定数量的文档。
Apart from limit() method, there is one more method skip() which also accepts number type argument and is used to skip the number of documents.
MongoDB - Sort Records
在本章中,我们将学习如何对 MongoDB 中的记录进行排序。
In this chapter, we will learn how to sort records in MongoDB.
The sort() Method
要在 MongoDB 中对文档排序,您需要使用 sort() 方法。该方法接受一个包含字段列表及其排序顺序的文档。要指定排序顺序,请使用 1 和 -1。1 用于升序,而 -1 用于降序。
To sort documents in MongoDB, you need to use sort() method. The method accepts a document containing a list of fields along with their sorting order. To specify sorting order 1 and -1 are used. 1 is used for ascending order while -1 is used for descending order.
Syntax
sort() 方法的基本语法如下 -
The basic syntax of sort() method is as follows −
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.find().sort({KEY:1})Example
考虑集合 myycol 具有以下数据。
Consider the collection myycol has the following data.
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec5), "title":"MongoDB Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec6), "title":"NoSQL Overview"}
{ "_id" : ObjectId(5983548781331adf45ec7), "title":"Tutorials Point Overview"}以下示例将按标题降序显示文档。
Following example will display the documents sorted by title in the descending order.
>db.mycol.find({},{"title":1,_id:0}).sort({"title":-1})
{"title":"Tutorials Point Overview"}
{"title":"NoSQL Overview"}
{"title":"MongoDB Overview"}
>请注意,如果您未指定排序首选项,则 sort() 方法将按升序显示文档。
Please note, if you don’t specify the sorting preference, then sort() method will display the documents in ascending order.
MongoDB - Indexing
索引支持查询的高效解析。如果没有索引,MongoDB 必须扫描集合的每个文档,以选择与查询语句匹配的那些文档。此扫描效率极低,并且要求 MongoDB 处理大量数据。
Indexes support the efficient resolution of queries. Without indexes, MongoDB must scan every document of a collection to select those documents that match the query statement. This scan is highly inefficient and require MongoDB to process a large volume of data.
索引是一种特殊数据结构,使用易于遍历的形式存储一小部分数据集。索引按索引中指定的字段值对特定字段的值或多组字段的值进行排序并存储这些值。
Indexes are special data structures, that store a small portion of the data set in an easy-to-traverse form. The index stores the value of a specific field or set of fields, ordered by the value of the field as specified in the index.
The createIndex() Method
要创建索引,您需要使用 MongoDB 的 createIndex() 方法。
To create an index, you need to use createIndex() method of MongoDB.
Syntax
createIndex() 方法的基本语法如下()。
The basic syntax of createIndex() method is as follows().
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.createIndex({KEY:1})此处 key 是您希望创建索引的字段的名称,1 表示升序。要以降序创建索引,您需要使用 -1。
Here key is the name of the field on which you want to create index and 1 is for ascending order. To create index in descending order you need to use -1.
Example
>db.mycol.createIndex({"title":1})
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
>在 createIndex() 方法中,您可以传递多个字段,以便在多个字段上创建索引。
In createIndex() method you can pass multiple fields, to create index on multiple fields.
>db.mycol.createIndex({"title":1,"description":-1})
>此方法还接受选项列表(这些选项是可选的)。以下是列表 −
This method also accepts list of options (which are optional). Following is the list −
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
background |
Boolean |
Builds the index in the background so that building an index does not block other database activities. Specify true to build in the background. The default value is false. |
unique |
Boolean |
Creates a unique index so that the collection will not accept insertion of documents where the index key or keys match an existing value in the index. Specify true to create a unique index. The default value is false. |
name |
string |
The name of the index. If unspecified, MongoDB generates an index name by concatenating the names of the indexed fields and the sort order. |
sparse |
Boolean |
If true, the index only references documents with the specified field. These indexes use less space but behave differently in some situations (particularly sorts). The default value is false. |
expireAfterSeconds |
integer |
Specifies a value, in seconds, as a TTL to control how long MongoDB retains documents in this collection. |
weights |
document |
The weight is a number ranging from 1 to 99,999 and denotes the significance of the field relative to the other indexed fields in terms of the score. |
default_language |
string |
For a text index, the language that determines the list of stop words and the rules for the stemmer and tokenizer. The default value is English. |
language_override |
string |
For a text index, specify the name of the field in the document that contains, the language to override the default language. The default value is language. |
The dropIndex() method
您可以使用 MongoDB 的 dropIndex() 方法删除特定索引。
You can drop a particular index using the dropIndex() method of MongoDB.
Syntax
DropIndex() 方法的基本语法如下()。
The basic syntax of DropIndex() method is as follows().
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.dropIndex({KEY:1})此处,“key”是希望删除现有索引的文件名称。除了索引规范文档(以上语法)之外,还可以直接指定索引名称,如下所示:
Here, "key" is the name of the file on which you want to remove an existing index. Instead of the index specification document (above syntax), you can also specify the name of the index directly as:
dropIndex("name_of_the_index")The dropIndexes() method
此方法删除集合中的多个(已指定的)索引。
This method deletes multiple (specified) indexes on a collection.
Syntax
DropIndexes() 方法的基本语法如下():
The basic syntax of DropIndexes() method is as follows() −
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.dropIndexes()Example
假设我们在命名的 mycol 集合中创建了 2 个索引,如下所示:
Assume we have created 2 indexes in the named mycol collection as shown below −
> db.mycol.createIndex({"title":1,"description":-1})下面的示例删除上面创建的 mycol 中的索引:
Following example removes the above created indexes of mycol −
>db.mycol.dropIndexes({"title":1,"description":-1})
{ "nIndexesWas" : 2, "ok" : 1 }
>The getIndexes() method
此方法返回集合中所有索引的描述。
This method returns the description of all the indexes int the collection.
Syntax
以下是 getIndexes() 方法的基本语法:
Following is the basic syntax od the getIndexes() method −
db.COLLECTION_NAME.getIndexes()Example
假设我们在命名的 mycol 集合中创建了 2 个索引,如下所示:
Assume we have created 2 indexes in the named mycol collection as shown below −
> db.mycol.createIndex({"title":1,"description":-1})下面的示例检索集合 mycol 中的所有索引:
Following example retrieves all the indexes in the collection mycol −
> db.mycol.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "test.mycol"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"title" : 1,
"description" : -1
},
"name" : "title_1_description_-1",
"ns" : "test.mycol"
}
]
>MongoDB - Aggregation
聚合操作处理数据记录并返回计算结果。聚合操作将来自多个文档的值组合在一起,并可以对组合后的数据执行各种操作以返回单个结果。在 SQL 中,count(*) 和 with group by 等效于 mongodb 聚合。
Aggregations operations process data records and return computed results. Aggregation operations group values from multiple documents together, and can perform a variety of operations on the grouped data to return a single result. In SQL count(*) and with group by is an equivalent of mongodb aggregation.
The aggregate() Method
对于 MongoDB 中的聚合,您应该使用 aggregate() 方法。
For the aggregation in MongoDB, you should use aggregate() method.
Syntax
aggregate() 方法的基本语法如下 -
Basic syntax of aggregate() method is as follows −
>db.COLLECTION_NAME.aggregate(AGGREGATE_OPERATION)Example
在集合中,您有以下数据 -
In the collection you have the following data −
{
_id: ObjectId(7df78ad8902c)
title: 'MongoDB Overview',
description: 'MongoDB is no sql database',
by_user: 'tutorials point',
url: 'http://www.tutorialspoint.com',
tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'],
likes: 100
},
{
_id: ObjectId(7df78ad8902d)
title: 'NoSQL Overview',
description: 'No sql database is very fast',
by_user: 'tutorials point',
url: 'http://www.tutorialspoint.com',
tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'],
likes: 10
},
{
_id: ObjectId(7df78ad8902e)
title: 'Neo4j Overview',
description: 'Neo4j is no sql database',
by_user: 'Neo4j',
url: 'http://www.neo4j.com',
tags: ['neo4j', 'database', 'NoSQL'],
likes: 750
},现在,从上述集合中,如果您想显示一个列出每个用户编写的教程数量的列表,则您将使用以下 aggregate() 方法 -
Now from the above collection, if you want to display a list stating how many tutorials are written by each user, then you will use the following aggregate() method −
> db.mycol.aggregate([{$group : {_id : "$by_user", num_tutorial : {$sum : 1}}}])
{
"result" : [
{
"_id" : "tutorials point",
"num_tutorial" : 2
},
{
"_id" : "Neo4j",
"num_tutorial" : 1
}
],
"ok" : 1
}
>上述用例的 SQL 等效查询将是 select by_user, count( ) from mycol group by by_user*。
Sql equivalent query for the above use case will be select by_user, count() from mycol group by by_user*.
在上面的示例中,我们已按字段对文档进行分组 by_user ,并且在 by_user 的每次出现时,sum 的前一个值都会递增。以下是可用聚合表达式的列表。
In the above example, we have grouped documents by field by_user and on each occurrence of by_user previous value of sum is incremented. Following is a list of available aggregation expressions.
Expression |
Description |
Example |
$sum |
Sums up the defined value from all documents in the collection. |
db.mycol.aggregate([{$group : {_id : "$by_user", num_tutorial : {$sum : "$likes"}}}]) |
$avg |
Calculates the average of all given values from all documents in the collection. |
db.mycol.aggregate([{$group : {_id : "$by_user", num_tutorial : {$avg : "$likes"}}}]) |
$min |
Gets the minimum of the corresponding values from all documents in the collection. |
db.mycol.aggregate([{$group : {_id : "$by_user", num_tutorial : {$min : "$likes"}}}]) |
$max |
Gets the maximum of the corresponding values from all documents in the collection. |
db.mycol.aggregate([{$group : {_id : "$by_user", num_tutorial : {$max : "$likes"}}}]) |
$push |
Inserts the value to an array in the resulting document. |
db.mycol.aggregate([{$group : {_id : "$by_user", url : {$push: "$url"}}}]) |
$addToSet |
Inserts the value to an array in the resulting document but does not create duplicates. |
db.mycol.aggregate([{$group : {_id : "$by_user", url : {$addToSet : "$url"}}}]) |
$first |
Gets the first document from the source documents according to the grouping. Typically this makes only sense together with some previously applied “$sort”-stage. |
db.mycol.aggregate([{$group : {_id : "$by_user", first_url : {$first : "$url"}}}]) |
$last |
Gets the last document from the source documents according to the grouping. Typically this makes only sense together with some previously applied “$sort”-stage. |
db.mycol.aggregate([{$group : {_id : "$by_user", last_url : {$last : "$url"}}}]) |
Pipeline Concept
在 UNIX 命令中,shell 管道表示在一些输入上执行操作并使用输出作为下一个命令的输入,依此类推的可能性。MongoDB 在聚合框架中也支持相同概念。有一组可能的阶段,每个阶段都将一组文档作为输入并生成一组结果文档(或管道末尾的最终结果 JSON 文档)。它随后依次可用于下一个阶段,依此类推。
In UNIX command, shell pipeline means the possibility to execute an operation on some input and use the output as the input for the next command and so on. MongoDB also supports same concept in aggregation framework. There is a set of possible stages and each of those is taken as a set of documents as an input and produces a resulting set of documents (or the final resulting JSON document at the end of the pipeline). This can then in turn be used for the next stage and so on.
