Matplotlib 简明教程
Matplotlib - Latex
What is LaTeX?
LaTeX 是一种广泛用于制作科学和技术文档的排版系统,尤其是在数学、物理、计算机科学、工程学和学术写作等学科中。它以其对复杂的数学公式、科学符号和结构化文本格式的卓越排版而备受推崇。
LaTeX is a typesetting system widely used for producing scientific and technical documents, particularly in disciplines such as mathematics, physics, computer science, engineering and academic writing. It’s highly regarded for its superior typesetting of complex mathematical equations, scientific notations, and structured text formatting.
Key Aspects of LaTeX
以下是 LaTeX 的主要方面。
The below are the key aspects of LaTeX.
-
Markup Language − LaTeX is a markup language, meaning it uses commands and tags to format text rather than WYSIWYG which is abbreviated as What You See Is What You Get editors. Users write plain text with embedded commands that specify the structure and formatting.
-
High-Quality Typesetting − LaTeX excels in producing professional-looking documents with precise typographical and typesetting features. It handles complex structures like mathematical formulas, tables, bibliographies and cross-references exceptionally well.
-
Package System − LaTeX offers a vast array of packages that extend its functionality for specific tasks or document types, providing templates, styles and additional features.
-
Free and Open Source − LaTeX is free to use and is supported by a strong open-source community by ensuring continuous development and a rich ecosystem of packages and resources.
-
Components of LaTeX − The LaTex of matplotlib library have the following components. Let’s see each of them in detail.
-
Document Class − The document class specifies the type of document being created and defines its overall structure, layout and formatting. It acts as a template that sets the style and behaviour for the entire document. Different document classes are available to suit various types of documents such as articles, reports, books, presentations and more.
-
Preamble − In LaTeX the preamble is the section of the document that precedes the main content and the \begin{document} command. It is where we define the document settings, load packages, set parameters and configure global settings that apply to the entire document. The preamble acts as a setup area where we prepare LaTeX for processing the main body of the document.
-
Document Body − The document body in LaTeX is the main section where the content of our document resides. It starts after the preamble and the \begin{document} command and continues until the \end{document} command. This section includes the actual text, sections, subsections, equations, figures, tables and any other elements that constitute the core content of the document.
Advantages of LaTeX
以下是 LaTex 的优点。
The following are the advantages of LaTex.
-
Quality Typesetting − Produces high-quality output, especially for scientific and technical documents.
-
Cross-Referencing − Simplifies referencing and cross-referencing of equations, figures, tables, and sections.
-
Version Control − Facilitates version control and collaboration through plain text-based files.
-
Customization − Allows extensive customization of document styles, layouts and formatting.
Disadvantages of LaTeX
-
Learning Curve − Requires learning its syntax and commands which can be daunting for beginners.
-
Limited WYSIWYG − Lack of immediate visual feedback (WYSIWYG) might be challenging for some users accustomed to graphical editors.
Usage of LaTeX
-
Academic Writing − Academic papers, theses, dissertations
-
Scientific − Scientific reports, articles, and journals
-
Technical Documents − Technical documentation, manuals
-
Presentations − Presentations using tools like Beamer
Basic document structure of the LaTex
Syntax
基本 LaTeX 文档结构包括 −
A basic LaTeX document structure includes −
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
\section{Introduction}
This is a simple LaTeX document.
\subsection{Subsection}
Some text in a subsection.
\end{document}上述代码使用具有包含章节和子章节的层级结构的基本文章文档进行定义。
The above code defines a basic article document with a hierarchical structure comprising a section and a subsection.
Writing our own LaTeX preamble
要在 Matplotlib 中编写自己的 LaTeX 导言,我们可以使用此示例作为参考。
To write our own LaTeX preamble in Matplotlib we can use this example as reference.
Example 1
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = [7.50, 3.50]
plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"] = True
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
y = np.exp(x)
plt.plot(x, y, color='red', label="$y=e^{x}$")
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.show()这会产生以下输出 −
This will generate the following output −

Example 2
在此示例中,我们正在 .py 文件内的绘图图例中使用 Latex 公式。
In this example we are using the Latex formula in the legend of a plot inside a .py file.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = [7.50, 3.50]
plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"] = True
x = np.linspace(1, 10, 1000)
y = np.sin(x)
plt.plot(x, y, label=r'$\sin (x)$', c="red", lw=2)
plt.legend()
plt.show()这会产生以下输出 −
This will generate the following output −

在标签中放置一个更复杂的方程式,例如,label=r’αiπ+1=0'。现在看看绘图右上角的图例。
Put a little more complex equation in the label, for example, label=r’αiπ+1=0'. Now look at the legend at the top-right corner of the plot.
Example 3
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = [7.50, 3.50]
plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"] = True
x = np.linspace(1, 10, 1000)
y = np.sin(x)
plt.plot(x, y, label=r'$\sin (x)$', c="red", lw=2)
plt.legend(r'αiπ+1=0')
plt.show()这会产生以下输出 −
This will generate the following output −

