Digital-electronics 简明教程
Don’t Care Condition in K-Maps
@s2或@s3是化简布尔表达式的图形方法。由相邻方块或单元格组成的卡诺图,其中每个单元格代表变量在求和或乘积形式中的特定组合。
K-Map or Karnaugh Map is a graphical method of simplifying Boolean expression. A K-Map composed of an arrangement of adjacent squares or cells, where each cell represent a particular combination of variables in sum or product form.
在卡诺图方法中,有一种有用的条件,即@s4,它有助于化简布尔函数。“不管”条件使得卡诺图中变量分组变容易。在本教程中,我们将借助已解决的示例来理解卡诺图约简中的“不管”概念。
In the K-map method, there is a useful condition namely, Don’t Care Condition, which helps in simplifying a Boolean function. The don’t care condition makes the grouping of variables in K-map easy. In this tutorial, we will understand the "don’t care" concept in K-map reduction with the help of solved examples.
有时,在布尔表达式中,对于某些输入组合,输出的值未指定,原因是由于输入组合无效或由于输出的精确值不重要。对于这些值未指定的布尔函数的输入组合称为“不管”组合。@s5也称为@s6。在卡诺图中,“不管”组合用“X”或“d”或“ϕ”表示。
Sometimes, in a Boolean expression for certain input combinations, the value of the output is not specified either due to invalid input combinations or due to the precise value of output is of no importance. These input combinations for which the values of the Boolean function are not specified are called don’t care combinations. Don’t care combinations are also referred to as optional combinations. In K-map, don’t care combinations are represented by "X" or "d" or "ϕ".
例如,在 8421 二进制码中,二进制组合 1010、1011、1100、1101、1110 和 1111 是无效项,其对应的输出是“不管”组合。类似地,在补码 3 中,组合 0000、0001、0010、1101、1110 和 1111 不会出现,因此这些被称为“不管”组合。
For example, in 8421 binary code, the binary combination 1010, 1011, 1100, 1101, 1110, and 1111 are the invalid terms and their corresponding outputs are don’t care combinations. Similarly, in Excess-3 code, the combinations 0000, 0001, 0010, 1101, 1110, and 1111 do not occur, hence these are called don’t care combinations.
当我们处理 SOP(积和式)卡诺图时,如果每个“不管”项有助于化简表达式,则将它视为 1,否则将它视为 0 并置之不理。
When we deal with SOP (Sum of Products) K-map, each don’t care term is treated as a 1, if it helps in reduction of the expression, otherwise it is considered as a 0 and left alone.
另一方面,当我们使用 POS(乘积之和)K 地图时,认为每一个任择态都为 0,如果它有助于缩减表达式,否则它将被视为 1 并单独留下来。
On the other hand, when we are using POS (Product of Sums) K-map, each don’t care term is considered as a 0, if it is helpful in reduction of the expression, otherwise it is treated as a 1 and left alone.
此外,我们还可以将带有任择态的产品标准和(SSOP)表达式转换为带有任择态的和标准积(SPOS)表达式,方法是保持任择态不变,并将 SSOP 格式中缺少的 minterm 写成 SPOS 格式的 maxt 们。
Also, we can convert a Standard Sum of Products (SSOP) expression with don’t care terms into a Standard Product of Sums (SPOS) expression by keeping the don’t care terms as they are, and writing the missing minterms of the SSOP form as the maxterms of the SPOS form.
同样,我们还可以将带有任择态的和标准积(SPOS)表达式转换为带有任择态的产品标准和(SSOP)表达式,方法是保持 SPOS 表达式的任择态不变,并将 SPOS 表达式中缺少的 maxt 写成 SSOP 表达式的 minterm。
Similarly, we can convert a standard product of sums (SPOS) expression with don’t care terms into a standard sum of products (SSOP) expression by keeping the don’t care terms of the SPOS expression as they are, and writing the missing maxterms of the SPOS expression as the minterms of the SSOP expression.
现在,我们来讨论一些已解决的示例,以了解 K 地图中的任择态条件。
Now, let us discuss some solved examples to understand the don’t care condition in K-map.
Example 1
使用 K 地图最小化以下 4 变量布尔表达式以获取 SOP 格式。
Minimize the following 4-variable Boolean expression in SOP form using K-map.
\(\mathrm{\mathit{f}\lgroup A,B,C,D\rgroup=\sum m \lgroup 0,1,4,5,6,10,13\rgroup +d \lgroup 2,3 \rgroup}\)
\mathrm{\mathit{f}\lgroup A,B,C,D\rgroup=\sum m \lgroup 0,1,4,5,6,10,13\rgroup +d \lgroup 2,3 \rgroup}
Solution
给定布尔函数的 SOP K 地图表示形式如图 1 所示。
The SOP K-map representation of the given Boolean function is shown in Figure 1.