聚合框架中的可能阶段如下:
Following are the possible stages in aggregation framework −
-
$project − Used to select some specific fields from a collection.
-
$match − This is a filtering operation and thus this can reduce the amount of documents that are given as input to the next stage.
-
$group − This does the actual aggregation as discussed above.
-
$sort − Sorts the documents.
-
$skip − With this, it is possible to skip forward in the list of documents for a given amount of documents.
-
$limit − This limits the amount of documents to look at, by the given number starting from the current positions.
-
$unwind − This is used to unwind document that are using arrays. When using an array, the data is kind of pre-joined and this operation will be undone with this to have individual documents again. Thus with this stage we will increase the amount of documents for the next stage.
MongoDB - Replication
复制是指在多个服务器之间同步数据的过程。复制提供冗余并且使用多个数据库服务器中的多份数据副本提高数据可用性。复制可以防止因单个服务器丢失而导致数据库丢失数据。复制还允许从硬件故障和服务中断中恢复。通过额外的数据副本,您可以分配一份副本到灾难恢复、报告或备份中。
Replication is the process of synchronizing data across multiple servers. Replication provides redundancy and increases data availability with multiple copies of data on different database servers. Replication protects a database from the loss of a single server. Replication also allows you to recover from hardware failure and service interruptions. With additional copies of the data, you can dedicate one to disaster recovery, reporting, or backup.
Why Replication?
-
To keep your data safe
-
High (24*7) availability of data
-
Disaster recovery
-
No downtime for maintenance (like backups, index rebuilds, compaction)
-
Read scaling (extra copies to read from)
-
Replica set is transparent to the application
How Replication Works in MongoDB
MongoDB 通过使用副本集来实现复制。副本集是一组承载同一数据集的 mongod 实例。在副本中,一个节点是接收所有写入操作的主节点。所有其他实例(如辅助节点)都会从主节点应用操作,以便具有相同的数据集。副本集中只能有一个主节点。
MongoDB achieves replication by the use of replica set. A replica set is a group of mongod instances that host the same data set. In a replica, one node is primary node that receives all write operations. All other instances, such as secondaries, apply operations from the primary so that they have the same data set. Replica set can have only one primary node.
-
Replica set is a group of two or more nodes (generally minimum 3 nodes are required).
-
In a replica set, one node is primary node and remaining nodes are secondary.
-
All data replicates from primary to secondary node.
-
At the time of automatic failover or maintenance, election establishes for primary and a new primary node is elected.
-
After the recovery of failed node, it again join the replica set and works as a secondary node.
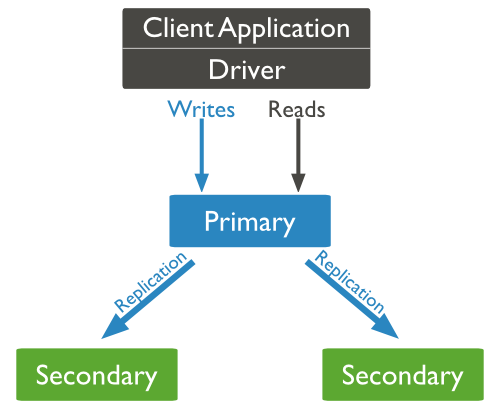
MongoDB 复制的典型示意图中,客户端应用程序始终与主节点交互,然后主节点将数据复制到辅助节点。
A typical diagram of MongoDB replication is shown in which client application always interact with the primary node and the primary node then replicates the data to the secondary nodes.
Replica Set Features
-
A cluster of N nodes
-
Any one node can be primary
-
All write operations go to primary
-
Automatic failover
-
Automatic recovery
-
Consensus election of primary
Set Up a Replica Set
在本教程中,我们将把独立的 MongoDB 实例转换为副本集。若要转换为副本集,请执行以下步骤:
In this tutorial, we will convert standalone MongoDB instance to a replica set. To convert to replica set, following are the steps −
-
Shutdown already running MongoDB server.
.
-
Start the MongoDB server by specifying — replSet option. Following is the basic syntax of --replSet −
mongod --port "PORT" --dbpath "YOUR_DB_DATA_PATH" --replSet "REPLICA_SET_INSTANCE_NAME"Example
mongod --port 27017 --dbpath "D:\set up\mongodb\data" --replSet rs0-
It will start a mongod instance with the name rs0, on port 27017.
-
Now start the command prompt and connect to this mongod instance.
-
In Mongo client, issue the command rs.initiate() to initiate a new replica set.
-
To check the replica set configuration, issue the command rs.conf(). To check the status of replica set issue the command rs.status().
Add Members to Replica Set
若要向副本集添加成员,请在多台机器上启动 mongod 实例。现在启动一个 mongo 客户端并发出命令 rs.add() 。
To add members to replica set, start mongod instances on multiple machines. Now start a mongo client and issue a command rs.add().
Syntax
rs.add() 命令的基本语法如下:
The basic syntax of rs.add() command is as follows −
>rs.add(HOST_NAME:PORT)Example
假设你的 mongod 实例名称是 mongod1.net 且它在端口 27017 上运行。若要将此实例添加到副本集中,请在 Mongo 客户端中发出命令 rs.add() 。
Suppose your mongod instance name is mongod1.net and it is running on port 27017. To add this instance to replica set, issue the command rs.add() in Mongo client.
>rs.add("mongod1.net:27017")
>你只能在连接到主节点时将 mongod 实例添加到副本集中。若要检查你是否已连接到主节点,请在 mongo 客户端中发出命令 db.isMaster() 。
You can add mongod instance to replica set only when you are connected to primary node. To check whether you are connected to primary or not, issue the command db.isMaster() in mongo client.
MongoDB - Sharding
分片是指在多台机器上存储数据记录的过程,并且是 MongoDB 满足数据增长需求的方法。随着数据大小的增加,单台机器可能不足以存储数据或提供可接受的读写吞吐量。分片通过横向扩展解决了该问题。使用分片,可以添加更多机器来支持数据增长以及读写操作的需求。
Sharding is the process of storing data records across multiple machines and it is MongoDB’s approach to meeting the demands of data growth. As the size of the data increases, a single machine may not be sufficient to store the data nor provide an acceptable read and write throughput. Sharding solves the problem with horizontal scaling. With sharding, you add more machines to support data growth and the demands of read and write operations.
Why Sharding?
-
In replication, all writes go to master node
-
Latency sensitive queries still go to master
-
Single replica set has limitation of 12 nodes
-
Memory can’t be large enough when active dataset is big
-
Local disk is not big enough
-
Vertical scaling is too expensive
Sharding in MongoDB
下图显示了使用分片集群在 MongoDB 中分片的情况。
The following diagram shows the sharding in MongoDB using sharded cluster.

在下图中,有三个主要组件:
In the following diagram, there are three main components −
-
Shards − Shards are used to store data. They provide high availability and data consistency. In production environment, each shard is a separate replica set.
-
Config Servers − Config servers store the cluster’s metadata. This data contains a mapping of the cluster’s data set to the shards. The query router uses this metadata to target operations to specific shards. In production environment, sharded clusters have exactly 3 config servers.
-
Query Routers − Query routers are basically mongo instances, interface with client applications and direct operations to the appropriate shard. The query router processes and targets the operations to shards and then returns results to the clients. A sharded cluster can contain more than one query router to divide the client request load. A client sends requests to one query router. Generally, a sharded cluster have many query routers.
MongoDB - Create Backup
在本章中,我们将了解如何在 MongoDB 中创建备份。
In this chapter, we will see how to create a backup in MongoDB.
Dump MongoDB Data
若要创建 MongoDB 中数据库的备份,你应使用 mongodump 命令。此命令将把你的服务器的全部数据转储到转储目录。可以使用许多选项来限制数据量或创建远程服务器的备份。
To create backup of database in MongoDB, you should use mongodump command. This command will dump the entire data of your server into the dump directory. There are many options available by which you can limit the amount of data or create backup of your remote server.
Example
启动你的 mongod 服务器。假设你的 mongod 服务器在 localhost 和端口 27017 上运行,则请打开命令提示符并转到 mongodb 实例的 bin 目录,然后键入命令 mongodump
Start your mongod server. Assuming that your mongod server is running on the localhost and port 27017, open a command prompt and go to the bin directory of your mongodb instance and type the command mongodump
考虑 mycol 集合具有以下数据。
Consider the mycol collection has the following data.
>mongodump此命令将连接到在 127.0.0.1 和端口 27017 上运行的服务器,并将服务器的所有数据备份到目录 /bin/dump/ 。以下是该命令的输出:
The command will connect to the server running at 127.0.0.1 and port 27017 and back all data of the server to directory /bin/dump/. Following is the output of the command −

以下是可与 mongodump 命令一起使用的可用选项列表。
Following is a list of available options that can be used with the mongodump command.
Syntax |
Description |
Example |
mongodump --host HOST_NAME --port PORT_NUMBER |
This commmand will backup all databases of specified mongod instance. |
mongodump --host tutorialspoint.com --port 27017 |
mongodump --dbpath DB_PATH --out BACKUP_DIRECTORY |
This command will backup only specified database at specified path. |
mongodump --dbpath /data/db/ --out /data/backup/ |
mongodump --collection COLLECTION --db DB_NAME |
This command will backup only specified collection of specified database. |
mongodump --collection mycol --db test |
MongoDB - Deployment
在准备 MongoDB 部署时,您应尝试了解您的应用程序将在生产环境中的表现。最好开发一个一致、可重复的方法来管理您的部署环境,以最大限度地减少在生产过程中出现的意外事件。
When you are preparing a MongoDB deployment, you should try to understand how your application is going to hold up in production. It’s a good idea to develop a consistent, repeatable approach to managing your deployment environment so that you can minimize any surprises once you’re in production.
最佳方法是构建原型设置、执行负载测试、监控关键指标并使用这些信息扩展您的设置。该方法的关键部分是主动监控您的整个系统——它将帮助您了解您的生产系统将如何在部署前表现,并确定您需要提升容量的位置。例如,了解您内存使用率中的潜在高峰,可以帮助在锁定之前解决写锁定错误。
The best approach incorporates prototyping your set up, conducting load testing, monitoring key metrics, and using that information to scale your set up. The key part of the approach is to proactively monitor your entire system - this will help you understand how your production system will hold up before deploying, and determine where you will need to add capacity. Having insight into potential spikes in your memory usage, for example, could help put out a write-lock fire before it starts.