Rendering mathematical expressions
在 LaTeX 中呈现数学表达式,需要使用 LaTeX 语法来编写数学方程、符号和公式。LaTeX 提供了一套全面的命令和符号,以便以精确和清晰的方式创建复杂的数学表达式。
Rendering mathematical expressions in LaTeX involves using LaTeX syntax to write mathematical equations, symbols and formulas. LaTeX provides a comprehensive set of commands and notation to create complex mathematical expressions with precision and clarity.
Importance of LaTeX for Mathematics
-
Precision and Clarity − LaTeX allows precise typesetting of mathematical notation and symbols.
-
Consistency − Maintains consistency in formatting across mathematical documents.
-
Publication-Quality − Produces high-quality mathematical expressions suitable for academic and scientific publications.
-
LaTeX’s support for mathematical typesetting makes it a preferred choice for researchers, mathematicians, scientists and academics when writing technical or mathematical documents that require accurate and well-formatted mathematical notation.
LaTeX for Mathematical Expressions
以下是在数学表达式中 LaTex 的组成部分。
The below are the components of LaTex in Mathematical Expressions.
-
Inline Math Mode − Inline math mode in LaTeX is used to include mathematical expressions within the text of a document. We can use inline math mode by enclosing the mathematical expression between a pair of single dollar signs $…$.
-
Using the inline math mode − In this example the mathematical expression
\frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}is included within the text using inline math mode. The result is that the mathematical expression is rendered within the line of text.
Example
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
equation = r'$x = \frac{{-b \pm \sqrt{{b^2 - 4ac}}}}{{2a}}$'
plt.text(0.5, 0.5, equation, fontsize=12, ha='center')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()这会产生以下输出 −
This will generate the following output −

Display Math Mode
LaTeX 中的显示数学模式用于在单独的块中展示数学表达式,居中显示并区别于周围文本。它通常用于文档中更大或独立的方程,这些方程值得突出显示。
Display math mode in LaTeX is used to showcase mathematical expressions in a separate block, centered and distinct from the surrounding text. It’s commonly used for larger or stand-alone equations that deserve prominence in a document.
要在 LaTeX 中使用显示数学模式,我们有若干选项,逐个来了解。
To use display math mode in LaTeX we have several options let’s see them one by one.
用 Gemini 将数学表达式放在 @ {s0} − 之间
Enclose the mathematical expression between * symbols for displayed equations. In the following example we are displaying the given input equation by using the *..$$ −
$$
f(x) = \int_{a}^{b} g(x) \, dx
$$这会产生以下输出 −
This will generate the following output −

The 'equation' Environment
使用 equation 环境创建可编号的方程式。
Use the 'equation' environment to create a numbered equation.
\begin{equation}
f(x) = \int_{a}^{b} g(x) \, dx
\end{equation}这会产生以下输出 −
This will generate the following output −

@ {s1} - 以上代码行可以在 Jupyter Notebook 标记模式中执行。
Note − The above code lines can be executed in the Jupyter Notebook markdown mode.
Symbols and Operators
在 LaTeX 中,我们可以使用各种符号和运算符,来表示数学符号、表达式和运算。以下是一些常用的符号和运算符以及它们的 LaTeX 命令。
In LaTeX we can use a wide range of symbols and operators to represent mathematical notation, expressions and operations. Here are some commonly used symbols and operators along with their LaTeX commands.
-
Greek Letters − Alpha:
\alpha, Beta:\beta, Gamma:\gamma, Delta:\deltaand so on. -
Arithmetic Operators − Plus:
+, Minus:-, Multiplication:\timesor*, Division:\divor/ -
Relations and Comparisons − Equals:
=, Not equals:\neq, Less than:<, Greater than:>and so on. -
Set Theory − Union:
\cup, Intersection:\cap, Subset:\subset, Superset:\supsetand so on -
Calculus and Limits − Integral:
\int, Summation:\sum, Limit:\lim, Derivative:\frac{dy}{dx} -
Functions − Sine:
\sin, Cosine:\cos, Tangent:\tan, Logarithm:\log, Exponential:\exp -
Roots and Exponents − Square root:
\sqrt{x}, Exponent:x^2, Subscript:x_1, Superscript:x^i
Other Notations
-
Fractions −
\frac{numerator}{denominator} -
Matrices −
bmatrix,pmatrix,vmatrix, etc., using theamsmathpackage -
Special Symbols − For example,
\inftyfor infinity,\emptysetfor an empty set, etc.
在此示例中,我们使用 @ {s10} 在 matplotlib 库的 LaTex 中显示符号和运算符。
In this example we are using the $..$, to display the symbols and operators in the LaTex of matplotlib library.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
equation = r'$(\alpha + \beta = \gamma \times \delta)$'
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3))
plt.text(0.5, 0.5, equation, fontsize=12, ha='center', va='center')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()这将显示以下方程式:
This will display the following equation −

