Automata Theory 简明教程
Moore and Mealy Machines
有限自动机可以有对应于每个转换的输出。有两种类型的产生输出的有限状态机 -
Finite automata may have outputs corresponding to each transition. There are two types of finite state machines that generate output −
-
Mealy Machine
-
Moore machine
Mealy Machine
Mealy 机是一种 FSM,其输出取决于当前状态以及当前输入。
A Mealy Machine is an FSM whose output depends on the present state as well as the present input.
它可以用 6 元组 (Q,∑,O,δ,X,q0) 来描述,其中 -
It can be described by a 6 tuple (Q, ∑, O, δ, X, q0) where −
-
Q is a finite set of states.
-
∑ is a finite set of symbols called the input alphabet.
-
O is a finite set of symbols called the output alphabet.
-
δ is the input transition function where δ: Q × ∑ → Q
-
X is the output transition function where X: Q × ∑ → O
-
q0 is the initial state from where any input is processed (q0 ∈ Q).
Mealy 机的状态表如下所示 -
The state table of a Mealy Machine is shown below −
Present state |
Next state |
input = 0 |
input = 1 |
State |
Output |
State |
Output |
→ |
b |
x1 |
c |
x1 |
b |
b |
x2 |
d |
x3 |
c |
d |
x3 |
c |
x1 |
d |
d |
x3 |
d |
x2 |
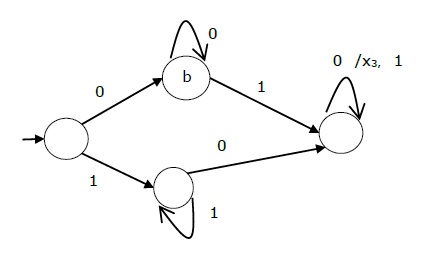
上述 Mealy 机的状态图如下 -
The state diagram of the above Mealy Machine is −
Moore Machine
Moore 机是一种 FSM,其输出仅取决于当前状态。
Moore machine is an FSM whose outputs depend on only the present state.
摩尔机可以用 6 元组 (Q, ∑, O, δ, X, q0) 来描述,其中 -
A Moore machine can be described by a 6 tuple (Q, ∑, O, δ, X, q0) where −
-
Q is a finite set of states.
-
∑ is a finite set of symbols called the input alphabet.
-
O is a finite set of symbols called the output alphabet.
-
δ is the input transition function where δ: Q × ∑ → Q
-
X is the output transition function where X: Q → O
-
q0 is the initial state from where any input is processed (q0 ∈ Q).
摩尔机的状态表如下所示 -
The state table of a Moore Machine is shown below −
Present state |
Next State |
Output |
Input = 0 |
Input = 1 |
→ |
b |
c |
x2 |
b |
b |
d |
x1 |
c |
c |
d |
x2 |
d |
d |
d |
x3 |
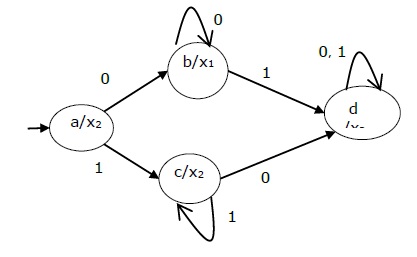
上述 Moore 机的状态图是 −
The state diagram of the above Moore Machine is −
Mealy Machine vs. Moore Machine
下表重点介绍了 Mealy 机与 Moore 机之间的不同点。
The following table highlights the points that differentiate a Mealy Machine from a Moore Machine.
Mealy Machine |
Moore Machine |
Output depends both upon the present state and the present input |
Output depends only upon the present state. |
Generally, it has fewer states than Moore Machine. |
Generally, it has more states than Mealy Machine. |
The value of the output function is a function of the transitions and the changes, when the input logic on the present state is done. |
The value of the output function is a function of the current state and the changes at the clock edges, whenever state changes occur. |
Mealy machines react faster to inputs. They generally react in the same clock cycle. |
In Moore machines, more logic is required to decode the outputs resulting in more circuit delays. They generally react one clock cycle later. |
Moore Machine to Mealy Machine
Algorithm 4
Input − Moore 机
Input − Moore Machine
Output − Mealy 机
Output − Mealy Machine
Step 1 − 采用一个空白的 Mealy 机转移状态表格式。
Step 1 − Take a blank Mealy Machine transition table format.