要监视您的部署,MongoDB 提供以下部分指令:
To monitor your deployment, MongoDB provides some of the following commands −
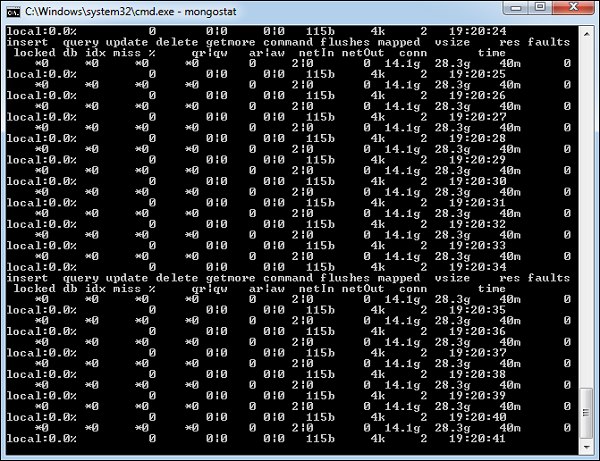
mongostat
此指令检查所有正在运行的 mongod 实例的状态,并返回数据库操作计数器。这些计数器包括插入、查询、更新、删除和游标。此指令还显示您何时遇到页面错误,以及您的锁定百分比。这意味着您的内存不足、达到写容量,或遇到某些性能问题。
This command checks the status of all running mongod instances and return counters of database operations. These counters include inserts, queries, updates, deletes, and cursors. Command also shows when you’re hitting page faults, and showcase your lock percentage. This means that you’re running low on memory, hitting write capacity or have some performance issue.
要运行此指令,请启动您的 mongod 实例。在另一个命令提示符中,转到 mongodb 安装的 bin 目录并键入 mongostat 。
To run the command, start your mongod instance. In another command prompt, go to bin directory of your mongodb installation and type mongostat.
D:\set up\mongodb\bin>mongostat以下为指令输出:
Following is the output of the command −
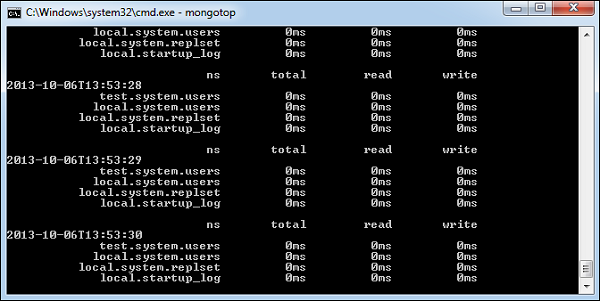
mongotop
此指令在集合的基础上跟踪并报告 MongoDB 实例的读写活动。默认情况下, mongotop 每秒返回一次信息,您可以根据需要更改信息。您应检查此读写活动是否符合您的应用程序预期,并且您不会一次向数据库写入太多信息、不会从磁盘读取过于频繁或超过您的工作集大小。
This command tracks and reports the read and write activity of MongoDB instance on a collection basis. By default, mongotop returns information in each second, which you can change it accordingly. You should check that this read and write activity matches your application intention, and you’re not firing too many writes to the database at a time, reading too frequently from a disk, or are exceeding your working set size.
要运行此指令,请启动您的 mongod 实例。在另一个命令提示符中,转到 mongodb 安装的 bin 目录并键入 mongotop 。
To run the command, start your mongod instance. In another command prompt, go to bin directory of your mongodb installation and type mongotop.
D:\set up\mongodb\bin>mongotop以下为指令输出:
Following is the output of the command −
要更改 mongotop 指令以减少返回信息的频率,请在 mongotop 指令后指定一个特定的数字。
To change mongotop command to return information less frequently, specify a specific number after the mongotop command.
D:\set up\mongodb\bin>mongotop 30上述示例会每隔 30 秒返回一次值。
The above example will return values every 30 seconds.
除了 MongoDB 工具之外,10gen 还提供了一项免费托管式监控服务,即 MongoDB 管理服务 (MMS),它提供了一个仪表盘,让你可以查看整个群集的指标。
Apart from the MongoDB tools, 10gen provides a free, hosted monitoring service, MongoDB Management Service (MMS), that provides a dashboard and gives you a view of the metrics from your entire cluster.
MongoDB - Java
在本章中,我们将了解如何设置 MongoDB JDBC 驱动程序。
In this chapter, we will learn how to set up MongoDB JDBC driver.
Installation
在 Java 程序中开始使用 MongoDB 之前,你需要确保你的机器上设置好了 MongoDB JDBC 驱动程序和 Java。你可以查看 Java 教程来安装机器上的 Java。现在,让我们检查如何设置 MongoDB JDBC 驱动程序。
Before you start using MongoDB in your Java programs, you need to make sure that you have MongoDB JDBC driver and Java set up on the machine. You can check Java tutorial for Java installation on your machine. Now, let us check how to set up MongoDB JDBC driver.
-
You need to download the jar from the path Download mongo.jar. Make sure to download the latest release of it.
-
You need to include the mongo.jar into your classpath.
Connect to Database
要连接数据库,你需要指定数据库名称;如果数据库不存在,则 MongoDB 会自动创建它。
To connect database, you need to specify the database name, if the database doesn’t exist then MongoDB creates it automatically.
以下是连接数据库的代码片段:
Following is the code snippet to connect to the database −
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class ConnectToDB {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// Creating a Mongo client
MongoClient mongo = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
// Creating Credentials
MongoCredential credential;
credential = MongoCredential.createCredential("sampleUser", "myDb",
"password".toCharArray());
System.out.println("Connected to the database successfully");
// Accessing the database
MongoDatabase database = mongo.getDatabase("myDb");
System.out.println("Credentials ::"+ credential);
}
}现在,让我们编译并运行上述程序来创建我们的数据库 myDb,如下所示。
Now, let’s compile and run the above program to create our database myDb as shown below.
$javac ConnectToDB.java
$java ConnectToDB在执行上述程序时,您将得到以下输出。
On executing, the above program gives you the following output.
Connected to the database successfully
Credentials ::MongoCredential{
mechanism = null,
userName = 'sampleUser',
source = 'myDb',
password = <hidden>,
mechanismProperties = {}
}Create a Collection
为了创建一个集合,使用 com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase 类的 createCollection() 方法。
To create a collection, createCollection() method of com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase class is used.
以下是创建集合的代码片段 −
Following is the code snippet to create a collection −
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class CreatingCollection {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// Creating a Mongo client
MongoClient mongo = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
// Creating Credentials
MongoCredential credential;
credential = MongoCredential.createCredential("sampleUser", "myDb",
"password".toCharArray());
System.out.println("Connected to the database successfully");
//Accessing the database
MongoDatabase database = mongo.getDatabase("myDb");
//Creating a collection
database.createCollection("sampleCollection");
System.out.println("Collection created successfully");
}
}在编译程序后,你会得到以下结果−
On compiling, the above program gives you the following result −
Connected to the database successfully
Collection created successfullyGetting/Selecting a Collection
为了从数据库中获取/选择一个集合,使用 com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase 类的 getCollection() 方法。
To get/select a collection from the database, getCollection() method of com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase class is used.
以下是用于获取/选择一个集合的程序−
Following is the program to get/select a collection −
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import org.bson.Document;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class selectingCollection {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// Creating a Mongo client
MongoClient mongo = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
// Creating Credentials
MongoCredential credential;
credential = MongoCredential.createCredential("sampleUser", "myDb",
"password".toCharArray());
System.out.println("Connected to the database successfully");
// Accessing the database
MongoDatabase database = mongo.getDatabase("myDb");
// Creating a collection
System.out.println("Collection created successfully");
// Retieving a collection
MongoCollection<Document> collection = database.getCollection("myCollection");
System.out.println("Collection myCollection selected successfully");
}
}在编译程序后,你会得到以下结果−
On compiling, the above program gives you the following result −
Connected to the database successfully
Collection created successfully
Collection myCollection selected successfullyInsert a Document
为了向 MongoDB 中插入一个文档,使用 com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection 类的 insert() 方法。
To insert a document into MongoDB, insert() method of com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection class is used.
以下是插入文档的代码片段:
Following is the code snippet to insert a document −
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import org.bson.Document;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class InsertingDocument {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// Creating a Mongo client
MongoClient mongo = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
// Creating Credentials
MongoCredential credential;
credential = MongoCredential.createCredential("sampleUser", "myDb",
"password".toCharArray());
System.out.println("Connected to the database successfully");
// Accessing the database
MongoDatabase database = mongo.getDatabase("myDb");
// Retrieving a collection
MongoCollection<Document> collection = database.getCollection("sampleCollection");
System.out.println("Collection sampleCollection selected successfully");
Document document = new Document("title", "MongoDB")
.append("id", 1)
.append("description", "database")
.append("likes", 100)
.append("url", "http://www.tutorialspoint.com/mongodb/")
.append("by", "tutorials point");
collection.insertOne(document);
System.out.println("Document inserted successfully");
}
}在编译程序后,你会得到以下结果−
On compiling, the above program gives you the following result −
Connected to the database successfully
Collection sampleCollection selected successfully
Document inserted successfullyRetrieve All Documents
为了从集合中选择所有文档,使用 com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection 类的 find() 方法。此方法返回一个游标,所以你需要遍历此游标。
To select all documents from the collection, find() method of com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection class is used. This method returns a cursor, so you need to iterate this cursor.
以下是用于选择所有文档的程序−
Following is the program to select all documents −
import com.mongodb.client.FindIterable;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.bson.Document;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class RetrievingAllDocuments {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// Creating a Mongo client
MongoClient mongo = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
// Creating Credentials
MongoCredential credential;
credential = MongoCredential.createCredential("sampleUser", "myDb",
"password".toCharArray());
System.out.println("Connected to the database successfully");
// Accessing the database
MongoDatabase database = mongo.getDatabase("myDb");
// Retrieving a collection
MongoCollection<Document> collection = database.getCollection("sampleCollection");
System.out.println("Collection sampleCollection selected successfully");
// Getting the iterable object
FindIterable<Document> iterDoc = collection.find();
int i = 1;
// Getting the iterator
Iterator it = iterDoc.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
i++;
}
}
}在编译程序后,你会得到以下结果−
On compiling, the above program gives you the following result −
Document{{
_id = 5967745223993a32646baab8,
title = MongoDB,
id = 1,
description = database,
likes = 100,
url = http://www.tutorialspoint.com/mongodb/, by = tutorials point
}}
Document{{
_id = 7452239959673a32646baab8,
title = RethinkDB,
id = 2,
description = database,
likes = 200,
url = http://www.tutorialspoint.com/rethinkdb/, by = tutorials point
}}Update Document
为了从集合中更新一个文档,使用 com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection 类的 updateOne() 方法。
To update a document from the collection, updateOne() method of com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection class is used.
以下是用于选择第一个文档的程序−
Following is the program to select the first document −
import com.mongodb.client.FindIterable;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Filters;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Updates;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.bson.Document;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class UpdatingDocuments {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// Creating a Mongo client
MongoClient mongo = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
// Creating Credentials
MongoCredential credential;
credential = MongoCredential.createCredential("sampleUser", "myDb",
"password".toCharArray());
System.out.println("Connected to the database successfully");
// Accessing the database
MongoDatabase database = mongo.getDatabase("myDb");
// Retrieving a collection
MongoCollection<Document> collection = database.getCollection("sampleCollection");
System.out.println("Collection myCollection selected successfully");
collection.updateOne(Filters.eq("id", 1), Updates.set("likes", 150));
System.out.println("Document update successfully...");
// Retrieving the documents after updation
// Getting the iterable object
FindIterable<Document> iterDoc = collection.find();
int i = 1;
// Getting the iterator
Iterator it = iterDoc.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
i++;
}
}
}在编译程序后,你会得到以下结果−
On compiling, the above program gives you the following result −
Document update successfully...