利用这些用于符号和运算符的 LaTeX 命令,我们可以在 LaTeX 文档中创建具有精准度和清晰度的复杂数学表达式。
By utilizing these LaTeX commands for symbols and operators we can create complex mathematical expressions with precision and clarity in our LaTeX documents.
Fractions
在 LaTeX 中,我们可以轻松地创建分数、下标和上标以使用特定命令和符号表示数学表达式。
In LaTeX we can easily create fractions, subscripts and superscripts to represent mathematical expressions using specific commands and notation.
要创建分数,我们可以使用 @ {s11} 命令。在此示例中,我们创建分数 3/4 ¾。
To create fractions we can use the \frac{numerator}{denominator} command. In this example we are creating the fraction \frac{3}{4} ¾.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
equation = r'The fraction is $\frac{3}{4}$'
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3))
plt.text(0.5, 0.5, equation, fontsize=12, ha='center', va='center')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()这将生成以下方程式:
This will generate the following equation −

Matrices and Arrays
LaTeX 中使用矩阵和数组以矩阵形式表示数据或显示方程组。 array 环境是 LaTeX 中创建矩阵和数组的基本结构,而 amsmath 软件包提供的 matrix 环境提供了额外的功能和更简单的矩阵语法。
In LaTeX matrices and arrays are used to represent data in matrix form or to display sets of equations. The array environment is the basic structure for creating matrices and arrays in LaTeX while the matrix environments provided by the amsmath package offer additional functionality and easier syntax for matrices.
Creating Matrices and Arrays
以下是如何使用各自的环境创建数组和矩阵。
Here are we are creating the arrays and matrices using respective environments.
‘array’ 环境允许我们在 LaTeX 中创建矩阵或数组。
The ‘array’ environment allows us to create matrices or arrays in LaTeX.
\[
\begin{array}{ccc}
1 & 2 & 3 \\
4 & 5 & 6 \\
7 & 8 & 9 \\
\end{array}
\]这将生成以下方程式:
This will generate the following equation −

@ {s1} - 以上代码行可以在 Jupyter Notebook 标记模式中执行。
Note − The above code lines can be executed in the Jupyter Notebook markdown mode.
Using ‘amsmath’ Package’s ‘matrix’ Environments
amsmath 包提供了 matrix, pmatrix, bmatrix, Bmatrix, vmatrix, Vmatrix 等方便的矩阵环境,简化了矩阵的创建。
The amsmath package provides convenient matrix environments such as matrix, pmatrix, bmatrix, Bmatrix, vmatrix, Vmatrix which simplify the creation of matrices.
\[
\begin{matrix}
1 & 2 & 3 \\
4 & 5 & 6 \\
7 & 8 & 9 \\
\end{matrix}
\]这将生成以下方程式:
This will generate the following equation −

@ {s1} - 以上代码行可以在 Jupyter Notebook 标记模式中执行。
Note − The above code lines can be executed in the Jupyter Notebook markdown mode.
Matrix Formatting
这里将使用 LaTeX 对齐矩阵的列。在矩阵或数组中,我们可以使用 c 表示居中、l 表示左对齐和 r 表示右对齐,在 array 环境中指定列对齐方式。
Here are going to align the columns of the matrix using the LaTex. In matrices or arrays we can specify column alignment using c for centered, l for left-aligned and r for right-aligned columns within the array environment.
下面是应用列对齐到矩阵的示例。
The below is the example of applying the column alignment on a matrix.
\[
\begin{array}{ccc}
1 & 222 & 3 \\
4 & 55555 & 6 \\
7 & 888 & 999999 \\
\end{array}
\]这将生成以下方程式:
This will generate the following equation −

@ {s1} - 以上代码行可以在 Jupyter Notebook 标记模式中执行。
Note − The above code lines can be executed in the Jupyter Notebook markdown mode.
Additional Notes
-
Matrices and arrays in LaTeX are enclosed within the \[ … \] or equation environment to display them as standalone equations.
-
The & symbol separates elements within a row and \\ starts a new row.
LaTeX 为显示矩阵和数组提供了多功能工具,允许我们以各种对齐方式和配置以矩阵形式表示数学数据或方程。LaTeX 可以创建矩阵和数组以用于数学符号。
LaTeX provides versatile tools for displaying matrices and arrays allowing us to represent mathematical data or equations in matrix form with various alignments and configurations. LaTeX enables the creation of matrices and arrays for mathematical notation.
\begin{bmatrix}
1 & 2 \\
3 & 4
\end{bmatrix}这将生成以下方程式:
This will generate the following equation −

