Python Pyramid 简明教程
Python Pyramid - Url Routing
在 MVC 架构出现之前,Web 应用使用一种机制:将用户在浏览器中输入的 URL 映射到程序文件,该程序文件的输出会作为对浏览器的响应渲染为 HTML。Pyramid 框架使用一种路由机制:在应用的注册表中,URL 的端点与不同的 URL 模式匹配,调用其映射的视图并渲染响应。
Before the advent of MVC architecture, web applications used the mechanism of mapping the URL entered by the user in the browser, to a program file whose output was rendered as HTML to as a response back to the browser. Pyramid framework uses a routing mechanism where the endpoint of the URL is matched with different URL patterns registered in the application’s registry, invokes its mapped view and renders the response.
典型的 URL 包含三个部分:协议(例如 http:// 或 https://),后面是 IP 地址或主机名。主机名之后,URL 的剩余部分称为路径或端点。
A typical URL comprises of three parts: The protocol (such as http:// or https://) followed by the IP address or hostname. The remaining part of the URL after first / after the hostname is called as the path or endpoint.

端点后面跟着一个或多个可变部分,形成路由。可变部分标识符用大括号括起来。例如,对于上述 URL,路由是 /blog/{id}
The endpoint followed by one or more variable parts forms the route. The variable part identifiers are surrounded by curly brackets. For example, for the above URL, the route is /blog/{id}
WSGI 应用充当路由器。它针对路由图中存在的 URL 模式检查传入请求。如果发现匹配,则执行与其关联的视图可调用对象,并返回响应。
The WSGI application acts as a router. It checks the incoming request against the URL patterns present in the route map. If a match is found, its associated view callable is executed and the response is returned.
Route Configuration
通过调用 Configurator 对象的 add_route() 方法,会向该应用添加一个新路由。路由有名称,该名称用作用于生成 URL 的标识符,还有一个模式,该模式用于与 URL 的 PATH_INFO 部分(方案和端口后面的部分,例如 URL http://example.com/blog/1). 中的 /blog/1)进行匹配。
A new route is added to the application by invoking add_route() method of the Configurator object. A route has a name, which acts as an identifier to be used for URL generation and a pattern that is meant to match against the PATH_INFO portion of a URL (the portion following the scheme and port, e.g., /blog/1 in the URL http://example.com/blog/1).
如前所述,add_route() 方法的 pattern 参数可以有一个或多个占位符标识符,这些标识符用大括号括起来,并用 / 分隔。以下语句将“index”指定为提供给 '/{name}/{age}' 模式的路由名称。
As mentioned earlier, the pattern parameter of add_route() method can have one or more placeholder identifiers surrounded by curly brackets and separated by /. Following statement assigns 'index' as the name of route given to '/{name}/{age}' pattern.
config.add_route('index', '/{name}/{age}')为将视图可调用对象与该路由关联起来,我们如下使用 add_view() 函数:
To associate a view callable to this route, we use add_view() function as follows −
config.add_view(index, route_name='index')index() 函数应该可用,以便将路由与它匹配。
The index() function should be available for the route to be matched to it.
def index(request):
return Response('Root Configuration Example')Example
我们在以下程序中放入这些语句:
We put these statements in the program below −
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
from pyramid.config import Configurator
from pyramid.response import Response
def index(request):
return Response('Root Configuration Example')
if __name__ == '__main__':
with Configurator() as config:
config.add_route('index', '/{name}/{age}')
config.add_view(index, route_name='index')
app = config.make_wsgi_app()
server = make_server('0.0.0.0', 6543, app)
server.serve_forever()Output
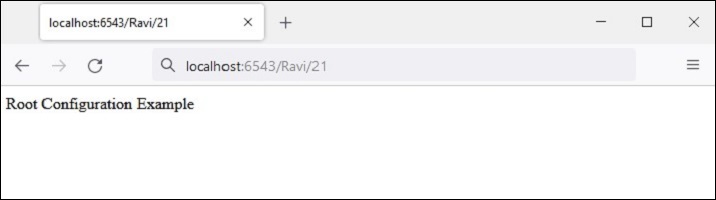
运行上述代码,在浏览器中访问 http://localhost:6543/Ravi/21 。由于该 URL 的 PATH_INFO 与 index 路由匹配,因此显示以下输出:
Run the above code and visit http://localhost:6543/Ravi/21 in the browser. As the URL’s PATH_INFO matches with the index route, the following output is displayed −
路由配置中使用的模式通常以正斜杠 (/) 字符开头。模式段(模式中 / 字符之间的单个项目)可以是字符串文字、占位符标记(例如,{name}),或二者的某种组合。替换标记无需以 / 字符开头。
The pattern used in route configuration usually starts with a forward slash (/) character. A pattern segment (an individual item between / characters in the pattern) may either be a literal string, or it may be a placeholder marker (e.g., {name}), or a certain combination of both. A replacement marker does not need to be preceded by a / character.