Document {{
_id = 5967745223993a32646baab8,
title = MongoDB,
id = 1,
description = database,
likes = 150,
url = http://www.tutorialspoint.com/mongodb/, by = tutorials point
}}Delete a Document
为了从集合中删除一个文档,你需要使用 com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection 类的 deleteOne() 方法。
To delete a document from the collection, you need to use the deleteOne() method of the com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection class.
以下是用于删除一个文档的程序−
Following is the program to delete a document −
import com.mongodb.client.FindIterable;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Filters;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.bson.Document;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class DeletingDocuments {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// Creating a Mongo client
MongoClient mongo = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
// Creating Credentials
MongoCredential credential;
credential = MongoCredential.createCredential("sampleUser", "myDb",
"password".toCharArray());
System.out.println("Connected to the database successfully");
// Accessing the database
MongoDatabase database = mongo.getDatabase("myDb");
// Retrieving a collection
MongoCollection<Document> collection = database.getCollection("sampleCollection");
System.out.println("Collection sampleCollection selected successfully");
// Deleting the documents
collection.deleteOne(Filters.eq("id", 1));
System.out.println("Document deleted successfully...");
// Retrieving the documents after updation
// Getting the iterable object
FindIterable<Document> iterDoc = collection.find();
int i = 1;
// Getting the iterator
Iterator it = iterDoc.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println("Inserted Document: "+i);
System.out.println(it.next());
i++;
}
}
}在编译程序后,你会得到以下结果−
On compiling, the above program gives you the following result −
Connected to the database successfully
Collection sampleCollection selected successfully
Document deleted successfully...Dropping a Collection
为了从数据库中删除一个集合,你需要使用 com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection 类的 drop() 方法。
To drop a collection from a database, you need to use the drop() method of the com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection class.
以下是删除集合的程序——
Following is the program to delete a collection −
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import org.bson.Document;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class DropingCollection {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// Creating a Mongo client
MongoClient mongo = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
// Creating Credentials
MongoCredential credential;
credential = MongoCredential.createCredential("sampleUser", "myDb",
"password".toCharArray());
System.out.println("Connected to the database successfully");
// Accessing the database
MongoDatabase database = mongo.getDatabase("myDb");
// Creating a collection
System.out.println("Collections created successfully");
// Retieving a collection
MongoCollection<Document> collection = database.getCollection("sampleCollection");
// Dropping a Collection
collection.drop();
System.out.println("Collection dropped successfully");
}
}在编译程序后,你会得到以下结果−
On compiling, the above program gives you the following result −
Connected to the database successfully
Collection sampleCollection selected successfully
Collection dropped successfullyListing All the Collections
若要列出数据库中的所有集合,则需要使用 com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase 类的 listCollectionNames() 方法。
To list all the collections in a database, you need to use the listCollectionNames() method of the com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase class.
以下是列出数据库内所有集合的程序——
Following is the program to list all the collections of a database −
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.MongoCredential;
public class ListOfCollection {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// Creating a Mongo client
MongoClient mongo = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
// Creating Credentials
MongoCredential credential;
credential = MongoCredential.createCredential("sampleUser", "myDb",
"password".toCharArray());
System.out.println("Connected to the database successfully");
// Accessing the database
MongoDatabase database = mongo.getDatabase("myDb");
System.out.println("Collection created successfully");
for (String name : database.listCollectionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}在编译程序后,你会得到以下结果−
On compiling, the above program gives you the following result −
Connected to the database successfully
Collection created successfully
myCollection
myCollection1
myCollection5其余的 MongoDB 方法 save(), limit(), skip(), sort() 等与后续教程中解释的相同。
Remaining MongoDB methods save(), limit(), skip(), sort() etc. work same as explained in the subsequent tutorial.
MongoDB - PHP
要将 MongoDB 与 PHP 一起使用,您需要使用 MongoDB PHP 驱动程序。从 url Download PHP Driver 下载该驱动程序。务必下载其最新版本。现在解压存档并将 php_mongo.dll 放在你的 PHP 扩展目录(默认情况下为 “ext”)中,并在你的 php.ini 文件中添加以下行:
To use MongoDB with PHP, you need to use MongoDB PHP driver. Download the driver from the url Download PHP Driver. Make sure to download the latest release of it. Now unzip the archive and put php_mongo.dll in your PHP extension directory ("ext" by default) and add the following line to your php.ini file −
extension = php_mongo.dllMake a Connection and Select a Database
为了连接,您需要指定数据库名称,如果数据库不存在,则 MongoDB 会自动创建它。
To make a connection, you need to specify the database name, if the database doesn’t exist then MongoDB creates it automatically.
以下是连接数据库的代码片段:
Following is the code snippet to connect to the database −
<?php
// connect to mongodb
$m = new MongoClient();
echo "Connection to database successfully";
// select a database
$db = $m->mydb;
echo "Database mydb selected";
?>程序执行后,将产生以下结果:
When the program is executed, it will produce the following result −
Connection to database successfully
Database mydb selectedCreate a Collection
以下是创建集合的代码片段 −
Following is the code snippet to create a collection −
<?php
// connect to mongodb
$m = new MongoClient();
echo "Connection to database successfully";
// select a database
$db = $m->mydb;
echo "Database mydb selected";
$collection = $db->createCollection("mycol");
echo "Collection created succsessfully";
?>程序执行后,将产生以下结果:
When the program is executed, it will produce the following result −
Connection to database successfully
Database mydb selected
Collection created succsessfullyInsert a Document
要将文档插入到 MongoDB 中,使用 insert() 方法。
To insert a document into MongoDB, insert() method is used.
以下是插入文档的代码片段:
Following is the code snippet to insert a document −
<?php
// connect to mongodb
$m = new MongoClient();
echo "Connection to database successfully";
// select a database
$db = $m->mydb;
echo "Database mydb selected";
$collection = $db->mycol;
echo "Collection selected succsessfully";
$document = array(
"title" => "MongoDB",
"description" => "database",
"likes" => 100,
"url" => "http://www.tutorialspoint.com/mongodb/",
"by" => "tutorials point"
);
$collection->insert($document);
echo "Document inserted successfully";
?>程序执行后,将产生以下结果:
When the program is executed, it will produce the following result −
Connection to database successfully
Database mydb selected
Collection selected succsessfully
Document inserted successfullyFind All Documents
要从集合中选择所有文档,使用 find() 方法。
To select all documents from the collection, find() method is used.
以下是选择所有文档的代码片段:
Following is the code snippet to select all documents −
<?php
// connect to mongodb
$m = new MongoClient();
echo "Connection to database successfully";
// select a database
$db = $m->mydb;
echo "Database mydb selected";
$collection = $db->mycol;
echo "Collection selected succsessfully";
$cursor = $collection->find();
// iterate cursor to display title of documents
foreach ($cursor as $document) {
echo $document["title"] . "\n";
}
?>程序执行后,将产生以下结果:
When the program is executed, it will produce the following result −
Connection to database successfully
Database mydb selected
Collection selected succsessfully {
"title": "MongoDB"
}Update a Document
要更新文档,需要使用 update() 方法。
To update a document, you need to use the update() method.
在以下示例中,我们将会把已插入文档的标题更新为 MongoDB Tutorial 。以下是更新文档的代码片段:
In the following example, we will update the title of inserted document to MongoDB Tutorial. Following is the code snippet to update a document −
<?php
// connect to mongodb
$m = new MongoClient();
echo "Connection to database successfully";
// select a database
$db = $m->mydb;
echo "Database mydb selected";
$collection = $db->mycol;
echo "Collection selected succsessfully";
// now update the document
$collection->update(array("title"=>"MongoDB"),
array('$set'=>array("title"=>"MongoDB Tutorial")));
echo "Document updated successfully";
// now display the updated document
$cursor = $collection->find();
// iterate cursor to display title of documents
echo "Updated document";
foreach ($cursor as $document) {
echo $document["title"] . "\n";
}
?>程序执行后,将产生以下结果:
When the program is executed, it will produce the following result −
Connection to database successfully
Database mydb selected
Collection selected succsessfully
Document updated successfully
Updated document {
"title": "MongoDB Tutorial"
}Delete a Document
要删除文档,需要使用 remove() 方法。
To delete a document, you need to use remove() method.
在以下示例中,我们将移除标题为 MongoDB Tutorial 的文档。以下是删除文档的代码片段:
In the following example, we will remove the documents that has the title MongoDB Tutorial. Following is the code snippet to delete a document −
<?php
// connect to mongodb
$m = new MongoClient();
echo "Connection to database successfully";
// select a database
$db = $m->mydb;
echo "Database mydb selected";
$collection = $db->mycol;
echo "Collection selected succsessfully";
// now remove the document
$collection->remove(array("title"=>"MongoDB Tutorial"),false);
echo "Documents deleted successfully";
// now display the available documents
$cursor = $collection->find();
// iterate cursor to display title of documents
echo "Updated document";
foreach ($cursor as $document) {
echo $document["title"] . "\n";
}
?>程序执行后,将产生以下结果:
When the program is executed, it will produce the following result −
Connection to database successfully
Database mydb selected
Collection selected succsessfully
Documents deleted successfully在上述示例中,第二个参数是布尔类型,并用于 remove() 方法的 justOne 字段。
In the above example, the second parameter is boolean type and used for justOne field of remove() method.
剩余的 MongoDB 方法 findOne(), save(), limit(), skip(), sort() 等同于上述解释。
Remaining MongoDB methods findOne(), save(), limit(), skip(), sort() etc. works same as explained above.
MongoDB - Relationships
MongoDB 中的关系表示了各种文档如何在逻辑上相互关联。关系可以通过 Embedded 和 Referenced 方法建模。这种关系可以是 1:1、1:N、N:1 或 N:N。
Relationships in MongoDB represent how various documents are logically related to each other. Relationships can be modeled via Embedded and Referenced approaches. Such relationships can be either 1:1, 1:N, N:1 or N:N.
让我们考虑为用户存储地址的情况。因此,一个用户可以拥有多个地址,这是一种 1:N 关系。
Let us consider the case of storing addresses for users. So, one user can have multiple addresses making this a 1:N relationship.
以下是 user 文档的示例文档结构 −
Following is the sample document structure of user document −
{
"_id":ObjectId("52ffc33cd85242f436000001"),
"name": "Tom Hanks",
"contact": "987654321",
"dob": "01-01-1991"
}以下是 address 文档的示例文档结构 −
Following is the sample document structure of address document −
{
"_id":ObjectId("52ffc4a5d85242602e000000"),
"building": "22 A, Indiana Apt",
"pincode": 123456,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"state": "California"
}Modeling Embedded Relationships
在嵌入式方法中,我们将地址文档嵌入到用户文档中。
In the embedded approach, we will embed the address document inside the user document.