@ {s1} - 以上代码行可以在 Jupyter Notebook 标记模式中执行。
Note − The above code lines can be executed in the Jupyter Notebook markdown mode.
Special Functions
LaTeX 支持特殊函数的符号,例如三角函数、对数等。
LaTeX supports notation for special functions like trigonometric functions, logarithms, etc.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# LaTeX code for the bold text
bold_text = r'$\sin(\theta), \log(x), \lim_{x \to \infty} f(x)$'
# Create a figure and display the bold text
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3))
plt.text(0.5, 0.5, bold_text, fontsize=12, ha='center', va='center')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
Remove random unwanted space in LaTeX-style maths
在数学文本中,LaTeX 忽略您键入的空格并按照其方式使用空格。如果您想要不同的空格样式,可以使用以下四个命令。
LaTeX ignores the spaces you type and uses spacing the way it’s done in mathematics texts. You can use the following four commands in case you want a different spacing style.
-
\; − thick space
-
\: − medium space
-
\, − a thin space
-
\! − a negative thin space
若要在 matplotlib 图中消除 LaTeX 样式数学中的随机多余空格,可以使用 "\!",这将减少多余的间距。
To remove random unwanted space in LaTeX-style maths in matplotlib plot we can use "\!" which will reduce the extra spacing.
下面是应用列对齐到矩阵的示例。
The below is the example of applying the column alignment on a matrix.
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = [7.00, 3.50]
plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"] = True
plt.subplot(211)
plt.text(0.4, 0.4, r'$\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}\; \frac{-e^{i\pi}}{2^n}!\left[a^2+\delta ^2- \frac{\pi}{2} \right ]$', fontsize=16, color='r')
plt.title("With thick space")
plt.subplot(212)
plt.text(0.4, 0.4, r'$\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}\! \frac{-e^{i\pi}}{2^n}!\left[a^2+\delta ^2- \frac{\pi}{2} \right ]$', fontsize=16, color='r')
plt.title("With thin space")
plt.show()这将生成以下方程式:
This will generate the following equation −

请注意“Σ(西格玛)”符号后的间距差异。在第一种情况下,我们使用了粗间距 (\;),在第二种情况下,我们使用了细间距 (\!) 来减少多余的间距。
Notice the difference in spacing after the "Σ (sigma)" symbol. In the first case, we have used thick space (\;) and in the second case, we have used the thin space (\!) to reduce extra spacing.
What is Text formatting in LaTex?
在注释中,在图、图形或绘图中对 LaTeX 文本进行格式化,例如创建的那些。Matplotlib 库可以在注释文本中使用 LaTeX 命令的一个子集来完成。注释有助于为图形中的元素添加说明性标签、说明或注释。
In LaTeX text formatting in annotations within figures, graphs or plots such as those created. Matplotlib library can be accomplished using a subset of LaTeX commands within the annotation text. Annotations help add explanatory labels, descriptions or notes to elements within a graph.
在使用诸如 Matplotlib 之类的工具处理注释中支持 LaTeX 文本渲染时,我们可以使用 LaTeX 命令的子集来格式化这些注释中的文本。这允许在注释中合并样式文本、数学表达式和特殊格式。
When working with tools like Matplotlib that support LaTeX for text rendering in annotations we can use a subset of LaTeX commands to format the text within these annotations. This allows for the incorporation of styled text, mathematical expressions and special formatting within annotations.
LaTeX Formatting in Annotations Includes
以下是注释中的 LaTex 格式。我们逐个看一遍。
The below are the LaTex formatting in Annotations. Let’s see them one by one.
-
Mathematical Expressions − The mathematical expressions are given as fractions, Greek letters, superscripts and subscripts using LaTeX math mode.
-
Text Styling − The text styling includes bold, italics, underline or different font sizes using LaTeX commands like \textbf{}, \textit{}, \underline{} and font size commands.
-
Special Characters − Escaping special characters like dollar signs, percentage signs or underscores using LaTeX escape sequences.
-
Alignment − Control over alignment, though limited, using
\begin{flushleft}...\end{flushleft},
\begin{center}...\end{center},
\begin{flushright}...\end{flushright}.以上我们已经浏览了 LaTeX 中提供的不同样式格式,现在让我们看看在标注中使用 LaTeX 的文本格式。
In the above we have gone through different styling formats available in LaTex, now let’s see the text formatting in Annotations using LaTex.
LaTeX Text Formatting in Annotations
以下是使用 LaTeX 在标注中进行各种文本格式化的方法。
The below are the various text formatting in Annotations using LaTex.
Basic Text Formatting
可以在标注中使用 LaTeX 命令进行基本的文本格式化。以下是一些命令。
LaTeX commands for basic text formatting can be used in annotations. The following are some.
Bold − 使文本变粗
Bold − To make text bold
\textbf{Bold Text}@ {s1} - 以上代码行可以在 Jupyter Notebook 标记模式中执行。
Note − The above code lines can be executed in the Jupyter Notebook markdown mode.
Italics − 使文本变斜体
Italics − To make text italic
\textit{Italic Text}@ {s1} - 以上代码行可以在 Jupyter Notebook 标记模式中执行。
Note − The above code lines can be executed in the Jupyter Notebook markdown mode.
Underline − 给文本添加下划线
Underline − To add an underline to text
\underline{Underlined Text}@ {s1} - 以上代码行可以在 Jupyter Notebook 标记模式中执行。
Note − The above code lines can be executed in the Jupyter Notebook markdown mode.
Font Size − LaTeX 提供了不同的字体大小命令,例如 \tiny、\small、\large、\Large、\huge、\Huge
Font Size − LaTeX provides different font size commands such as \tiny, \small, \large, \Large, \huge, \Huge
Annotations with Bold text using LaTex
此示例中,我们在标注中使用 LaTeX 文本格式,使绘图上的文本看起来更粗。
Here in this example we are using the LaText text formatting in the Annotations for making the text to look bold on a plot.
Example
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create a simple plot
x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y = [2, 5, 7, 10]
plt.plot(x, y, marker='o', linestyle='-')
# Add an annotation with LaTeX text formatting
plt.annotate(r'\textbf{Max Value}',
xy=(x[y.index(max(y))], max(y)),
xytext=(2.5, 8),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),
fontsize=12,
color='blue',
bbox=dict(boxstyle='round,pad=0.3', edgecolor='blue', facecolor='lightblue'))
# Set axis labels and title
plt.xlabel('X-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y-axis')
plt.title('Example Plot with LaTeX Annotation')
# Show the plot
plt.show()这将生成以下方程式:
This will generate the following equation −