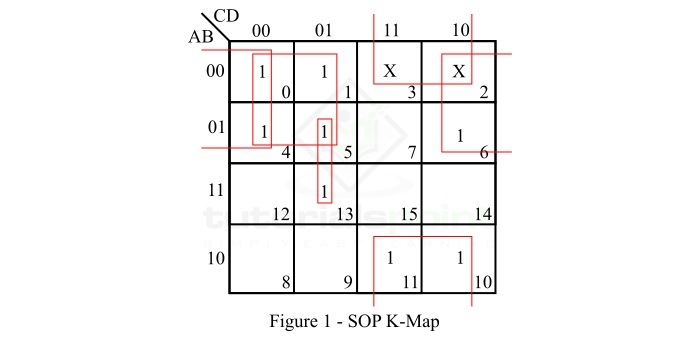
正如我们从给定表达式中所见,存在两个由 K 地图上的 X 表示的任择态。
As we can see in the given expression, there are two don’t care terms which are denoted by X on the K-map.
Explanation
根据以下步骤对表达式进行缩减 -
The reduction of the expression is done as per the following steps −
-
The minterms m0, m1, m4 and m5 form a 4-square. Make it and read it as $\mathrm{\lgroup \bar{A} \: \bar{C}\rgroup}$.
-
The minterms m10 and m11 form a 4-sqaure with two don’t care terms m2 and m3. Make it and read it as $\mathrm{\bar{B}C}$.
-
The minterms m0, m4, m6 and the don’t care term m2 together form a 4-square. Make it and read it as $\mathrm{\bar{A} \: \bar{D}}$.
-
The minterms m5 and m13 form a 2-square. Make it and read it as $\mathrm{B\bar{C}D}$.
-
Finally, write all the product terms in SOP form.
因此,最小布尔表达式为:
Therefore, the minimal Boolean expression is,
\(\mathrm{\mathit{f} \lgroup A,B,C,D \rgroup \: = \: \bar{A} \: \bar{C} \: + \: \bar{B}C \: + \: \bar{A} \: \bar{D} \: + \: B \bar{C}D}\)
\mathrm{\mathit{f} \lgroup A,B,C,D \rgroup \: = \: \bar{A} \: \bar{C} \: + \: \bar{B}C \: + \: \bar{A} \: \bar{D} \: + \: B \bar{C}D}
Example 2
使用 K 地图最小化以下 4 变量布尔表达式以获取 POS 格式。
Minimize the following 4-variable Boolean expression in POS form using K map.
\(\mathrm{\mathit{f} \lgroup A,B,C,D \rgroup \: = \: \prod M \lgroup 1,5,6,12,13,14 \rgroup \: + \: d \lgroup 2,4 \rgroup}\)
\mathrm{\mathit{f} \lgroup A,B,C,D \rgroup \: = \: \prod M \lgroup 1,5,6,12,13,14 \rgroup \: + \: d \lgroup 2,4 \rgroup}
Solution
图 2 中显示了给定布尔函数的 POS K 地图表示。
The POS K-map representation of the given Boolean function is shown in Figure-2.
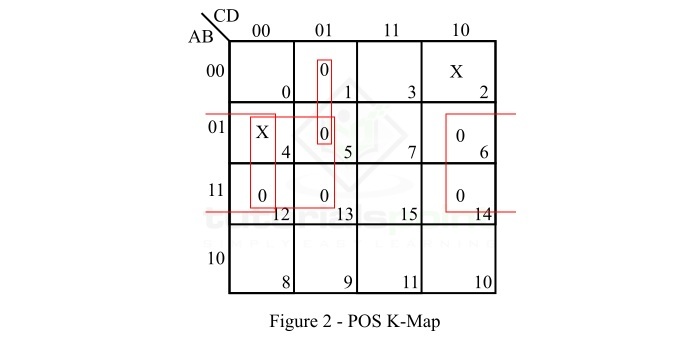
该表达式中有两个任择态,由 K 地图上的 X 表示。
There are two don’t care terms in the expression which are represented by X on the K-map.
Explanation
根据以下步骤对给定函数进行缩减 -
The reduction of the given function is done as per the following steps −
-
The maxterms M5, M12 and M13 and don’t care term M4 form a 4-square. Make it and read it as $\mathrm{\bar{B} \: + \: C}$.
-
The maxterms M6, M12, and M14 and don’t care term M4 form a 4-square. Make it and read it as $\mathrm{\bar{B} \: + \: D}$.
-
The maxterms M1 and M5 form a 2-square. Make it and read it as $\mathrm{A \: + \: C \: + \: \bar{D}}$
-
Write all the sum terms in POS form.
因此,最小布尔表达式为:
Therefore, the minimal Boolean expression is,
\mathrm{\mathit{f} \lgroup A,B,C,D \rgroup \: = \: \lgroup \bar{B} \: + \: C \rgroup \: + \: \lgroup \bar{B} \: + \: D \rgroup \: + \: \lgroup A \: + \: C \: + \: \bar{D} \rgroup}
Conclusion
这些都是关于 K 映射中的不管条件。正如我们在本教程的上述部分中所讨论的那样,不管条件是一个重要且功能强大的概念,它有助于使用 K 映射最小化布尔函数。
This is all about don’t care conditions in K-maps. As we discussed in the above sections of this tutorial, that the don’t care condition is a significant and powerful concept that helps in minimization of Boolean function using K-map.