{
"_id":ObjectId("52ffc33cd85242f436000001"),
"contact": "987654321",
"dob": "01-01-1991",
"name": "Tom Benzamin",
"address": [
{
"building": "22 A, Indiana Apt",
"pincode": 123456,
"city": "Los Angeles",
"state": "California"
},
{
"building": "170 A, Acropolis Apt",
"pincode": 456789,
"city": "Chicago",
"state": "Illinois"
}
]
}这种方法在一个文档中维护所有相关数据,使其易于检索和维护。可以通过单个查询(例如)检索整个文档,例如 −
This approach maintains all the related data in a single document, which makes it easy to retrieve and maintain. The whole document can be retrieved in a single query such as −
>db.users.findOne({"name":"Tom Benzamin"},{"address":1})请注意,在上面的查询中, db 和 users 分别是数据库和集合。
Note that in the above query, db and users are the database and collection respectively.
缺点是如果嵌入式文档持续增长且变得过大,则可能会影响读/写性能。
The drawback is that if the embedded document keeps on growing too much in size, it can impact the read/write performance.
Modeling Referenced Relationships
这是设计规范化关系的方法。在此方法中,用户和地址文档将被分别维护,但用户文档将包含一个引用地址文档 id 字段的字段。
This is the approach of designing normalized relationship. In this approach, both the user and address documents will be maintained separately but the user document will contain a field that will reference the address document’s id field.
{
"_id":ObjectId("52ffc33cd85242f436000001"),
"contact": "987654321",
"dob": "01-01-1991",
"name": "Tom Benzamin",
"address_ids": [
ObjectId("52ffc4a5d85242602e000000"),
ObjectId("52ffc4a5d85242602e000001")
]
}如上所示,用户文档包含数组字段 address_ids ,其中包含对应地址的 ObjectId。使用这些 ObjectId,我们可以查询地址文档并从中获取地址详细信息。使用此方法,我们需要两个查询:首先从 user 文档中获取 address_ids 字段,其次从 address 集合中获取这些地址。
As shown above, the user document contains the array field address_ids which contains ObjectIds of corresponding addresses. Using these ObjectIds, we can query the address documents and get address details from there. With this approach, we will need two queries: first to fetch the address_ids fields from user document and second to fetch these addresses from address collection.
>var result = db.users.findOne({"name":"Tom Benzamin"},{"address_ids":1})
>var addresses = db.address.find({"_id":{"$in":result["address_ids"]}})MongoDB - Database References
如 MongoDB 关系的最后一章中所述,为了在 MongoDB 中实现规范化的数据库结构,我们使用了称为 Referenced Relationships (在中也称为 Manual References )的概念,其中我们手动存储其他文档 ID 被引用的文档。但是,如果一份文档包含来自不同集合的引用,则我们可以使用 MongoDB DBRefs 。
As seen in the last chapter of MongoDB relationships, to implement a normalized database structure in MongoDB, we use the concept of Referenced Relationships also referred to as Manual References in which we manually store the referenced document’s id inside other document. However, in cases where a document contains references from different collections, we can use MongoDB DBRefs.
DBRefs vs Manual References
作为示例场景,我们在其中使用 DBRefs 而不是手动引用,考虑一个数据库,其中我们在不同的集合(address_home、address_office、address_mailing 等)中存储不同类型的地址(家庭、办公室、邮件等)。现在,当 user 集合的文档引用地址时,它还需要根据地址类型指定要查找的集合。在文档引用来自多个集合的文档的此类场景中,我们应该使用 DBRefs。
As an example scenario, where we would use DBRefs instead of manual references, consider a database where we are storing different types of addresses (home, office, mailing, etc.) in different collections (address_home, address_office, address_mailing, etc). Now, when a user collection’s document references an address, it also needs to specify which collection to look into based on the address type. In such scenarios where a document references documents from many collections, we should use DBRefs.
Using DBRefs
DBRefs 中有三个字段 −
There are three fields in DBRefs −
-
$ref − This field specifies the collection of the referenced document
-
$id − This field specifies the _id field of the referenced document
-
$db − This is an optional field and contains the name of the database in which the referenced document lies
考虑一个示例用户文档,其中 DBRef 字段 address ,如代码片段所示 −
Consider a sample user document having DBRef field address as shown in the code snippet −
{
"_id":ObjectId("53402597d852426020000002"),
"address": {
"$ref": "address_home",
"$id": ObjectId("534009e4d852427820000002"),
"$db": "tutorialspoint"},
"contact": "987654321",
"dob": "01-01-1991",
"name": "Tom Benzamin"
}address 此处的 DBRef 字段指定引用的地址文档位于 address_home 数据库下的 tutorialspoint 集合中,并且 ID 为 534009e4d852427820000002。
The address DBRef field here specifies that the referenced address document lies in address_home collection under tutorialspoint database and has an id of 534009e4d852427820000002.
以下代码根据 $ref 参数(在我们的示例中为 address_home )指定的集合中动态查找文档,其中 ID 为 DBRef 中的 $id 参数指定。
The following code dynamically looks in the collection specified by $ref parameter (address_home in our case) for a document with id as specified by $id parameter in DBRef.
>var user = db.users.findOne({"name":"Tom Benzamin"})
>var dbRef = user.address
>db[dbRef.$ref].findOne({"_id":(dbRef.$id)})上面的代码返回存在于 address_home 集合中的以下地址文档 −
The above code returns the following address document present in address_home collection −
{
"_id" : ObjectId("534009e4d852427820000002"),
"building" : "22 A, Indiana Apt",
"pincode" : 123456,
"city" : "Los Angeles",
"state" : "California"
}MongoDB - Covered Queries
在本章中,我们将了解覆盖查询。
In this chapter, we will learn about covered queries.
What is a Covered Query?
根据官方 MongoDB 文档,覆盖查询是一个查询,其中 −
As per the official MongoDB documentation, a covered query is a query in which −
-
All the fields in the query are part of an index.
-
All the fields returned in the query are in the same index.
由于查询中显示的所有字段都是索引的一部分,因此 MongoDB 匹配查询条件并使用同一索引返回结果,而无需实际查看文档内部。由于索引存在于 RAM 中,所以与通过扫描文档获取数据相比,从索引中获取数据快得多。
Since all the fields present in the query are part of an index, MongoDB matches the query conditions and returns the result using the same index without actually looking inside the documents. Since indexes are present in RAM, fetching data from indexes is much faster as compared to fetching data by scanning documents.
Using Covered Queries
要测试覆盖查询,请考虑 users 集合中的以下文档 −
To test covered queries, consider the following document in the users collection −
{
"_id": ObjectId("53402597d852426020000002"),
"contact": "987654321",
"dob": "01-01-1991",
"gender": "M",
"name": "Tom Benzamin",
"user_name": "tombenzamin"
}我们首先使用以下查询在 users 集合的 gender 和 user_name 字段上创建复合索引 −
We will first create a compound index for the users collection on the fields gender and user_name using the following query −
>db.users.ensureIndex({gender:1,user_name:1})现在,此索引将涵盖以下查询 −
Now, this index will cover the following query −
>db.users.find({gender:"M"},{user_name:1,_id:0})也就是说,对于上面的查询,MongoDB 不会进入数据库文档中查找。相反,它将从索引数据中获取必需的数据,这是非常快速的。
That is to say that for the above query, MongoDB would not go looking into database documents. Instead it would fetch the required data from indexed data which is very fast.
由于我们的索引不包含 _id 字段,因此我们已将其明确地从查询结果集中排除,因为 MongoDB 默认在每个查询中返回 _id 字段。因此,以下查询不会覆盖在上面创建的索引中 −
Since our index does not include _id field, we have explicitly excluded it from result set of our query, as MongoDB by default returns _id field in every query. So the following query would not have been covered inside the index created above −
>db.users.find({gender:"M"},{user_name:1})最后,请记住,如果 −
Lastly, remember that an index cannot cover a query if −
-
Any of the indexed fields is an array
-
Any of the indexed fields is a subdocument
MongoDB - Analyzing Queries
分析查询是衡量数据库和索引设计有效性的一个非常重要的方面。我们来了解一下经常使用的 $explain 和 $hint 查询。
Analyzing queries is a very important aspect of measuring how effective the database and indexing design is. We will learn about the frequently used $explain and $hint queries.
Using $explain
$explain 运算符提供有关查询、查询中使用的索引以及其他统计信息的信息。分析索引的优化程度时,此运算符非常有用。
The $explain operator provides information on the query, indexes used in a query and other statistics. It is very useful when analyzing how well your indexes are optimized.
在上一章中,我们已经使用以下查询在字段 gender 和 user_name 上为 users 集合创建了一个索引:
In the last chapter, we had already created an index for the users collection on fields gender and user_name using the following query −
>db.users.ensureIndex({gender:1,user_name:1})我们现在将对以下查询使用 $explain :
We will now use $explain on the following query −
>db.users.find({gender:"M"},{user_name:1,_id:0}).explain()上述 explain() 查询返回以下分析结果:
The above explain() query returns the following analyzed result −
{
"cursor" : "BtreeCursor gender_1_user_name_1",
"isMultiKey" : false,
"n" : 1,
"nscannedObjects" : 0,
"nscanned" : 1,
"nscannedObjectsAllPlans" : 0,
"nscannedAllPlans" : 1,
"scanAndOrder" : false,
"indexOnly" : true,
"nYields" : 0,
"nChunkSkips" : 0,
"millis" : 0,
"indexBounds" : {
"gender" : [
[
"M",
"M"
]
],
"user_name" : [
[
{
"$minElement" : 1
},
{
"$maxElement" : 1
}
]
]
}
}我们现在将查看此结果集中的字段:
We will now look at the fields in this result set −
-
The true value of indexOnly indicates that this query has used indexing.
-
The cursor field specifies the type of cursor used. BTreeCursor type indicates that an index was used and also gives the name of the index used. BasicCursor indicates that a full scan was made without using any indexes.
-
n indicates the number of documents matching returned.
-
nscannedObjects indicates the total number of documents scanned.
-
nscanned indicates the total number of documents or index entries scanned.
Using $hint
$hint 运算符强制查询优化器使用指定的索引来运行查询。当你想要测试具有不同索引的查询性能时,这尤其有用。例如,以下查询指定在字段 gender 和 user_name 上的索引用于该查询:
The $hint operator forces the query optimizer to use the specified index to run a query. This is particularly useful when you want to test performance of a query with different indexes. For example, the following query specifies the index on fields gender and user_name to be used for this query −
>db.users.find({gender:"M"},{user_name:1,_id:0}).hint({gender:1,user_name:1})要使用 $explain 分析以上查询:
To analyze the above query using $explain −
>db.users.find({gender:"M"},{user_name:1,_id:0}).hint({gender:1,user_name:1}).explain()MongoDB - Atomic Operations
Model Data for Atomic Operations
推荐的原子性维护方法是将所有相关信息保存在使用 embedded documents 的单文档中,该文档经常一起更新。这将确保针对单文档的所有更新都是原子的。
The recommended approach to maintain atomicity would be to keep all the related information, which is frequently updated together in a single document using embedded documents. This would make sure that all the updates for a single document are atomic.