Mathematical Notation
在 LaTeX 中,数学符号中的文本格式化涉及在数学模式中使用命令和语法,在表达数学内容时为文本元素设置样式。它支持在数学表达式或等式中整合文本格式化功能。
In LaTeX text formatting within mathematical notation involves using commands and syntax within math mode to stylize text elements while expressing mathematical content. It allows for the integration of text formatting features within mathematical expressions or equations.
Basic Text Formatting within Mathematical Notation
数学符号中的基本文本格式如下。
The basic text formatting within the mathematical notations are as follows.
此文本格式使封闭文本在数学表达式中变粗。
This text formatting renders the enclosed text in bold within a mathematical expression.
\mathbf{Bold Text}斜体文本在数学表达式中以斜体显示封闭文本。
The Italic text displays the enclosed text in italics within a mathematical expression.
\textit{Italic Text}此文本格式在数学模式中文本以无衬线字体样式显示封闭文本。
This renders the enclosed text in sans-serif font style within math mode.
\textsf{Sans-serif Text}此文本格式在数学模式下以打字机或等宽字体显示封闭文本。
This displays the enclosed text in a typewriter or monospaced font within math mode.
\texttt{Typewriter Text}Important points to remember
-
Text formatting within mathematical notation can be achieved using \text{} or specific formatting commands within math mode.
-
Some formatting commands may not work in all math environments or may need additional packages or configurations.
-
LaTeX offers a variety of text formatting options that can be applied within mathematical expressions to enhance the presentation of text-based content.
-
By utilizing text formatting commands within mathematical notation LaTeX allows for the integration of styled text elements within mathematical expressions by aiding in the clarity and visual appeal of mathematical content.
Subscripts and Superscripts
在 LaTeX 中,下标和上标用于在数学表达式的基线下方或上方放置文本或符号。它们通常用于表示数学符号中的指数、指数或特殊标注。
In LaTeX subscripts and superscripts are used to position text or symbols below subscripts or above superscripts the baseline of a mathematical expression. They’re commonly employed to denote indices, exponents or special annotations within mathematical notation.
Subscripts
下标用于创建下标,在 LaTeX 中我们可以使用下划线 _ 。
Subscripts are used to create a subscript in LaTeX we can use the underscore _.
Superscripts
上标用于创建上标,在 LaTeX 中我们可以使用插入符号 ^ 。
Superscripts to create a superscript in LaTeX we can use the caret ^.
Subscripts and Superscripts usage in Annotation of a plot
在这个示例中,我们使用 LaTex 通过绘图的注解来使用下标和上标用法。
In this example we are using the subscripts and superscripts usage in annotations of a plot by using the LaTex.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Generating some data points
x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y = [2, 5, 7, 10]
plt.plot(x, y, 'o-', label='Data')
# Annotating a point with a subscript and a superscript
plt.annotate(r'$\mathrm{Point}_{\mathrm{max}}^{(4, 10)}$',
xy=(x[y.index(max(y))], max(y)),
xytext=(3, 8),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', arrowstyle='->'),
fontsize=12,
color='red')
plt.xlabel('X-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y-axis')
plt.title('Example Plot with Annotation')
plt.legend()
plt.show()这将生成以下方程式:
This will generate the following equation −

Subscripts and Superscripts
可以使用“_”添加下标并使用“^”添加上标。在以下示例中我们显示脚本内容。
Subscripts and superscripts can be added using the ‘_’ for subscripts and ‘^’ for superscripts. In the following example we are displaying a script content.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
equation = r'$x_i^2$ denotes $x$ raised to the power of $i$ squared.'
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3))
plt.text(0.5, 0.5, equation, fontsize=12, ha='center', va='center')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()这将显示以下方程式 −
This is will display the following equation −

我们也可以通过用花括号 {} 来封闭内容来嵌套下标和上标。在下面给出的示例中,我们显示嵌套下标。
We can also nest subscripts and superscripts by enclosing the content in curly braces {}. In the example given below we are displaying the nested subscripts.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
equation = r'$x_{i_j}^{2k}$ represents a nested subscript and superscript.'
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3))
plt.text(0.5, 0.5, equation, fontsize=12, ha='center', va='center')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()结果方程式如下 −
The resultant equation is as follows −