Step 2 − 将所有 Moore 机转移状态复制到此表格式中。
Step 2 − Copy all the Moore Machine transition states into this table format.
Step 3 − 检查 Moore 机状态表中的当前状态及其相应的输出;如果某个状态 Q 的输出为 m,将其复制到 Mealy 机状态表输出栏,Qi 出现于下一个状态的任何地方。
Step 3 − Check the present states and their corresponding outputs in the Moore Machine state table; if for a state Qi output is m, copy it into the output columns of the Mealy Machine state table wherever Qi appears in the next state.
Example
让我们考虑以下 Moore 机 −
Let us consider the following Moore machine −
Present State |
Next State |
Output |
a = 0 |
a = 1 |
→ |
d |
b |
1 |
b |
a |
d |
0 |
c |
c |
c |
0 |
d |
b |
a |
1 |
现在我们将算法 4 应用于将其转换到 Mealy 机。
Now we apply Algorithm 4 to convert it to Mealy Machine.
Step 1 & 2 −
Step 1 & 2 −
Present State |
Next State |
a = 0 |
a = 1 |
State |
Output |
State |
Output |
→ |
d |
b |
|
b |
|
a |
|
d |
|
c |
c |
c |
|
d |
|
b |
|
a |
Step 3 -
Step 3 −
Present State |
Next State |
a = 0 |
a = 1 |
State |
Output |
State |
Output |
⇒ |
d |
1 |
b |
0 |
b |
a |
1 |
d |
1 |
c |
c |
0 |
c |
0 |
d |
b |
0 |
a |
1 |
Mealy Machine to Moore Machine
Algorithm 5
Input − Mealy 机
Input − Mealy Machine
Output − 穆尔机
Output − Moore Machine
Step 1 − 计算 Mealy 机状态表中每个状态 (Qi) 可用不同输出数。
Step 1 − Calculate the number of different outputs for each state (Qi) that are available in the state table of the Mealy machine.
Step 2 − 如果 Qi 的所有输出相同,复制状态 Qi。如果它有 n 个不同的输出,将 Qi 分解为 n 个状态,其中 Qin n = 0, 1, 2……。
Step 2 − If all the outputs of Qi are same, copy state Qi. If it has n distinct outputs, break Qi into n states as Qin where n = 0, 1, 2…….
Step 3 − 如果初始状态的输出为 1,在开头插入一个新的初始状态,其输出为 0。
Step 3 − If the output of the initial state is 1, insert a new initial state at the beginning which gives 0 output.
Example
让我们考虑一下以下 Mealy 机 −
Let us consider the following Mealy Machine −
Present State |
Next State |
a = 0 |
a = 1 |
Next State |
Output |
Next State |
Output |
→ |
d |
0 |
b |
1 |
b |
a |
1 |
d |
0 |
c |
c |
1 |
c |
0 |
d |
b |
0 |
a |
1 |
此处,状态“a”和“d”分别仅提供输出 1 和 0,因此我们保留状态“a”和“d”。但状态“b”和“c”产生不同的输出(1 和 0)。因此,我们将 b 划分为 b0, b1 和 c 划分为 c0, c1 。
Here, states ‘a’ and ‘d’ give only 1 and 0 outputs respectively, so we retain states ‘a’ and ‘d’. But states ‘b’ and ‘c’ produce different outputs (1 and 0). So, we divide b into b0, b1 and c into c0, c1.
Present State |
Next State |
Output |
a = 0 |
a = 1 |
→ |
d |
b1 |
1 |
b0 |
a |
d |
0 |
b1 |
a |
d |
1 |
c0 |
c1 |
C0 |
0 |
c1 |
c1 |
C0 |
1 |
d |
b0 |