考虑以下产品文档——
Consider the following products document −
{
"_id":1,
"product_name": "Samsung S3",
"category": "mobiles",
"product_total": 5,
"product_available": 3,
"product_bought_by": [
{
"customer": "john",
"date": "7-Jan-2014"
},
{
"customer": "mark",
"date": "8-Jan-2014"
}
]
}在此文档中,我们已将购买该产品的客户信息嵌入到 product_bought_by 域中。现在,每当有新客户购买该产品时,我们首先会使用 product_available 域检查该产品是否仍然可用。如果可用,我们将减小 product_available 域的值,并在 product_bought_by 域中插入新客户的嵌入式文档。我们将为此功能使用 findAndModify 命令,因为它在同一执行步骤中搜索并更新文档。
In this document, we have embedded the information of the customer who buys the product in the product_bought_by field. Now, whenever a new customer buys the product, we will first check if the product is still available using product_available field. If available, we will reduce the value of product_available field as well as insert the new customer’s embedded document in the product_bought_by field. We will use findAndModify command for this functionality because it searches and updates the document in the same go.
>db.products.findAndModify({
query:{_id:2,product_available:{$gt:0}},
update:{
$inc:{product_available:-1},
$push:{product_bought_by:{customer:"rob",date:"9-Jan-2014"}}
}
})我们的嵌入式文档方法和使用 findAndModify 查询可确保仅在产品可用时才会更新产品购买信息。而且,这项事务的全部内容都在同一查询中,是原子的。
Our approach of embedded document and using findAndModify query makes sure that the product purchase information is updated only if it the product is available. And the whole of this transaction being in the same query, is atomic.
与之相反,考虑一下可能将产品可用性和关于谁已购买该产品的信息分开保存的情况。在这种情况下,我们将首先使用第一个查询检查产品是否可用。然后,在第二个查询中,我们将更新购买信息。然而,在执行这两个查询的过程中,另一些用户可能已购买该产品,而产品已不再可用。在不知道这种情况之下,我们的第二个查询将根据第一个查询的结果更新购买信息。这将使数据库不一致,因为我们已销售了不可用的产品。
In contrast to this, consider the scenario where we may have kept the product availability and the information on who has bought the product, separately. In this case, we will first check if the product is available using the first query. Then in the second query we will update the purchase information. However, it is possible that between the executions of these two queries, some other user has purchased the product and it is no more available. Without knowing this, our second query will update the purchase information based on the result of our first query. This will make the database inconsistent because we have sold a product which is not available.
MongoDB - Advanced Indexing
考虑以下 users 集合的文档——
Consider the following document of the users collection −
{
"address": {
"city": "Los Angeles",
"state": "California",
"pincode": "123"
},
"tags": [
"music",
"cricket",
"blogs"
],
"name": "Tom Benzamin"
}上述文档包含一个 address sub-document 和一个 tags array 。
The above document contains an address sub-document and a tags array.
Indexing Array Fields
假设我们希望根据用户的标签搜索用户文档。为此,我们将在集合中的 tags 数组上创建一个索引。
Suppose we want to search user documents based on the user’s tags. For this, we will create an index on tags array in the collection.
依次在数组上创建索引会针对其每个字段创建单独的索引项。因此,当我们在 tags 数组上创建索引时,将针对其值 music、cricket 和 blogs 创建单独的索引。
Creating an index on array in turn creates separate index entries for each of its fields. So in our case when we create an index on tags array, separate indexes will be created for its values music, cricket and blogs.
若要针对 tags 数组创建索引,请使用下列代码:
To create an index on tags array, use the following code −
>db.users.ensureIndex({"tags":1})创建索引后,我们可以像这样搜索集合的 tags 字段:
After creating the index, we can search on the tags field of the collection like this −
>db.users.find({tags:"cricket"})若要验证使用了正确的索引,请使用下列 explain 命令:
To verify that proper indexing is used, use the following explain command −
>db.users.find({tags:"cricket"}).explain()上述命令生成的 "cursor" : "BtreeCursor tags_1" 证实使用了正确的索引。
The above command resulted in "cursor" : "BtreeCursor tags_1" which confirms that proper indexing is used.
Indexing Sub-Document Fields
假设我们希望根据 city、state 和 pincode 字段搜索文档。由于所有这些字段都是 address 子文档字段的一部分,我们将针对子文档的所有字段创建一个索引。
Suppose that we want to search documents based on city, state and pincode fields. Since all these fields are part of address sub-document field, we will create an index on all the fields of the sub-document.
若要针对子文档的所有三个字段创建索引,请使用下列代码:
For creating an index on all the three fields of the sub-document, use the following code −
>db.users.ensureIndex({"address.city":1,"address.state":1,"address.pincode":1})在创建索引后,我们可以利用这个索引搜索任何子文档字段,如下: −
Once the index is created, we can search for any of the sub-document fields utilizing this index as follows −
>db.users.find({"address.city":"Los Angeles"})记住,查询表达式必须遵循指定的索引顺序。因此,上面创建的索引将支持以下查询 −
Remember that the query expression has to follow the order of the index specified. So the index created above would support the following queries −
>db.users.find({"address.city":"Los Angeles","address.state":"California"})它还将支持以下查询——
It will also support the following query −
>db.users.find({"address.city":"LosAngeles","address.state":"California",
"address.pincode":"123"})MongoDB - Indexing Limitations
在本章中,我们将了解索引限制及其其他组件。
In this chapter, we will learn about Indexing Limitations and its other components.
Extra Overhead
每个索引都会占用一些空间,并导致每个插入、更新和删除操作产生开销。因此,如果你很少将你的集合用于读取操作,那么不使用索引是有道理的。
Every index occupies some space as well as causes an overhead on each insert, update and delete. So if you rarely use your collection for read operations, it makes sense not to use indexes.
RAM Usage
由于索引存储在 RAM 中,因此你应该确保索引的总大小不超过 RAM 限制。如果总大小增加到超过 RAM 大小,它将开始删除某些索引,导致性能下降。
Since indexes are stored in RAM, you should make sure that the total size of the index does not exceed the RAM limit. If the total size increases the RAM size, it will start deleting some indexes, causing performance loss.
Query Limitations
索引无法用于使用以下内容的查询中 −
Indexing can’t be used in queries which use −
-
Regular expressions or negation operators like $nin, $not, etc.
-
Arithmetic operators like $mod, etc.
-
$where clause
因此,建议始终检查查询的索引用法。
Hence, it is always advisable to check the index usage for your queries.
Index Key Limits
从 2.6 版本开始,如果现有索引字段的值超过索引键限制,MongoDB 将不会创建索引。
Starting from version 2.6, MongoDB will not create an index if the value of existing index field exceeds the index key limit.
Inserting Documents Exceeding Index Key Limit
如果文档的索引字段值超过索引键限制,MongoDB 将不会插入任何文档到索引集合中。对于 mongorestore 和 mongoimport 实用程序也有同样的情况。
MongoDB will not insert any document into an indexed collection if the indexed field value of this document exceeds the index key limit. Same is the case with mongorestore and mongoimport utilities.
MongoDB - ObjectId
在所有前面的章节中,我们一直在使用 MongoDB 对象 Id。在本章中,我们将了解 ObjectId 的结构。
We have been using MongoDB Object Id in all the previous chapters. In this chapter, we will understand the structure of ObjectId.
ObjectId 是一个 12 字节 BSON 类型,具有以下结构: −
An ObjectId is a 12-byte BSON type having the following structure −
-
The first 4 bytes representing the seconds since the unix epoch
-
The next 3 bytes are the machine identifier
-
The next 2 bytes consists of process id
-
The last 3 bytes are a random counter value
MongoDB 使用 ObjectId 作为每个文档的 _id 字段的默认值,该值是在创建任何文档时生成的。ObjectId 的复杂组合使所有 _id 字段都是唯一的。
MongoDB uses ObjectIds as the default value of _id field of each document, which is generated while the creation of any document. The complex combination of ObjectId makes all the _id fields unique.
Creating New ObjectId
若要生成一个新的 ObjectId,请使用以下代码: −
To generate a new ObjectId use the following code −
>newObjectId = ObjectId()上面的语句返回了以下唯一生成的 id: −
The above statement returned the following uniquely generated id −
ObjectId("5349b4ddd2781d08c09890f3")除了让 MongoDB 生成 ObjectId 外,您还可以提供一个 12 字节的 id: −
Instead of MongoDB generating the ObjectId, you can also provide a 12-byte id −
>myObjectId = ObjectId("5349b4ddd2781d08c09890f4")Creating Timestamp of a Document
由于 _id ObjectId 默认存储 4 字节的时间戳,因此在大多数情况下,您不需要存储任何文档的创建时间。您可以使用 getTimestamp 方法获取文档的创建时间: −
Since the _id ObjectId by default stores the 4-byte timestamp, in most cases you do not need to store the creation time of any document. You can fetch the creation time of a document using getTimestamp method −
>ObjectId("5349b4ddd2781d08c09890f4").getTimestamp()这将以 ISO 日期格式返回此文档的创建时间: −
This will return the creation time of this document in ISO date format −
ISODate("2014-04-12T21:49:17Z")Converting ObjectId to String
在某些情况下,您可能需要 ObjectId 在字符串格式中的值。若要将 ObjectId 转换为字符串,请使用以下代码: −
In some cases, you may need the value of ObjectId in a string format. To convert the ObjectId in string, use the following code −
>newObjectId.str上面的代码将返回 Guid 的字符串格式: −
The above code will return the string format of the Guid −
5349b4ddd2781d08c09890f3MongoDB - Map Reduce
根据 MongoDB 文档, Map-reduce 是一个用于将大量数据浓缩为有用的聚合结果的数据处理范例。MongoDB 使用 mapReduce 命令用于 map-reduce 操作。MapReduce 通常用于处理大型数据集。
As per the MongoDB documentation, Map-reduce is a data processing paradigm for condensing large volumes of data into useful aggregated results. MongoDB uses mapReduce command for map-reduce operations. MapReduce is generally used for processing large data sets.
MapReduce Command
以下是基本 mapReduce 命令的语法:
Following is the syntax of the basic mapReduce command −
>db.collection.mapReduce(
function() {emit(key,value);}, //map function
function(key,values) {return reduceFunction}, { //reduce function
out: collection,
query: document,
sort: document,
limit: number
}
)map-reduce 函数首先查询集合,然后映射结果文档以发出键值对,这些键值对接着基于具有多个值的键进行化简。
The map-reduce function first queries the collection, then maps the result documents to emit key-value pairs, which is then reduced based on the keys that have multiple values.