Using Commands
对于更复杂的表达式或者为了确保一致的格式化,我们可以使用 _ 的命令 \subscript{} 和 ^ 的命令*\superscript{}*,它由诸如 fixltx2e 的包提供。
For more complex expressions or to ensure consistent formatting we can use commands _ for \subscript{} and ^ for*\superscript{}* provided by packages like fixltx2e.
在此示例中,我们显示复杂表达式。
In this example we are displaying the complex expressions.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
equation = r'$x_{i}^{2}$'
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3))
plt.text(0.5, 0.5, equation, fontsize=12, ha='center', va='center')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()结果方程式如下 −
The resultant equation is as follows −

LaTeX 提供了创建分数、下标和上标的简单方法,让我们能够准确有效地表示数学表达式。
LaTeX offers straightforward ways to create fractions, subscripts and superscripts, allowing us to represent mathematical expressions accurately and efficiently.
Important points to remember
-
Subscripts and superscripts can be used independently or combined within LaTeX mathematical notation.
-
They are crucial for denoting variables, indices, exponents and other related mathematical annotations.
-
LaTeX automatically handles the positioning and sizing of subscripts and superscripts based on the context and surrounding elements within the mathematical expression.
-
By using subscripts and superscripts in LaTeX we can precisely express mathematical formulas and notations, improving clarity and readability within mathematical content.
Combining Text and Math
在注释中结合文本和数学涉及以连贯且视觉上有效的方式将常规文本和数学表达式嵌入到注释中。
Combining text and math in annotations using LaTeX involves embedding both regular text and mathematical expressions within annotations in a coherent and visually effective manner.
Combining Text and Math using Latex on a plot
在本示例中,我们使用 LaTex 通过注释来结合文本和数学。
Here in this example we are combining the text and math in annotations by using the LaTex.
Example
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Generating some data points
x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y = [2, 5, 7, 10]
plt.plot(x, y, 'o-', label='Data')
# Annotating a point with combined text and math in LaTeX
plt.annotate(r'$\frac{dx}{dt} = \alpha \cdot x(t) + \beta$ is the differential equation',
xy=(x[2], y[2]),
xytext=(2, 6),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', arrowstyle='->'),
fontsize=12,
color='blue')
plt.xlabel('X-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y-axis')
plt.title('Example Plot with Annotation by Latex')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Text Color and Font Styles
在 Matplotlib 中的 LaTeX 注释中,我们可以使用 LaTeX 命令设置文本颜色和字体样式以增强注释的视觉外观。
In LaTeX annotations within Matplotlib we can set text color and font styles using LaTeX commands to enhance the visual appearance of the annotations.
Text Color
要在 LaTeX 注释中设置文本颜色,我们可以使用诸如以下内容的 LaTeX 颜色命令:
To set text color within a LaTeX annotation we can use LaTeX color commands like
\textcolor{color_name}{text}Font styles
以下是在绘图注释中应用的不同字体样式。
The following are the different font styles applied on an annotation of a plot.
-
Bold Text − To display text in bold by using the command \textbf{}.
-
Italics − To display the text in italic style we can use \textit{}.
-
Underline − To underline the text we use \underline{}.
Combined Usage of text and font styles on annotations
В этом примере мы используем LaTex. \text для смены цвета текста и применения указанного стиля для аннотаций графика.
In this example we are using the LaTex for changing the text color and applying the defined style to the annotations of a plot.
Example
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Generating some data points
x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y = [2, 5, 7, 10]
plt.plot(x, y, 'o-', label='Data')
# Annotating a point with different text color and font style
plt.annotate(r'\mathbf{\textcolor{red}{Max value:}} \ \textit{\textcolor{blue}{y_{\text{max}} = 10}}',
xy=(x[y.index(max(y))], max(y)),
xytext=(3, 8),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', arrowstyle='->'),
fontsize=12)
plt.xlabel('X-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y-axis')
plt.title('Example Plot with Annotation of color and font style')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Important Points to be noted
-
Ensure that LaTeX is correctly interpreted within Matplotlib annotations by using the
rprefix before the string. -
Adjust the colors, font styles and other formatting parameters as needed to suit our visualization requirements.
-
By leveraging LaTeX commands for text color and font styles within Matplotlib annotations we can create visually appealing and informative annotations in our plots. Adjusting these attributes helps in highlighting important information and improving the overall aesthetics of the visualization.
Наконец, мы можем заявить, что, используя LaTeX в аннотациях Matplotlib, мы можем обогащать наши графики и фигуры форматированным текстом, математическими обозначениями и стилизованными метками, что позволяет создавать более четкие и информативные визуализации.
Finally, we can say by using LaTeX within Matplotlib’s annotations we can enrich our graphs and figures with formatted text, mathematical notations and stylized labels by allowing for clearer and more informative visualizations.
Bold font weight for LaTeX axes label
В этом примере мы устанавливаем для метки оси LaTeX полужирный вес шрифта.
In this example we are setting the LaTex axes label as Bold font weight.
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt, font_manager as fm
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = [7.50, 3.50]
plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"] = True
plt.rcParams["font.fantasy"] = "Comic Sans MS"
x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
y = np.exp(x)
ax1 = plt.subplot()
ax1.set_xticks(x)
ax1.set_yticks(y)
ax1.plot(x, y, c="red")
ax1.set_xticklabels([r"$\bf{one}$", r"$\bf{two}$", r"$\bf{three}$",
r"$\bf{four}$"], rotation=45)
ax1.set_yticklabels([r"$\bf{:.2f}$".format(y[0]), r"$\bf{:.2f}$".format(y[1]),
r"$\bf{:.2f}$".format(y[2]), r"$\bf{:.2f}$".format(y[3])], rotation=45)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()Приведенный выше код создаст следующий вывод —
The above code will generate the follwing output −

