Production-ready Features
Spring Modulith 提供支持,将有关您系统的架构信息公开为 Spring Boot 执行器端点,以及通过捕获指标和跟踪来观察应用程序模块之间的交互。由于生产就绪应用程序可能需要两者,因此激活这些功能最方便的方式是按如下方式使用 Spring Modulith Insight starter:
Spring Modulith provides support to expose architectural information about your system as a Spring Boot actuator endpoint as well as observing the interaction between application modules by capturing metrics and traces. As a production-ready application is likely to require both, the most convenient way to activate those features is to use the Spring Modulith Insight starter as follows:
-
Maven
-
Gradle
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.modulith</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-modulith-starter-insight</artifactId>
<version>{projectVersion}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>dependencies {
runtimeOnly 'org.springframework.modulith:spring-modulith-starter-insight:{projectVersion}'
}这将包括执行器和可观察性支持以及 Spring Boot 的执行器启动,以提供对执行器的常规支持。请注意,你仍然必须添加其他依赖性,以将应用程序连接到监控工具,例如 Zipkin、 Wavefront 等,通常通过 OpenTelemetry 或 Brave 完成。请参见 Spring Boot 参考文档中的 the corresponding section 获取更多信息。
This will include the actuator and observability support as well as Spring Boot’s actuator startup for general support for actuators. Note, that you will still have to add further dependencies to connect your application to your monitoring tools such as Zipkin, Wavefront etc. usually via OpenTelemetry or Brave. Find more information on that in the corresponding section of Spring Boot’s reference documentation.
[id="observability.actuator"]Application Module Actuator
应用程序模块结构可以被公开为 Spring Boot 执行器。要启用执行器,请将 spring-modulith-actuator 依赖项添加到项目:
The application module structure can be exposed as Spring Boot actuator.
To enable the actuator, add the spring-modulith-actuator dependency to the project:
-
Maven
-
Gradle
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.modulith</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-modulith-actuator</artifactId>
<version>{projectVersion}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Boot actuator starter required to enable actuators in general -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
<version>…</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>dependencies {
runtimeOnly 'org.springframework.modulith:spring-modulith-actuator:{projectVersion}'
}
<!-- Spring Boot actuator starter required to enable actuators in general -->
dependencies {
runtimeOnly 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator'
}现在,运行应用程序将公开一个 modulith 执行器资源:
Running the application will now expose an modulith actuator resource:
GET http://localhost:8080/actuator
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator",
"templated": false
},
"health-path": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/health/{*path}",
"templated": true
},
"health": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/health",
"templated": false
},
"modulith": { 1
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/modulith",
"templated": false
}
}
}| 1 | The modulith actuator resource advertised. |
modulith 资源遵守以下结构:
The modulith resource adheres to the following structure:
| JSONPath | Description |
|---|---|
|
The technical name of an application module. Target for module references in |
|
The human-readable name of the application module. |
|
The application module’s base package. |
|
All outgoing dependencies of the application module |
|
The name of the application module depended on. A reference to a |
|
The types of dependencies towards the target module. Can either be |
一个示例模块安排看起来如下:
An example module arrangement would look like this:
{
"a": {
"basePackage": "example.a",
"displayName": "A",
"dependencies": []
},
"b": {
"basePackage": "example.b",
"displayName": "B",
"dependencies": [ {
"target": "a",
"types": [ "EVENT_LISTENER", "USES_COMPONENT" ]
} ]
}
}[id="observability"]Observing Application Modules
应用程序模块之间的交互可以进行拦截,以创建微米范围,最终可在像 Zipkin 这样的工具中可视化中出现你追踪的线。为激活检测项,将以下运行时依赖性添加到项目:
The interaction between application modules can be intercepted to create Micrometer spans to ultimately end up in traces you can visualize in tools like Zipkin. To activate the instrumentation add the following runtime dependency to your project:
-
Maven
-
Gradle
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.modulith</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-modulith-observability</artifactId>
<version>{projectVersion}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>dependencies {
runtimeOnly 'org.springframework.modulith:spring-modulith-observability:{projectVersion}'
}|
您必须配置额外的基础设施依赖项,具体取决于您希望从中提取可观察元数据的工具。有关详细信息,请查看相应的 Spring Boot documentation ,了解要包含在您的设置中的依赖项。 |
|
You will have to configure additional infrastructure dependencies depending on the tooling you want to pipe the observability metadata in. For details, please check the corresponding Spring Boot documentation on which dependencies to include for your setup. |
这将使应用程序模块 API 的一部分的所有 Spring 组件使用切面进行修饰,该切面会拦截调用并为它们创建 Micrometer span。示例调用跟踪可在下面看到:
This will cause all Spring components that are part of the application module’s API being decorated with an aspect that will intercept invocations and create Micrometer spans for them. A sample invocation trace can be seen below:
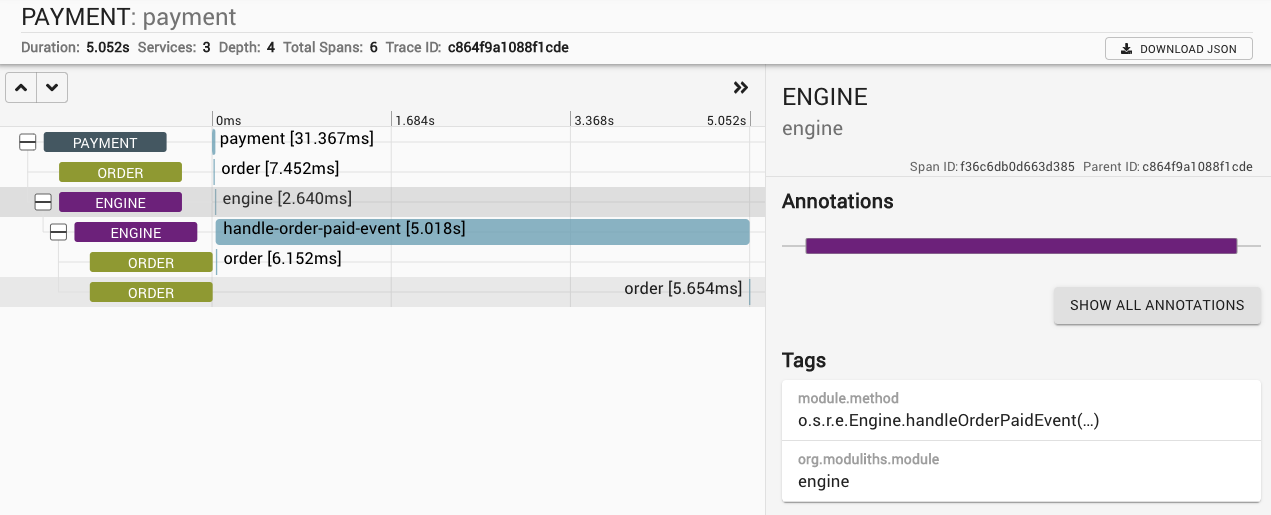
在这种特定情况下,触发支付会更改订单的状态,然后导致触发订单完成事件。发动机异步拾取此事件,从而触发订单上的另一个状态更改,持续几秒钟,然后依次触发订单的最终状态更改。
In this particular case, triggering the payment changes the state of the order which then causes an order completion event being triggered. This gets picked up asynchronously by the engine that triggers another state change on the order, works for a couple of seconds and triggers the final state change on the order in turn.