在以上语法中 −
In the above syntax −
-
map is a javascript function that maps a value with a key and emits a key-value pair
-
reduce is a javascript function that reduces or groups all the documents having the same key
-
out specifies the location of the map-reduce query result
-
query specifies the optional selection criteria for selecting documents
-
sort specifies the optional sort criteria
-
limit specifies the optional maximum number of documents to be returned
Using MapReduce
考虑存储用户帖子的以下文档结构。文档存储用户的 user_name 和帖子的状态。
Consider the following document structure storing user posts. The document stores user_name of the user and the status of post.
{
"post_text": "tutorialspoint is an awesome website for tutorials",
"user_name": "mark",
"status":"active"
}现在,我们将在 posts 集合上使用 mapReduce 函数,以选择所有处于活动状态的帖子,根据 user_name 分组,然后使用以下代码按每个用户计算帖子的数量 −
Now, we will use a mapReduce function on our posts collection to select all the active posts, group them on the basis of user_name and then count the number of posts by each user using the following code −
>db.posts.mapReduce(
function() { emit(this.user_id,1); },
function(key, values) {return Array.sum(values)}, {
query:{status:"active"},
out:"post_total"
}
)上面的 mapReduce 查询输出以下结果 −
The above mapReduce query outputs the following result −
{
"result" : "post_total",
"timeMillis" : 9,
"counts" : {
"input" : 4,
"emit" : 4,
"reduce" : 2,
"output" : 2
},
"ok" : 1,
}结果表明共有 4 份文档符合查询条件 (status:"active"),映射函数发出了 4 份文档,带有键值对,最后化简函数将具有相同键的已映射文档分组为 2。
The result shows that a total of 4 documents matched the query (status:"active"), the map function emitted 4 documents with key-value pairs and finally the reduce function grouped mapped documents having the same keys into 2.
要查看此 mapReduce 查询的结果,请使用 find 运算符 −
To see the result of this mapReduce query, use the find operator −
>db.posts.mapReduce(
function() { emit(this.user_id,1); },
function(key, values) {return Array.sum(values)}, {
query:{status:"active"},
out:"post_total"
}
).find()上面的查询给出了以下结果,表明用户 tom 和 mark 都在活动状态下有两篇帖子 −
The above query gives the following result which indicates that both users tom and mark have two posts in active states −
{ "_id" : "tom", "value" : 2 }
{ "_id" : "mark", "value" : 2 }以类似的方式,可以使用 MapReduce 查询来构建大型的复杂聚合查询。使用自定义的 Javascript 函数可以利用 MapReduce,它非常灵活且强大。
In a similar manner, MapReduce queries can be used to construct large complex aggregation queries. The use of custom Javascript functions make use of MapReduce which is very flexible and powerful.
MongoDB - Text Search
从 2.4 版本开始,MongoDB 开始支持文本索引以搜索字符串内容。 Text Search 使用词干提取技巧在字符串字段中查找指定词语,方法是省略诸如 a, an, the, 这样的词干停用词。目前,MongoDB 支持约 15 种语言。
Starting from version 2.4, MongoDB started supporting text indexes to search inside string content. The Text Search uses stemming techniques to look for specified words in the string fields by dropping stemming stop words like a, an, the, etc. At present, MongoDB supports around 15 languages.
Enabling Text Search
最初,文本搜索是一项实验性功能,但从 2.6 版本开始,该配置默认启用。但是,如果你使用的是以前版本的 MongoDB,则必须通过以下代码启用文本搜索——
Initially, Text Search was an experimental feature but starting from version 2.6, the configuration is enabled by default. But if you are using the previous version of MongoDB, you have to enable text search with the following code −
>db.adminCommand({setParameter:true,textSearchEnabled:true})Creating Text Index
考虑以下 posts 集合中的文档,它包含文章文本及其标签——
Consider the following document under posts collection containing the post text and its tags −
{
"post_text": "enjoy the mongodb articles on tutorialspoint",
"tags": [
"mongodb",
"tutorialspoint"
]
}我们将在 post_text 字段上创建一个文本索引以便我们可以在文章的文本中进行搜索——
We will create a text index on post_text field so that we can search inside our posts' text −
>db.posts.ensureIndex({post_text:"text"})Using Text Index
现在我们在 post_text 字段上创建了文本索引,我们将在其文本中搜索所有包含单词 tutorialspoint 的文章。
Now that we have created the text index on post_text field, we will search for all the posts having the word tutorialspoint in their text.
>db.posts.find({$text:{$search:"tutorialspoint"}})上面的命令返回了以下结果文档,它们在文章文本中包含单词 tutorialspoint ——
The above command returned the following result documents having the word tutorialspoint in their post text −
{
"_id" : ObjectId("53493d14d852429c10000002"),
"post_text" : "enjoy the mongodb articles on tutorialspoint",
"tags" : [ "mongodb", "tutorialspoint" ]
}
{
"_id" : ObjectId("53493d1fd852429c10000003"),
"post_text" : "writing tutorials on mongodb",
"tags" : [ "mongodb", "tutorial" ]
}如果你正在使用旧版本 MongoDB,则必须使用以下命令——
If you are using old versions of MongoDB, you have to use the following command −
>db.posts.runCommand("text",{search:" tutorialspoint "})与普通搜索相比,使用文本搜索极大地提高了搜索效率。
Using Text Search highly improves the search efficiency as compared to normal search.
Deleting Text Index
要删除现有文本索引,首先使用以下查询查找索引的名称——
To delete an existing text index, first find the name of index using the following query −
>db.posts.getIndexes()在上面的查询中获取索引的名称后,运行以下命令。在这里, post_text_text 是索引的名称。
After getting the name of your index from above query, run the following command. Here, post_text_text is the name of the index.
>db.posts.dropIndex("post_text_text")MongoDB - Regular Expression
正则表达式经常用于各种语言中,以在任意字符串中搜索某个模式或单词。MongoDB 还提供正则表达式功能,用于使用 $regex 运算符进行字符串模式匹配。MongoDB 将 PCRE(Perl 兼容正则表达式)用作正则表达式语言。
Regular Expressions are frequently used in all languages to search for a pattern or word in any string. MongoDB also provides functionality of regular expression for string pattern matching using the $regex operator. MongoDB uses PCRE (Perl Compatible Regular Expression) as regular expression language.
不同于文本搜索,我们无需执行任何配置或命令即可使用正则表达式。
Unlike text search, we do not need to do any configuration or command to use regular expressions.
考虑 posts 集合中以下文档结构,它包含文章文本及其标签——
Consider the following document structure under posts collection containing the post text and its tags −
{
"post_text": "enjoy the mongodb articles on tutorialspoint",
"tags": [
"mongodb",
"tutorialspoint"
]
}Using regex Expression
以下正则表达式查询搜索其中包含字符串 tutorialspoint 的所有帖子:
The following regex query searches for all the posts containing string tutorialspoint in it −
>db.posts.find({post_text:{$regex:"tutorialspoint"}})同样的查询还可以这样编写:
The same query can also be written as −
>db.posts.find({post_text:/tutorialspoint/})Using regex Expression with Case Insensitive
要使搜索不区分大小写,我们可以使用值 $i 的 $options 参数。以下命令无论大小写都会查找包含单词 tutorialspoint 的字符串:
To make the search case insensitive, we use the $options parameter with value $i. The following command will look for strings having the word tutorialspoint, irrespective of smaller or capital case −
>db.posts.find({post_text:{$regex:"tutorialspoint",$options:"$i"}})此查询返回的结果之一是包含单词 tutorialspoint (大小写不一致)的以下文档:
One of the results returned from this query is the following document which contains the word tutorialspoint in different cases −
{
"_id" : ObjectId("53493d37d852429c10000004"),
"post_text" : "hey! this is my post on TutorialsPoint",
"tags" : [ "tutorialspoint" ]
}Using regex for Array Elements
我们还可以在数组字段上使用正则表达式概念。当我们实现标签功能时,这尤其重要。因此,如果要搜索所有标签以单词教程(教程、教程或 tutorialpoint 或 tutorialphp)开头的帖子,可以使用以下代码:
We can also use the concept of regex on array field. This is particularly very important when we implement the functionality of tags. So, if you want to search for all the posts having tags beginning from the word tutorial (either tutorial or tutorials or tutorialpoint or tutorialphp), you can use the following code −
>db.posts.find({tags:{$regex:"tutorial"}})Optimizing Regular Expression Queries
-
If the document fields are indexed, the query will use make use of indexed values to match the regular expression. This makes the search very fast as compared to the regular expression scanning the whole collection.
-
If the regular expression is a prefix expression, all the matches are meant to start with a certain string characters. For e.g., if the regex expression is ^tut, then the query has to search for only those strings that begin with tut.
Working with RockMongo
RockMongo 是一款 MongoDB 管理工具,您可以使用它来管理服务器、数据库、集合、文档、索引以及更多内容。它提供了非常用户友好的方式来读取、写入和创建文档。它类似于用于 PHP 和 MySQL 的 PHPMyAdmin 工具。
RockMongo is a MongoDB administration tool using which you can manage your server, databases, collections, documents, indexes, and a lot more. It provides a very user-friendly way for reading, writing, and creating documents. It is similar to PHPMyAdmin tool for PHP and MySQL.
Downloading RockMongo
您可以从此处下载最新版的 RockMongo: https://github.com/iwind/rockmongo
You can download the latest version of RockMongo from here: https://github.com/iwind/rockmongo
Installing RockMongo
下载后,您可以将软件包解压缩到服务器根文件夹中,并将提取的文件夹重命名为 rockmongo 。打开任意 Web 浏览器,并从 rockmongo 文件夹中访问 index.php 页面。分别输入 admin/admin 作为用户名/密码。
Once downloaded, you can unzip the package in your server root folder and rename the extracted folder to rockmongo. Open any web browser and access the index.php page from the folder rockmongo. Enter admin/admin as username/password respectively.
Working with RockMongo
现在我们将了解可以在 RockMongo 中执行的一些基本操作。
We will now be looking at some basic operations that you can perform with RockMongo.
Creating New Database
要创建新数据库,请单击 Databases 选项卡。单击 Create New Database 。在下一个屏幕上,提供新数据库的名称,然后单击 Create 。您将看到在左面板中添加了一个新数据库。
To create a new database, click Databases tab. Click Create New Database. On the next screen, provide the name of the new database and click on Create. You will see a new database getting added in the left panel.
Creating New Collection
要在数据库内创建新集合,请从左面板中单击该数据库。单击顶部的 New Collection 链接。提供所需的集合名称。不必担心 Is Capped、Size 和 Max 的其他字段。单击 Create 。系统将创建一个新集合,您将在左面板中看到它。
To create a new collection inside a database, click on that database from the left panel. Click on the New Collection link on top. Provide the required name of the collection. Do not worry about the other fields of Is Capped, Size and Max. Click on Create. A new collection will be created and you will be able to see it in the left panel.
Creating New Document
要创建新文档,请单击想要在其中添加文档的集合。当您单击某个集合时,您将可以看到该集合内列出的所有文档。要创建新文档,请单击顶部的 Insert 链接。您可以采用 JSON 或数组格式输入文档数据,然后单击 Save 。
To create a new document, click on the collection under which you want to add documents. When you click on a collection, you will be able to see all the documents within that collection listed there. To create a new document, click on the Insert link at the top. You can enter the document’s data either in JSON or array format and click on Save.