Format a float using matplotlib’s LaTeX formatter
Здесь, в этом примере, мы форматируем float, используя форматтер Latex от matplotlib.
Here in this example we are formatting a float using matplotlib’s Latex formatter.
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# Set the figures size
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = [7.50, 3.50]
plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"] = True
# x and y data points
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100)
y = x**3/3
# Plot the data points
plt.plot(x, y)
# Fill the area between the curve
plt.fill_between(x, y)
# LaTex representation
plt.title("$area=\int_a^b{x^2dx}$=83.3")
# Display the plot
plt.show()这将生成以下方程式:
This will generate the following equation −

Obtain the same font in Matplotlib output as in LaTex output
Здесь, в этом примере, мы форматируем float, используя форматтер Latex от matplotlib.
Here in this example we are formatting a float using matplotlib’s Latex formatter.
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# Set the figures size
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = [7.50, 3.50]
plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"] = True
# x and y data points
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100)
y = x**3/3
# Plot the data points
plt.plot(x, y)
# Fill the area between the curve
plt.fill_between(x, y)
# LaTex representation
plt.title("$area=\int_a^b{x^2dx}$=83.3")
# Display the plot
plt.show()这将生成以下方程式:
This will generate the following equation −

What is LaTex Rendering?
LaTeX 渲染是指将包含排版指令和命令的 LaTeX 标记语言转换为格式化输出的过程。此输出通常是高质量文档、数学公式、科学论文或具有精确且一致排版的技术报告。
LaTeX rendering refers to the process of converting LaTeX markup language which contains typesetting instructions and commands, into formatted output. This output is typically high-quality documents, mathematical formulas, scientific papers or technical reports with precise and consistent typography.
LaTeX 渲染广泛应用于学术界、科学研究、技术文档和出版中,因为它具有强大的排版功能,并且能够生成专业外观的文档。
LaTeX rendering is widely used in academia, scientific research, technical documentation and publishing due to its robust typesetting capabilities and its ability to produce professional-looking documents.
Key Aspects of LaTeX Rendering
-
Typesetting − LaTeX is renowned for its superior typesetting capabilities ensuring professional-grade document formatting for academic and technical content.
-
Mathematical Formulas − LaTeX is extensively used for its exceptional support in typesetting complex mathematical equations by making it a preferred choice for academic and scientific publications.
-
Markup Language − LaTeX uses a markup language in which, where users write documents with plain text and include commands to specify formatting, structure and content.
-
Compilation − The LaTeX source code needs to be compiled using a LaTeX compiler such as pdflatex, xelatex, lualatex. During compilation the compiler interprets the LaTeX commands and generates the final output in various formats like PDF, DVI or PostScript.
-
Customization − LaTeX allows users to create custom styles, templates and packages by enabling precise control over document formatting and layout.
Benefits of LaTeX Rendering
-
Quality and Consistency − LaTeX ensures high-quality and consistent document formatting across various platforms and devices.
-
Mathematical Typesetting − It excels in handling complex mathematical notation and making it indispensable for scientific and mathematical content.
-
Cross-Platform Compatibility − LaTeX documents can be easily compiled and viewed on different operating systems.
-
Version Control − Plain text-based source files facilitate version control systems by making collaboration and document history management easier.
Enabling Latex Rendering
为了启用 LaTeX 渲染以便创建文档、公式或注释,我们通常需要以下内容。
To enable LaTeX rendering for creating documents, equations or annotations we typically need the following.
-
LaTeX Installation − Install a LaTeX distribution like TeX Live, MiKTeX or MacTeX which includes the necessary LaTeX compiler and packages.
