Android 简明教程
Android - TextureView
如果你想显示活动视频流或任何视频或 OpenGL 场景等内容流,可以为此使用 Android 提供的 TextureView。
If you want to display a live video stream or any content stream such as video or an OpenGL scene, you can use TextureView provided by android in order to do that.
为了使用 TextureView,你需要做的就是获取它的 SurfaceTexture。然后 SurfaceTexture 可用于呈现内容。为了做到这一点,你只需要创建一个该类的对象并实现 SurfaceTextureListener 接口即可。其语法如下 −。
In order to use TextureView, all you need to do is get its SurfaceTexture.The SurfaceTexture can then be used to render content. In order to do this, you just need to do instantiate an object of this class and implement SurfaceTextureListener interface. Its syntax is given below −
private TextureView myTexture;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements SurfaceTextureListener{
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
myTexture = new TextureView(this);
myTexture.setSurfaceTextureListener(this);
setContentView(myTexture);
}
}之后,你需要做的是覆盖其方法。方法如下所示 −
After that, what you need to do is to override its methods. The methods are listed as follows −
@Override
public void onSurfaceTextureAvailable(SurfaceTexture arg0, int arg1, int arg2) {
}
@Override
public boolean onSurfaceTextureDestroyed(SurfaceTexture arg0) {
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceTextureSizeChanged(SurfaceTexture arg0, int arg1,int arg2) {
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceTextureUpdated(SurfaceTexture arg0) {
}可以在纹理视图中显示的任何视图都可以旋转,并且可以使用 setAlpha 和 setRotation 方法调整其 Alpha 属性。其语法如下 −
Any view that is displayed in the texture view can be rotated and its alpha property can be adjusted by using setAlpha and setRotation methods. Its syntax is given below −
myTexture.setAlpha(1.0f);
myTexture.setRotation(90.0f);除了这些方法之外,TextureView 类中还有其他可用方法。它们列在下面 -
Apart from these methods, there are other methods available in TextureView class. They are listed below −
Sr.No |
Method & description |
1 |
getSurfaceTexture() This method returns the SurfaceTexture used by this view. |
2 |
getBitmap(int width, int height) This method returns Returns a Bitmap representation of the content of the associated surface texture. |
3 |
getTransform(Matrix transform) This method returns the transform associated with this texture view. |
4 |
isOpaque() This method indicates whether this View is opaque. |
5 |
lockCanvas() This method start editing the pixels in the surface |
6 |
setOpaque(boolean opaque) This method indicates whether the content of this TextureView is opaque. |
7 |
setTransform(Matrix transform) This method sets the transform to associate with this texture view. |
8 |
unlockCanvasAndPost(Canvas canvas) This method finish editing pixels in the surface. |
Example
以下示例演示了 TextureView 类的使用。它创建一个基本的应用程序,允许您在纹理视图中查看摄像头并更改其角度、方向等。
The below example demonstrates the use of TextureView class. It crates a basic application that allows you to view camera inside a texture view and change its angle , orientation e.t.c.
要尝试此示例,您需要在实际设备上运行此示例,该设备上存在摄像头。
To experiment with this example , you need to run this on an actual device on which camera is present.
Steps |
Description |
1 |
You will use android studio IDE to create an Android application and name it as TextureView under a package com.example.textureview. |
2 |
Modify src/MainActivity.java file to add Activity code. |
3 |
Modify layout XML file res/layout/activity_main.xml add any GUI component if required. |
5 |
Run the application and choose a running android device and install the application on it and verify the results. |
以下是 src/com.example.textureview/MainActivity.java 的内容。
Here is the content of src/com.example.textureview/MainActivity.java.
package com.example.textureview;
import java.io.IOException;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.SurfaceTexture;
import android.hardware.Camera;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.TextureView;
import android.view.TextureView.SurfaceTextureListener;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements SurfaceTextureListener {
private TextureView myTexture;
private Camera mCamera;
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
myTexture = new TextureView(this);
myTexture.setSurfaceTextureListener(this);
setContentView(myTexture);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
@Override
public void onSurfaceTextureAvailable(SurfaceTexture arg0, int arg1, int arg2) {
mCamera = Camera.open();
Camera.Size previewSize = mCamera.getParameters().getPreviewSize();
myTexture.setLayoutParams(new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
previewSize.width, previewSize.height, Gravity.CENTER));
try {
mCamera.setPreviewTexture(arg0);
} catch (IOException t) {
}
mCamera.startPreview();
myTexture.setAlpha(1.0f);
myTexture.setRotation(90.0f);
}
@Override
public boolean onSurfaceTextureDestroyed(SurfaceTexture arg0) {
mCamera.stopPreview();
mCamera.release();
return true;
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceTextureSizeChanged(SurfaceTexture arg0, int arg1,
int arg2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceTextureUpdated(SurfaceTexture arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}以下是 activity_main.xml 的内容。
Here is the content of activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextureView
android:id="@+id/textureView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
</RelativeLayout>以下是 AndroidManifest.xml 的默认内容
Here is the default content of AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.textureview" >
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA"/>
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.textureview.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>让我们尝试运行您的 TextureView 应用程序。我假设您已将实际 Android 移动设备连接到计算机。要从 Android studio 运行应用程序,请打开其中一个项目的活动文件,然后单击工具栏中的“运行”图标。在启动应用程序之前,Android studio 将显示以下窗口以选择您希望运行 Android 应用程序的位置。
Let’s try to run your TextureView application. I assume you have connected your actual Android Mobile device with your computer. To run the app from Android studio, open one of your project’s activity files and click Run icon from the toolbar. Before starting your application, Android studio will display following window to select an option where you want to run your Android application.
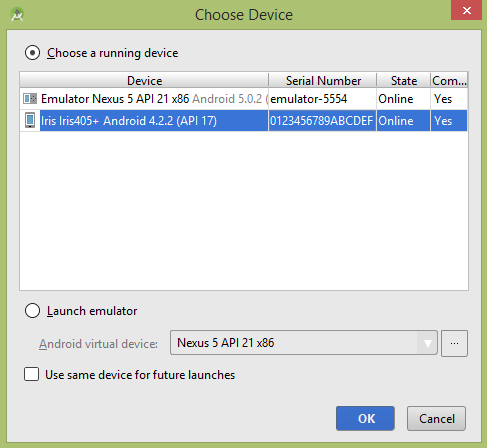
选择您的移动设备作为选项,然后查看将显示以下屏幕的移动设备。此屏幕的 alpha 属性设置为 0.5 ,旋转设置为 45.
Select your mobile device as an option and then check your mobile device which will display following screen. This screen has alpha property set to 0.5 and rotation set to 45.

此屏幕的 alpha 属性设置为 1.5 ,旋转设置为 45 。
This screen has alpha property set to 1.5 and rotation set to 45.

此屏幕的 alpha 属性设置为 1.0 ,旋转设置为 90 。
This screen has alpha property set to 1.0 and rotation set to 90.