Export/Import Data
要导入/导出任意集合的数据,请单击该集合,然后单击顶部面板中的 Export/Import 链接。按照后续说明,以 zip 格式导出数据,然后导入同一 zip 文件以重新导入数据。
To import/export data of any collection, click on that collection and then click on Export/Import link on the top panel. Follow the next instructions to export your data in a zip format and then import the same zip file to import back data.
MongoDB - GridFS
GridFS 是 MongoDB 用于存储和检索图像、音频文件、视频文件等大型文件而制定的规范。它是一种用于存储文件的类似文件系统,但其数据储存在 MongoDB 集合内。GridFS 的能力是存储大小甚至超过其 16MB 文档大小限制的文件。
GridFS is the MongoDB specification for storing and retrieving large files such as images, audio files, video files, etc. It is kind of a file system to store files but its data is stored within MongoDB collections. GridFS has the capability to store files even greater than its document size limit of 16MB.
GridFS 将文件分成区块,并将各个数据块存储在一个单独的文件中,每个文件的大小最大为 255k。
GridFS divides a file into chunks and stores each chunk of data in a separate document, each of maximum size 255k.
GridFS 默认使用两个集合 fs.files 和 fs.chunks 来存储文件的元数据和区块。每个区块通过其唯一的_id ObjectId字段进行标识。fs.files充当父文档。fs.chunks文档中的 files_id 字段链接区块到其父文档。
GridFS by default uses two collections fs.files and fs.chunks to store the file’s metadata and the chunks. Each chunk is identified by its unique _id ObjectId field. The fs.files serves as a parent document. The files_id field in the fs.chunks document links the chunk to its parent.
以下是一个示例文档fs.files集合 −
Following is a sample document of fs.files collection −
{
"filename": "test.txt",
"chunkSize": NumberInt(261120),
"uploadDate": ISODate("2014-04-13T11:32:33.557Z"),
"md5": "7b762939321e146569b07f72c62cca4f",
"length": NumberInt(646)
}文档指定文件名、区块大小、上传日期和长度。
The document specifies the file name, chunk size, uploaded date, and length.
以下是一个示例文档fs.chunks文档 −
Following is a sample document of fs.chunks document −
{
"files_id": ObjectId("534a75d19f54bfec8a2fe44b"),
"n": NumberInt(0),
"data": "Mongo Binary Data"
}Adding Files to GridFS
现在,我们将使用 put 命令通过GridFS存储一个mp3文件。为此,我们将使用MongoDB安装文件夹的bin文件夹中存在的 mongofiles.exe 实用程序。
Now, we will store an mp3 file using GridFS using the put command. For this, we will use the mongofiles.exe utility present in the bin folder of the MongoDB installation folder.
打开命令提示符,导航到MongoDB安装文件夹的bin文件夹中的mongofiles.exe,然后键入以下代码 −
Open your command prompt, navigate to the mongofiles.exe in the bin folder of MongoDB installation folder and type the following code −
>mongofiles.exe -d gridfs put song.mp3这里, gridfs 是存储文件的数据库的名称。如果没有数据库,MongoDB将自动创建新的文档。Song.mp3是上传文件的名称。若要查看文件在数据库中的文档,可以使用find查询 −
Here, gridfs is the name of the database in which the file will be stored. If the database is not present, MongoDB will automatically create a new document on the fly. Song.mp3 is the name of the file uploaded. To see the file’s document in database, you can use find query −
>db.fs.files.find()上述命令返回了以下文档 −
The above command returned the following document −
{
_id: ObjectId('534a811bf8b4aa4d33fdf94d'),
filename: "song.mp3",
chunkSize: 261120,
uploadDate: new Date(1397391643474), md5: "e4f53379c909f7bed2e9d631e15c1c41",
length: 10401959
}我们还可以使用上一个查询返回的文档id,使用以下代码看到与存储文件相关的fs.chunks集合中存在的所有区块 −
We can also see all the chunks present in fs.chunks collection related to the stored file with the following code, using the document id returned in the previous query −
>db.fs.chunks.find({files_id:ObjectId('534a811bf8b4aa4d33fdf94d')})在我的情况下,查询返回了40个文档,这意味着整个mp3文档被分成了40个数据区块。
In my case, the query returned 40 documents meaning that the whole mp3 document was divided in 40 chunks of data.
MongoDB - Capped Collections
Capped collections 是固定大小的循环集合,它遵循插入顺序来支持高性能创建、读取和删除操作。循环是指当分配给集合的固定大小用尽时,它将开始删除集合中最旧的文档,而无需提供任何显式命令。
Capped collections are fixed-size circular collections that follow the insertion order to support high performance for create, read, and delete operations. By circular, it means that when the fixed size allocated to the collection is exhausted, it will start deleting the oldest document in the collection without providing any explicit commands.
固定大小集合限制了文档的更新,如果更新会导致文档大小增加。由于固定大小集合按磁盘存储的顺序存储文档,因此它确保文档大小不会增加磁盘分配的大小。固定大小集合最适合存储日志信息、缓存数据或任何其他高容量数据。
Capped collections restrict updates to the documents if the update results in increased document size. Since capped collections store documents in the order of the disk storage, it ensures that the document size does not increase the size allocated on the disk. Capped collections are best for storing log information, cache data, or any other high volume data.
Creating Capped Collection
要创建固定大小集合,我们使用常规 createCollection 命令,但使用 capped 选项为 true ,并指定集合的最大大小(以字节为单位)。
To create a capped collection, we use the normal createCollection command but with capped option as true and specifying the maximum size of collection in bytes.
>db.createCollection("cappedLogCollection",{capped:true,size:10000})除了集合大小之外,我们还可以使用 max 参数限制集合中的文档数量:
In addition to collection size, we can also limit the number of documents in the collection using the max parameter −
>db.createCollection("cappedLogCollection",{capped:true,size:10000,max:1000})如果你想检查一个集合是否固定大小, hãy使用以下 isCapped 命令:
If you want to check whether a collection is capped or not, use the following isCapped command −
>db.cappedLogCollection.isCapped()如果有一个你正在计划转换为固定大小的现有集合,你可以使用以下代码执行:
If there is an existing collection which you are planning to convert to capped, you can do it with the following code −
>db.runCommand({"convertToCapped":"posts",size:10000})此代码会将我们现有的集合 posts 转换为固定大小集合。
This code would convert our existing collection posts to a capped collection.
Querying Capped Collection
默认情况下,对固定大小集合执行的 find 查询将按插入顺序显示结果。但是,如果你希望反向检索文档,请使用 sort 命令,如下代码所示:
By default, a find query on a capped collection will display results in insertion order. But if you want the documents to be retrieved in reverse order, use the sort command as shown in the following code −
>db.cappedLogCollection.find().sort({$natural:-1})关于固定大小集合还有一些其他值得了解的重要事项:
There are few other important points regarding capped collections worth knowing −
-
We cannot delete documents from a capped collection.
-
There are no default indexes present in a capped collection, not even on _id field.
-
While inserting a new document, MongoDB does not have to actually look for a place to accommodate new document on the disk. It can blindly insert the new document at the tail of the collection. This makes insert operations in capped collections very fast.
-
Similarly, while reading documents MongoDB returns the documents in the same order as present on disk. This makes the read operation very fast.
MongoDB - Auto-Increment Sequence
MongoDB 没有像 SQL 数据库那样的开箱即用的自增功能。默认情况下,它使用 12 字节的 ObjectId 作为 _id 字段以唯一标识文档。但是,在某些情况下,我们可能希望 _id 字段具有 ObjectId 之外的某个自增值。
MongoDB does not have out-of-the-box auto-increment functionality, like SQL databases. By default, it uses the 12-byte ObjectId for the _id field as the primary key to uniquely identify the documents. However, there may be scenarios where we may want the _id field to have some auto-incremented value other than the ObjectId.
由于这不是 MongoDB 中的默认功能,我们将按照 MongoDB 文档中的建议使用 counters 集合编程来实现此功能。
Since this is not a default feature in MongoDB, we will programmatically achieve this functionality by using a counters collection as suggested by the MongoDB documentation.
Using Counter Collection
考虑一下以下 products 文档。我们希望 _id 字段从 1、2、3、4 到 n 都自增。
Consider the following products document. We want the _id field to be an auto-incremented integer sequence starting from 1,2,3,4 upto n.
{
"_id":1,
"product_name": "Apple iPhone",
"category": "mobiles"
}为此,创建一个 counters 集合,它将跟踪所有序列字段的最后一个序列值。
For this, create a counters collection, which will keep track of the last sequence value for all the sequence fields.
>db.createCollection("counters")现在,我们将使用 productid 作为其键将以下文档插入到计数器集合中 −
Now, we will insert the following document in the counters collection with productid as its key −
{
"_id":"productid",
"sequence_value": 0
}字段 sequence_value 跟踪序列的最后一个值。
The field sequence_value keeps track of the last value of the sequence.
使用以下代码将此序列文档插入计数器集合中 −
Use the following code to insert this sequence document in the counters collection −
>db.counters.insert({_id:"productid",sequence_value:0})Creating Javascript Function
现在,我们将创建一个函数 getNextSequenceValue ,它将以序列名称作为输入,将序列号增加 1,然后返回更新后的序列号。在我们的示例中,序列名称是 productid 。
Now, we will create a function getNextSequenceValue which will take the sequence name as its input, increment the sequence number by 1 and return the updated sequence number. In our case, the sequence name is productid.
>function getNextSequenceValue(sequenceName){
var sequenceDocument = db.counters.findAndModify({
query:{_id: sequenceName },
update: {$inc:{sequence_value:1}},
new:true
});
return sequenceDocument.sequence_value;
}Using the Javascript Function
我们将在创建新文档并将其返回的序列值设为文档的 _id 字段时使用函数 getNextSequenceValue。
We will now use the function getNextSequenceValue while creating a new document and assigning the returned sequence value as document’s _id field.
使用以下代码插入两个示例文档 −
Insert two sample documents using the following code −
>db.products.insert({
"_id":getNextSequenceValue("productid"),
"product_name":"Apple iPhone",
"category":"mobiles"
})
>db.products.insert({
"_id":getNextSequenceValue("productid"),
"product_name":"Samsung S3",
"category":"mobiles"
})正如您所看到的,我们使用 getNextSequenceValue 函数为 _id 字段设置值。
As you can see, we have used the getNextSequenceValue function to set value for the _id field.
为了验证此功能,让我们使用 find 命令获取文档 −
To verify the functionality, let us fetch the documents using find command −
>db.products.find()上述查询返回了以下具有自增 _id 字段的文档 −
The above query returned the following documents having the auto-incremented _id field −
{ "_id" : 1, "product_name" : "Apple iPhone", "category" : "mobiles"}
{ "_id" : 2, "product_name" : "Samsung S3", "category" : "mobiles" }