-
Text Editor − Choose a text editor or an integrated development environment (IDE) that supports LaTeX such as TeXstudio, TeXworks, Overleaf or editors like Sublime Text, VS Code or Atom with LaTeX plugins/extensions.
-
Write LaTeX Code − Create a .tex file and write LaTeX code using the appropriate commands and syntax to structure our document which include equations or format text.
-
Compilation − Use the LaTeX compiler to compile the .tex file into the desired output format such as PDF, DVI, PS. Run the appropriate command in the terminal or use the integrated features of our chosen editor/IDE.
LaTeX Rendering in Matplotlib for Annotations
Для аннотаций Matplotlib, использующих LaTeX для форматирования текста в пределах графиков, мы должны выполнить указанные ниже задачи:
For Matplotlib annotations using LaTeX for text formatting within plots we have to ensure the below −
-
Matplotlib Support − Matplotlib supports LaTeX for annotations by using LaTeX syntax within plt.annotate() or similar functions.
-
LaTeX Installation − Ensure we have a working LaTeX installation on our system that Matplotlib can access for rendering LaTeX text within annotations.
-
Correct Syntax − Use the correct LaTeX syntax r'$…$' within Matplotlib functions for annotations to render the desired LaTeX-formatted text.
-
By following the above mentioned steps we can enable LaTeX rendering for various purposes such as document creation, mathematical notation or annotations in visualization libraries like Matplotlib.
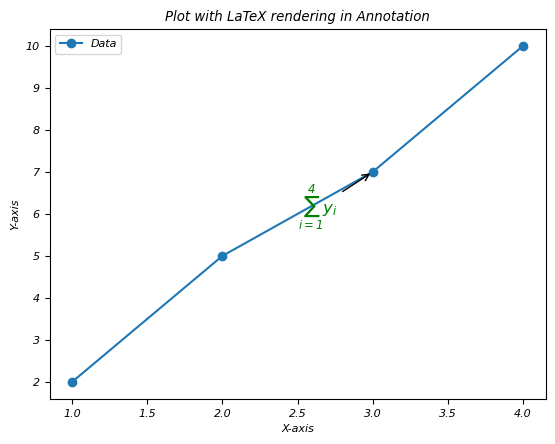
Example
在此示例中,我们将在绘图的注释中使用 LaTex 渲染。
In this example we are going to use the LaTex rendering in the annotations of the plot.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Sample data
x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y = [2, 5, 7, 10]
plt.plot(x, y, 'o-', label='Data')
# Annotating a point with LaTeX-rendered text
plt.annotate(r'$\sum_{i=1}^{4} y_i$', # LaTeX expression within the annotation
xy=(x[2], y[2]), # Coordinates of the annotation point
xytext=(2.5, 6), # Text position
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', arrowstyle='->'),
fontsize=12,
color='green')
# Labeling axes and title
plt.xlabel('X-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y-axis')
plt.title('Plot with LaTeX rendering in Annotation')
plt.legend()
plt.show()这会产生以下输出 −
This will generate the following output −
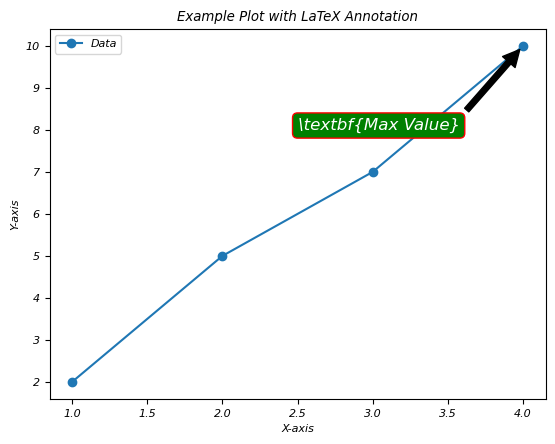
Example
这里有另一个在绘图注释中使用 LaTex 渲染的示例。
Here this is another example of using the LaTex rendering in annotations of a plot.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Generating some data points
x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y = [2, 5, 7, 10]
plt.plot(x, y, 'o-', label='Data')
# Annotating a point with LaTeX rendering
plt.annotate(r'\textbf{Max Value}',
xy=(x[y.index(max(y))], max(y)),
xytext=(2.5, 8),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),
fontsize=12,
color='white',
bbox=dict(boxstyle='round,pad=0.3', edgecolor='red', facecolor='green'))
plt.xlabel('X-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y-axis')
plt.title('Example Plot with LaTeX Annotation')
plt.legend()
plt.show()这将生成以下方程式:
This will generate the following equation −
Axis tick font in a Matplotlib plot using LaTex
这是使用 LaTeX 渲染时更改 matplotlib 中刻度标签字体的一个示例。
Here this is the example to change the axis tick font in matplotlib when rendering using LaTeX
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = [7.00, 3.50]
plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"] = True
x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
y = np.exp(x)
ax1 = plt.subplot()
ax1.set_xticks(x)
ax1.set_yticks(y)
ax1.plot(x, y, c="red")
ax1.set_xticklabels([r"$\bf{one}$", r"$\bf{two}$", r"$\bf{three}$", r"$\bf{four}$"], rotation=45)
ax1.set_yticklabels([r"$\bf{:.2f}$".format(y[0]), r"$\bf{:.2f}$".format(y[1]),
r"$\bf{:.2f}$".format(y[2]), r"$\bf{:.2f}$".format(y[3])], rotation=45)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()这会产生以下输出 −
This will generate the following output −