以下是路由模式的一些示例
Here are some examples of route patterns
/student/{name}/{marks}
/{id}/student/{name}/{marks}
/customer/{id}/item/{itemno}
/{name}/{age}占位符标识符必须是有效的 Python 标识符。因此,它必须以大写或小写 ASCII 字母或下划线开头,且只能包含大写或小写 ASCII 字母、下划线和数字。
The place holder identifier must be a valid Python identifier. Hence, it must begin with an uppercase or lowercase ASCII letter or an underscore, and it can only have uppercase or lowercase ASCII letters, underscores, and numbers.
Route Matching
当传入请求与与特定路由配置关联的 URL 模式匹配时,一个名为 matchdict 的字典对象作为请求对象的属性添加。
When the incoming request matches with the URL pattern associated with a particular route configuration, a dictionary object named matchdict is added as an attribute of the request object.
request.matchdict 包含匹配模式元素中替换模式的值。 matchdict 中的键为字符串,而其值为 Unicode 对象。
The request.matchdict contains the values that match replacement patterns in the pattern element. The keys in a matchdict are strings, while their values are Unicode objects.
在上一个示例中,将 index() 视图函数更改为以下内容 −
In the previous example, change the index() view function to following −
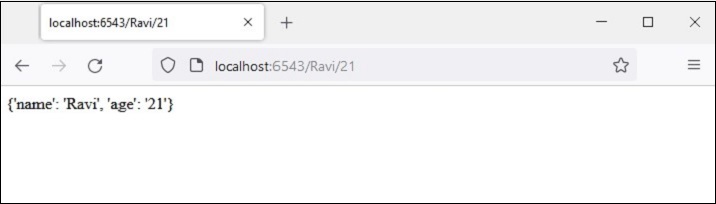
def index(request):
return Response(str(request.matchdict))浏览器显示路径参数,其形式为 dict 对象。
The browser displays the path parameters in the form of a dict object.
当请求与路由模式匹配时,传递给视图函数的请求对象还包括 matched_route 属性。匹配的路由名称可从其名称属性中获取。
When the request matches a route pattern, the request object passed to the view function also includes a matched_route attribute. The name of the matched route can be obtained from its name property.
Example
在以下示例中,我们定义了两个视图函数 student_view() 和 book_view() ,借助于 @view.config() 装饰器。
In the following example, we have two view functions student_view() and book_view() defined with the help of @view.config() decorator.
应用程序的注册表被配置为有两种对应的路由 - 映射到 '/student/{name}/{age}' 模式的 'student' 和映射到 '/book/{title}/{price}' 模式的 'book'。我们调用 configurator 对象的 scan() 方法来添加视图。
The application’s registry is configured to have two corresponding routes – 'student' mapped to '/student/{name}/{age}' pattern and 'book' mapped to '/book/{title}/{price}' pattern. We call the scan() method of configurator object to add the views.
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
from pyramid.config import Configurator
from pyramid.response import Response
from pyramid.view import view_config
@view_config(route_name='student')
def student_view(request):
return Response(str(request.matchdict))
@view_config(route_name='book')
def book_view(request):
title=request.matchdict['title']
price=request.matchdict['price']
return Response('Title: {}, Price: {}'.format(title,price))
if __name__ == '__main__':
with Configurator() as config:
config.add_route('student', '/student/{name}/{age}')
config.add_route('book', '/book/{title}/{price}')
config.scan()
app = config.make_wsgi_app()
server = make_server('0.0.0.0', 6543, app)
server.serve_forever()Output
当浏览器给出 http://localhost:6543/student/Ravi/21 URL 时,输出如下
When the browser is given http://localhost:6543/student/Ravi/21 URL, the output is
{'name': 'Ravi', 'age': '21'}如果输入的 URL 是 http://localhost:6543/book/Python/300 ,则输出如下
If the URL entered is http://localhost:6543/book/Python/300, the output is
Title: Python, Price: 300